Covid-19 Incidence Was Initially Associated with Posttransplant Kidney Graft Failure
1SRTR, Minneapolis, MN, 2Univ of San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, 3Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 438
Keywords: Adverse effects, Graft failure, Kidney, Outcome
Topic: Administrative » Quality Assurance Process Improvement & Regulatory Issues
Session Information
Session Name: Quality Assurance Process Improvement & Regulatory Issues
Session Type: Poster Video Chat
Date: Monday, June 7, 2021
Session Time: 7:30pm-8:30pm
 Presentation Time: 7:40pm-7:50pm
Presentation Time: 7:40pm-7:50pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: To better understand the effect of COVID-19 on kidney posttransplant outcomes, we estimated the association of county-level COVID-19 incidence with kidney posttransplant graft failure.
*Methods: The study used a period-prevalent cohort of kidney recipients from March 13, 2019 to July 31, 2020 who received a transplant on or after January 1, 2000. The county-level incidence of COVID-19 for each kidney transplant program was determined from the New York Times database and aggregated into cases per 1,000,000 for each week before and after the national emergency declaration for COVID-19.
*Results: For each week, recipients were given the county-level incidence of the transplant program during the previous week. A two-dimensional spline estimated the effect of COVID-19 across calendar time and incidence.
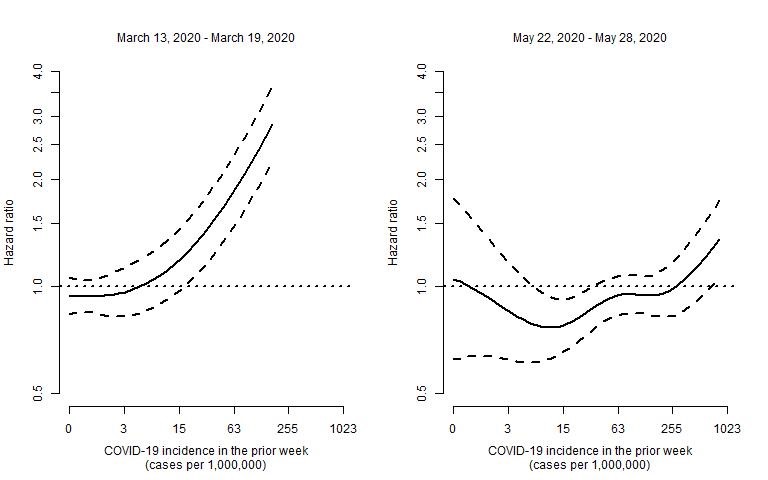
*Conclusions: The effect of COVID-19 incidence had a nonlinear relationship with kidney graft failure, and the effect changed over the course of the pandemic. At the time of the national emergency declaration (March 13 to 19, 2020), the incidence of COVID-19 had a nonlinear effect (Figure 1, left panel): relatively flat up to an incidence of about 16, then the effect rapidly increased to a hazard ratio of about 3, for an incidence of 1024. This nonlinear effect attenuated during the weeks after the declaration of a national emergency. Roughly 10 weeks after the emergency declaration (May 22 to 28, 2020), the incidence of COVID-19 had a less dramatic effect on posttransplant graft failure rates (Figure 1, right panel). Thus, the emergence of COVID-19 coincided with a significantly higher rate of kidney graft failure, potentially from COVID-19 infection or patients not seeking for-cause medical care. However, after the initial disruption, kidney graft failure rates were less strongly associated with COVID-19 incidence, suggesting that kidney recipients and/or transplant programs may have adapted to the new conditions imposed by COVID-19.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wey A, Miller J, Musgrove D, Salkowski N, Tabaka M, Hirose R, Massie A, Segev D, Israni A, Snyder J, Kasiske B. Covid-19 Incidence Was Initially Associated with Posttransplant Kidney Graft Failure [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/covid-19-incidence-was-initially-associated-with-posttransplant-kidney-graft-failure/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress