Comparison of Simultaneous Pancreas kidney Transplantation to Kidney Transplantation Alone for Type 2 Diabetes with End Stage Renal Disease
Y. Fu, Z. Shen
Kidney&Pancreas Transplant, Tianjin First Center Hospital, Tianjin, China
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D363
Keywords: Graft function, Kidney/pancreas transplantation, Metabolic complications, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Late Breaking
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: To compare the clinic outcomes of simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation (SPK) with kidney transplantation alone (KTA) in Type 2 Diabetes patients with ESRD.
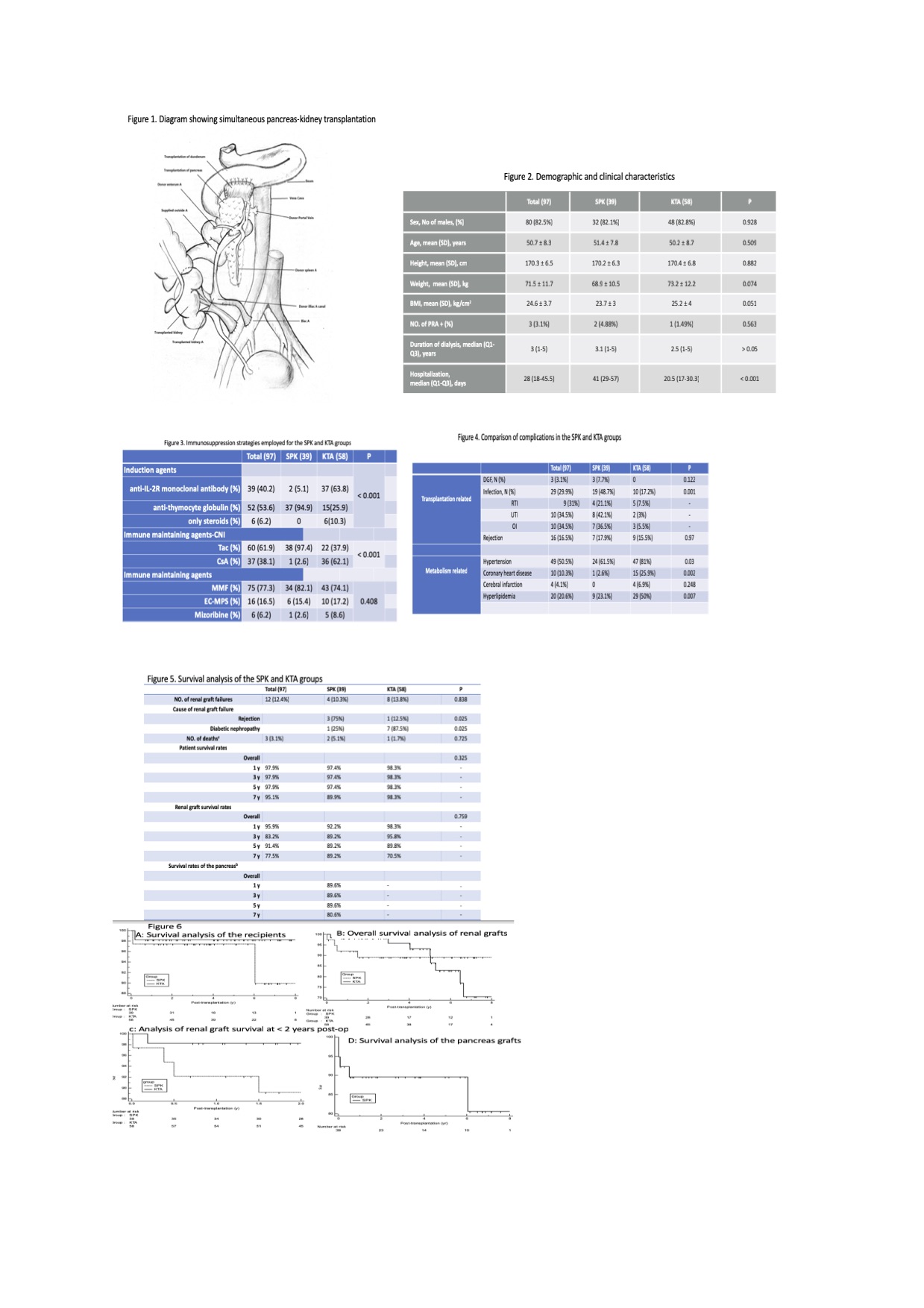
*Methods: 97 type 2 diabetes atients with ESRD, among which 39 patients underwent SPK and 58 underwent KTA between May 2010 and May 2017 in our center, were retrospected. SPK were performed as Figure1. General demographic characters were compared between these two cohorts of patients. Pre operative as well as post transplantation profiles of overall survival rate, renal graft survival, plasma glucose, blood lipid, renal function and complications rate were also compared.All organs were from deceased citizen donors and none were prisoners in this study.
*Results: There is no significant difference of gender age,BMI, preoperative PRA average dialysis time between SPK group and KTA group. However, the hospitalization days were significantly varied between the two cohorts, with the median hospitalization day of SPK recipients as 41((29-57), longer than that of KTA recipients, 20.5(17-30.3) (p<0.001) (Figure 2). In addition, the immunosuppression agents were significantly different between two groups. Specifically, 94.9% SPK recipients were administrated polyclonal antibody as induction agents, while majority (63.8%) KTA recipients were administrated monoclonal antibody. FK accounted for 97.4% of immune maintaining agents in SPK group, significantly different from that in KTA group (37.9%)(Figure 3). The overall post transplantation survival rate of recipients (p=0.325) , renal graft (p=0.676) as well as complications of rejection (17.9% vs 15.5%, p=0.97), delayed graft function (7.7% vs 0%; p=0.122), and cerebral infarction (0% vs 6.9%, p=0.248) all did not vary significantly between SPK and KTA cohorts(Figure4). Nevertheless, the long term survival rate of renal graft was significantly better in SPK cohort than KTA cohort, with 7-year renal survival rate being 89.2% vs.70.5% (P=0.04) respectively (Figure 5,6) with the 7 years pancreas graft survival rate 80.6%. The hypertension (61.5% vs. 81%, p=0.03), coronary heart disease (2.6% vs 25.9%, p=0.002), and hyperlipidemia (23.1% vs. 50%, p=0.007) were significantly lower in SPK cohort than in KTA cohort. Plasma glucose were dropped significantly more followed transplantation in the first a couple of years in SPK cohort than in KTA cohort.
*Conclusions: SPK can improve long term renal graft survival rate and less metabolism complication of post transplanted hypertension and coronary heart disease in type 2 Diabetes patients with ESRD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fu Y, Shen Z. Comparison of Simultaneous Pancreas kidney Transplantation to Kidney Transplantation Alone for Type 2 Diabetes with End Stage Renal Disease [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/comparison-of-simultaneous-pancreas-kidney-transplantation-to-kidney-transplantation-alone-for-type-2-diabetes-with-end-stage-renal-disease/. Accessed July 12, 2025.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress