Comparative Analysis of Patient Outcomes between Urology-Led versus General Surgery-Led Kidney Transplant Centers
1The University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH, 2George Mason University, Arlington, VA, 3Albany Medical College, Albany, NY
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: LB-006
Keywords: Graft failure, Graft survival, Renal failure, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Late Breaking
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: To assess renal patient outcomes between kidney transplant centers across the United States based on whether their surgical leader was initially trained via the urology versus general surgery graduate medical education pathway, providing novel information to determine whether differences in surgical residency training of kidney transplant leaders impact a center’s patient outcomes.
*Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed using the UNOS database to assess outcomes of 126,133 renal transplant patients across 179 transplant centers nationwide between the years 2010 and 2019. Graft failure and patient mortality of the transplant recipients at 21 urology-led and 158 general surgery-led transplant centers were compared using Kaplan-Meier (KM) survival curves at 3-, 6- months, and 1-, 3- and 5- years post-transplant. Graft survival and patient mortality rates were statistically compared using a log-rank test for equality of survivor functions. Cox regressions were performed to identify risk factors for graft failure and patient mortality.
*Results:
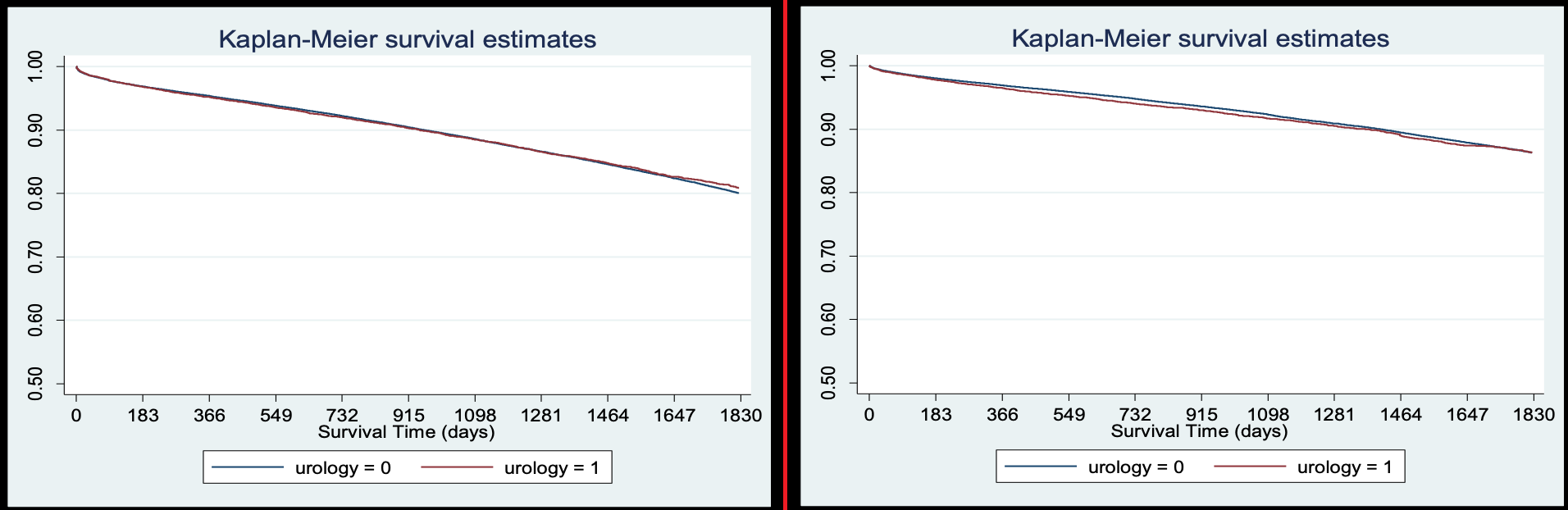
Graft Failure KM Estimates (Left) and Patient Mortality KM Estimates (Right):
The graft survival rates of urology-led and general surgery-led programs are not statistically significant (p-value of the log-rank test = 0.71). The patient survival rates of urology-led and general surgery-led programs are not statistically significant (p-value of the log-rank test = 0.79).
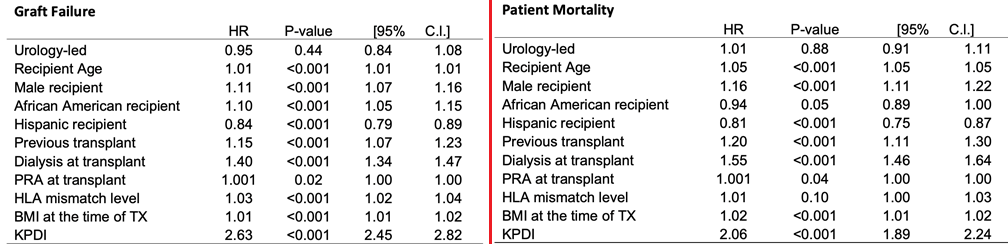
Cox Regression:
Urology-led programs do not have an increased overall graft failure rate (p=0.44). Urology-led programs do not have an increased overall patient mortality rate (p=0.88). Risk factors are listed.
*Conclusions: The preliminary results of this study suggest that a kidney transplant center’s overall patient outcomes are not impacted by the initial residency training of their surgical leader. Further efforts to compare the number of living donors, excess wait times, program locations, gender representation, and ethnicity representation between both groups are currently underway.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mishra A, Cohen A, Koizumi N, Ortiz A, Pai K, Bullock B, Sureddi S, Ortiz J. Comparative Analysis of Patient Outcomes between Urology-Led versus General Surgery-Led Kidney Transplant Centers [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/comparative-analysis-of-patient-outcomes-between-urology-led-versus-general-surgery-led-kidney-transplant-centers/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress