Combined CD11b/CD40 Blockade is Superior to CD40 Blockade Alone in Prolonging Survival in Pig-to-Nonhuman Primate Renal Xenotransplantation
1Surgery, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, 2Surgery, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 2
Keywords: Co-stimulation, Immunosuppression, Pig, Preclinical trails
Topic: Basic Science » Xenotransplantation
Session Information
Session Time: 10:30am-11:30am
 Presentation Time: 10:40am-10:50am
Presentation Time: 10:40am-10:50am
Location: Virtual
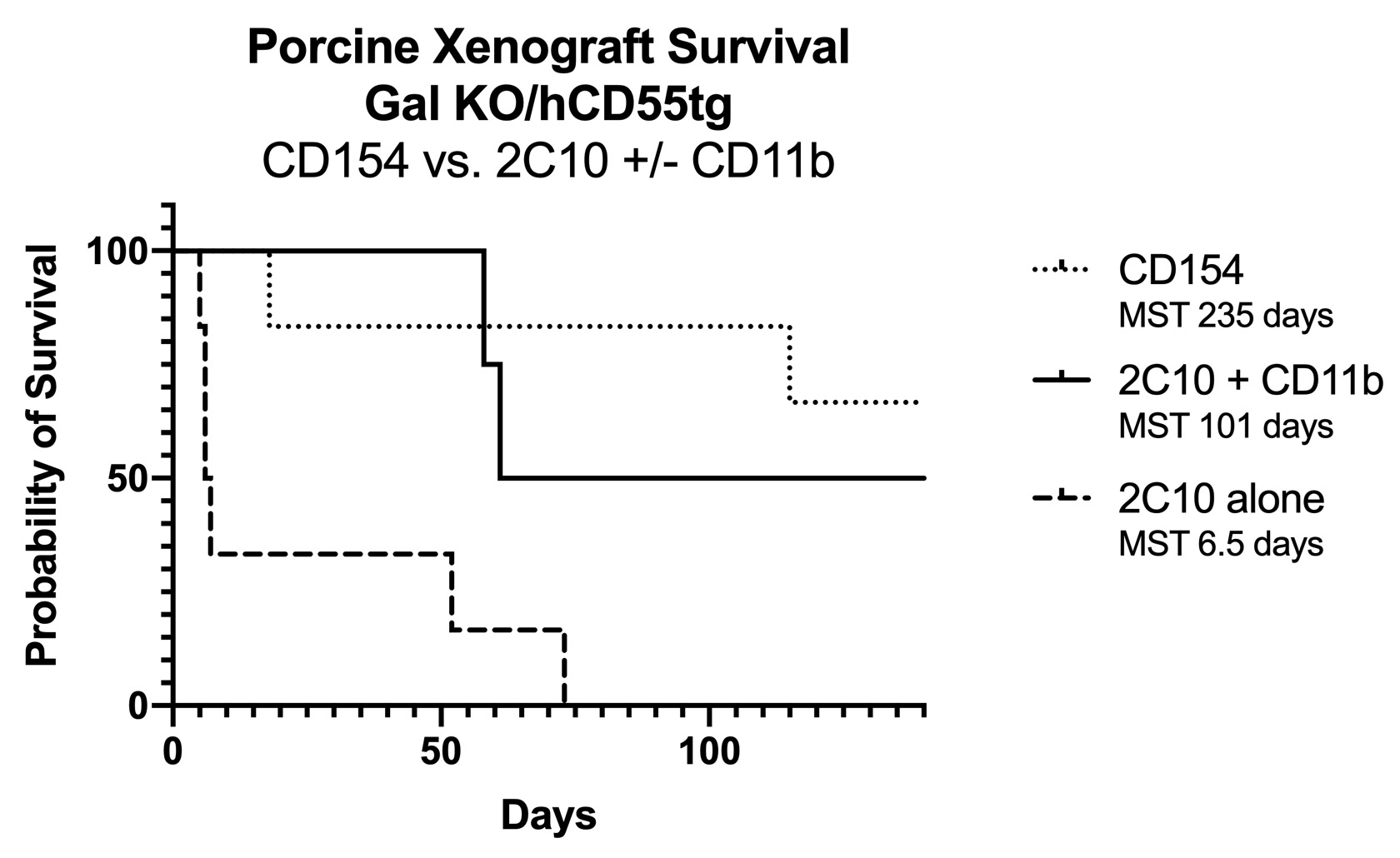
*Purpose: Blockade of the CD40/CD154 pathway is highly effective in preventing rejection in pig-to-nonhuman primate (NHP) xenotransplantation models. Clinical translation of anti-CD154 mAbs, however, has been plagued by elevated rates of thromboembolic events, and blockade of CD40 alone has not replicated the prolonged xenograft survival of anti-CD154 containing regimens. Recent reports demonstrated that CD11b, a second ligand for CD154, may provide an additional pathway by which rejection signals can bypass CD40 selective blockade, but not CD154 directed therapies. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy of CD11b blockade in combination with CD40 blockade in preventing rejection in a pig-to-NHP model of renal xenotransplantation.
*Methods: Rhesus macaques (n=16) with low pre-transplant xenoreactive antibody titers underwent bilateral nephrectomy and life-sustaining porcine renal xenotransplantation using GGTA1 KO/CD55 transgenic donor pigs. Animals underwent T cell depletion and were assigned to one of three maintenance treatment regimens: anti-CD154 (clone 5C8), anti-CD40 (clone 2C10R4) alone, or combined anti-CD40 plus anti-CD11b (clone M1/70); plus mycophenolic acid and steroids.
*Results: Recipients treated with anti-CD154 therapy (n=6) experienced the longest survival (MST=235 days), including three rhesus macaques with extended survival over 300 days (406, 400, 310 days). Recipients treated with combined anti-CD40/CD11b therapy (n=4) showed prolonged survival (MST=101 days) compared with recipients treated with anti-CD40 therapy alone (n=6, MST=6.5 days).
*Conclusions: Here we demonstrate that treatment with anti-CD11b mitigates early xenograft rejection seen with anti-CD40 therapy in a porcine-to-NHP model of renal xenotransplantation. Additionally, treatment with anti-CD40/CD11b is statistically similar to treatment with anti-CD154. Together, these data support the hypothesis that CD11b acts as an additional ligand of CD154 through which rejection signals can bypass CD40 selective blockade. These provide further rationale for the continued development and eventual clinical translation of therapeutics to block this pathway.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Faber DA, Lovasik B, Matar A, Breeden C, Kim S, Adams A. Combined CD11b/CD40 Blockade is Superior to CD40 Blockade Alone in Prolonging Survival in Pig-to-Nonhuman Primate Renal Xenotransplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/combined-cd11b-cd40-blockade-is-superior-to-cd40-blockade-alone-in-prolonging-survival-in-pig-to-nonhuman-primate-renal-xenotransplantation/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress