Combined Pre-Transplant Anti-Donor T-Cell Sensitization with Single Nucleotid Polimorphisms (SNPs) for CYP3A4 Tacrolimus Metabolism Identifies Kidney Transplant Patients at High Risk of Allograft Rejection
1Experimental Nephrology Laboratory, IDIBELL, L'Hospitalet de Llobregat. Barcelona, Spain, 2Nephrology, Charité Campus Virchow-Klinikum, Berlin, Germany, 3Kidney Transplant Unit, Bellvitge University Hospital- IDIBELL, L'Hospitalet de Llobregat. Barcelona, Spain
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B80
Keywords: Gene polymorphism, Immunosuppression, Rejection, T cell reactivity
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Preformed donor-specific (d-sp) T-cell alloimmunity has been associated to high risk of acute rejection (BPAR). Since the individual susceptibility related to specific single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of enzymes involved in TAC metabolism leads to different drug exposures, we hypothesized that assessing pre-transplant d-sp T-cell alloreactivity according to TAC pharmacogenetic phenotypes would improve the discrimination accuracy of at-risk patients of BPAR.
*Methods: We evaluated the presence of pre-transplant d-sp T-cell alloimmunity using an IFN-γ ELISPOT assay, and CYP3A4*22 SNPs in 274 consecutive kidney transplants from 2 different centers receiving a TAC immediate release formulation, mofetil mycophenolate (MMF) and steroids as main immunosuppression, either with basiliximab (n=170;62%) or Thymoglobulin (n=104;38%).
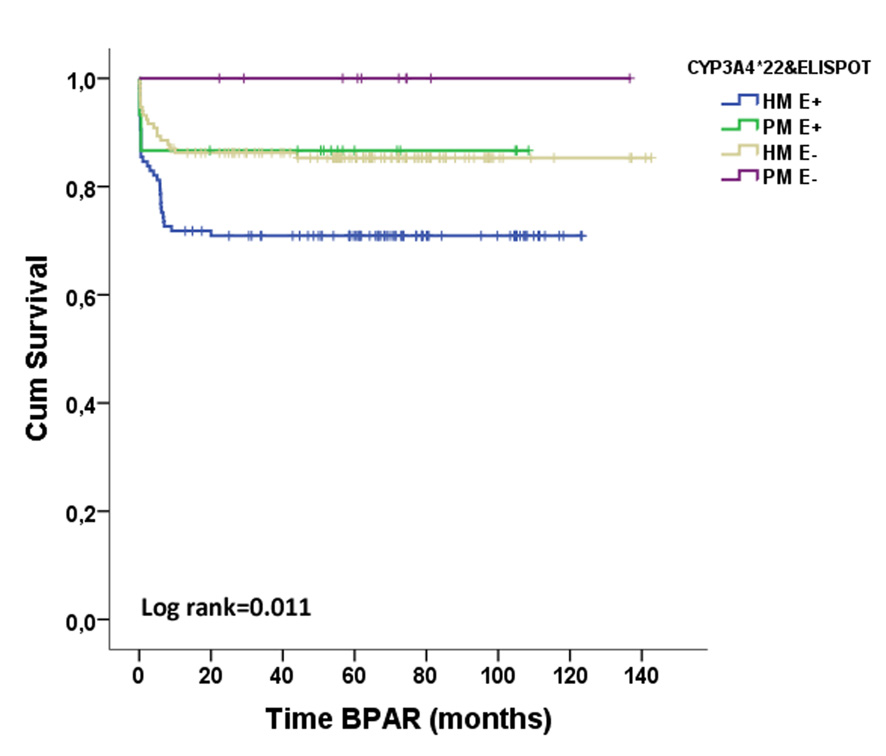
*Results: Fifty-six out of 274 patients (20.4%) displayed BPAR (36 TCMR, 8 ABMR and 1 mixed AR). Preformed T-cell alloreactivity was observed in 132(48.2%) patients whereas not in 142(51.8%). 249(90.9%) patients were high metabolizers for CYP3A4 (HM;*1/*1 genotype) and 25(9.1%) were poor metabolizers (PM;*22 expressers).
While pre-transplant positive d-sp T-cell alloreactivity (E+) was associated with BPAR (OR=2.191, p=0.006), the pharmacogenetic phenotype was not. HM required higher TAC doses to reach the same trough levels as PM (trough levels/dose ratios were 1.58±1.08 vs 1.99±1.32, p=0.07; 1.76±1.04 vs 2.18±1.28, p=0.06 and 1.88±1.26 vs 2.46±1.93, p=0.05 in HM vs PM patients, at 1, 3 and 6mo, respectively). When stratifying patients according to both factors, 117(42.7%) were HM/E+, 132(48.2%) HM/E-, 15(5.5%) PM/E+ and 10(3.6%) PM/E-. HM/E+ patients showed the highest BPAR risk (HR=2.342, p=0.002). Notably, when patients receiving Thymoglobulin were excluded, HM/E+ were at higher risk (HR=2.833, p=0.002)
. In multivariate analysis the combination of both variables and DGF independently predicted BPAR (HR=2.442, p=0.001; OR=2.072, p=0.007).
*Conclusions: Assessment of pre-transplant d-sp T-cell alloimmunity together with CYP3A4 SNPs may help to better recognize patients at risk of BPAR, despite the use of TAC-based immunosuppressive regimens.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Crespo E, Vidal A, Sefrin A, Fontova P, Stein M, Volk H, Grinyó J, Reinke P, Lloberas N, Bestard O. Combined Pre-Transplant Anti-Donor T-Cell Sensitization with Single Nucleotid Polimorphisms (SNPs) for CYP3A4 Tacrolimus Metabolism Identifies Kidney Transplant Patients at High Risk of Allograft Rejection [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/combined-pre-transplant-anti-donor-t-cell-sensitization-with-single-nucleotid-polimorphisms-snps-for-cyp3a4-tacrolimus-metabolism-identifies-kidney-transplant-patients-at-high-risk-of-allograft-reje/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress