Circulating Donor-Derived Cell-Free DNA: A Novel Non-Invasive Biomarker for Immune Surveillance in Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation
1Hansjörg Wyss Department of Plastic Surgery, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY, 2Transplant Institute, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 962
Keywords: Inflammation, Lymphocytes, Monitoring, Rejection
Topic: Basic & Clinical Science » Basic & Clinical Science » 20 - VCA
Session Information
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: The purpose of this study is to evaluate whether circulating donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cfDNA) could be used as a noninvasive biomarker to detect rejection in vascularized composite allotransplantation.
*Methods: One combined face/upper extremity transplant recipient was followed longitudinally, and plasma samples were collected prospectively at all follow-up appointments in combination with clinical photography and allograft biopsies as well as for any suspected rejection. Peripheral blood samples were collected and plasma levels of dd-cfDNA measured via targeted amplification and sequencing of a validated panel of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The percentage of dd-cfDNA to total cfDNA (dd-cfDNA%) was calculated for each sample and correlated with rejection status based on clinical exam and histopathology.
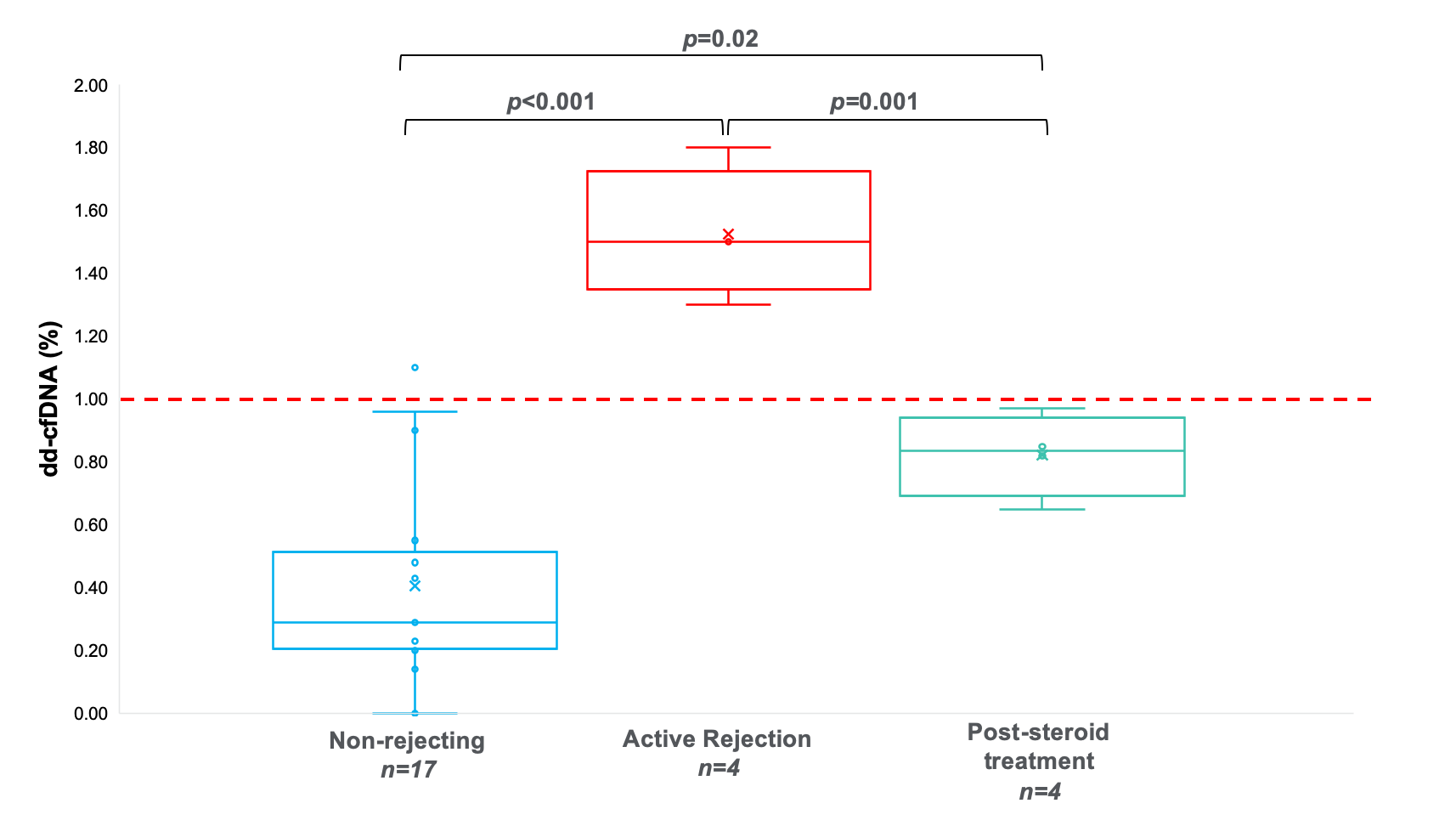
*Results: Recipient 1 demonstrated undetectable levels of dd-cfDNA pre-transplantation, a peak of 1.1% on postoperative day (POD) 26, with a subsequent decline to low levels (<1%), all in the absence of rejection episodes. He has acute rejection with corresponding elevated levels of dd-cfDNA, which in most cases preceded clinical signs/symptoms. During treatment of his rejection episodes, acute rejection resolved both clinically and histologically with correlating return to baseline levels of dd-cfDNA.
*Conclusions: These results suggest that elevated levels of dd-cfDNA, representing allograft injury, appear to correlate with acute rejection of the allograft, and have potential to detect rejection through non-invasive means before becoming clinically apparent. While further research and larger sample size is needed to confirm its validity, this safe, simple, and noninvasive test may be useful for rejection surveillance, enabling more frequent and quantitative assessment while complementing traditional clinical and histopathological data for decision-making.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rifkin WJ, Trilles J, Rabbani PS, Onuh OC, Gelb BE, Ceradini DJ, Rodriguez ED. Circulating Donor-Derived Cell-Free DNA: A Novel Non-Invasive Biomarker for Immune Surveillance in Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/circulating-donor-derived-cell-free-dna-a-novel-non-invasive-biomarker-for-immune-surveillance-in-vascularized-composite-allotransplantation/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress