Clinical Heterogeneity of Early Anamnestic Donor Specific Antibody Responses in Kidney Transplantation
1U of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH
2Christ Hospital, Cincinnati, OH.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A128
Keywords: HLA antibodies, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Anamnestic donor specific antibody(DSA) responses in the early post-transplant period may threaten the renal transplant(RTx). We hypothesize earlier DSA detection will allow minimization of RTx injury and enhance therapeutic responses. Methods:Between May 2016 and Nov 2017, intensive DSA monitoring(IDM) was prospectively implemented in high risk RTx. High risk was defined by:1) previous txp,2) female receiving allograft with paternal Ag,3) pre-transplant DSA,4) posttxp oliguric ATN or slow graft function in patients(pts) with previous HLA exposure,5) current cytotoxic PRA >25% or peak cytotoxic PRA >50%, or 6) positive T or B cell FXM. IDM included sampling on posttxp days 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7± 2, 14 ± 2, 30 ±2 , 90 ±14, 180 ± 14, and 360 ±14. Clustering of SABs expressing donor antigens(CL-DSA) was routinely evaluated by a senior HLA scientist for early DSA detection. Results: 64 pts underwent IDM with 27(42.2%) demonstrating progressive DSA increases. Multivariate analysis showed that pre transplant DSA was the strongest predictor of a progressive DSA increases (40.2 fold increased odds).10 pts with peak DSA values >5000MFI received AMR treatment with 6 of 10 showing >50% DSA decrease within 14d, with 5 of 10 pts showing longterm DSA resolution. Pts with peak DSA values <5000 MFI were treated at physician discretion. Of 13 pts with DSA peak <5000MFI were not treated, 9(69.2%) resolved spontaneously within 14d; 2 additional pts (11/13 total, 84.6%) eventually resolved without treatment. Of 4 pts with peak DSA <5000MFI who were treated, three(75%) had DSA eliminated by treatment. Five pts in whom early CL-DSA was detected underwent biopsy, each of which demonstrated AMR. 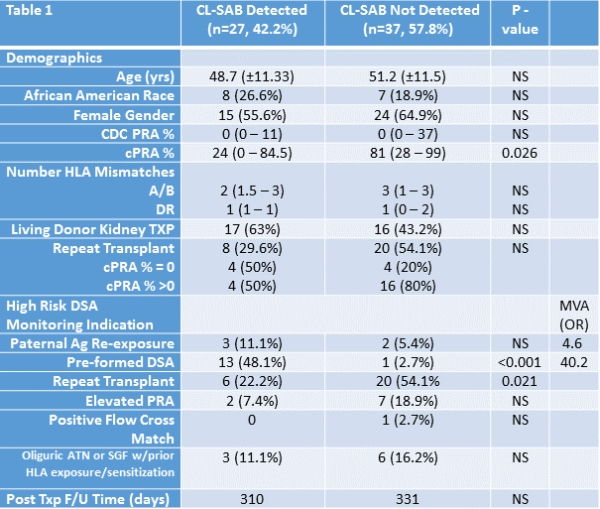 Conclusions: 1) IDM with routine evaluation for CL-DSA allows early detection of DSA responses, 2) DSA elevations <5000MFI may be observed without treatment with frequent spontaneous regression, 3) patients with progressive increases in DSA MFI values >5000 MFI had treatment responses inferior to those whose MFI <5000. Therefore, early severe AMR may be averted by IDM and early DSA treatment.
Conclusions: 1) IDM with routine evaluation for CL-DSA allows early detection of DSA responses, 2) DSA elevations <5000MFI may be observed without treatment with frequent spontaneous regression, 3) patients with progressive increases in DSA MFI values >5000 MFI had treatment responses inferior to those whose MFI <5000. Therefore, early severe AMR may be averted by IDM and early DSA treatment.
CITATION INFORMATION: Loethen A., Lichvar A., Tremblay S., Shields A., Dao A., Cardi M., Brailey P., Girnita A., Abu Jawdeh B., Alloway R., Woodle E. Clinical Heterogeneity of Early Anamnestic Donor Specific Antibody Responses in Kidney Transplantation Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Loethen A, Lichvar A, Tremblay S, Shields A, Dao A, Cardi M, Brailey P, Girnita A, Jawdeh BAbu, Alloway R, Woodle E. Clinical Heterogeneity of Early Anamnestic Donor Specific Antibody Responses in Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/clinical-heterogeneity-of-early-anamnestic-donor-specific-antibody-responses-in-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
