CD4 T Cells and Co-Engagement with Foreign Protein Are Required in Antibody Response to Non-Self Blood Group A-Antigen.
Micro &
Immunology, ATI, CNTRP, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Pediatrics, ATI, CNTRP, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Pediatrics, Surgerey, and Immunology, ATI, CNTRP, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B42
Keywords: Antibodies, B cells, Heart transplant patients, T cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Allorecognition and T Cell Biology
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Background: ABO-incompatible heart transplantation (ABOi HTx) is safe during infancy and allows increased donor access. B-cell tolerance develops to donor A/B-antigen(s) (Ag) after ABOi HTx by mechanisms not well defined. We developed A-transgenic (A-Tg) mice constitutivelyexpressing human A-Ag on vascular endothelium and RBC to study B cell immunity and tolerance. Here we studied A-incompatibility in the context of syngeneic, allogeneic and xenogeneic stimulation.
Methods: Part I: Adult wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 (B6; H-2b), BALB/c (BALB; H-2d), or C3H/He mice (C3H; H-2k) received i.p. injection weekly X3 of B6 or BALB A-Tg blood (100ul of 10%v/v); or human RBC membranes (100ul of 10%v/v) from blood group A (hu-A) or O (hu-O); or A-incompatible heart allografts as shown in [table] .Serum anti-A Ab was measured by hemagglutination and ELISA (IgG and IgM); graft survival was assessed by palpation. Part II: a) to assess requirement of foreign protein to stimulate anti-A, hu-O RBC were co-injected in WT B6 with syngeneic A-Tg cells; b) to assess T cell dependence of anti-A response, CD4+ T cells were depleted (mAb GK1.5) from WT B6 mice before hu-A RBC injection.
Results: Part I: Exposure to incompatible A-Ag in the context of allogeneic stimulation (MHC-mismatched A-Tg blood or heart graft) or xenogeneic stimulation (hu-RBC) induced abundant anti-A production [table] , whereas A-Tg syngeneic (MHC-matched) cells did not. Part II: a) a mixture of syngeneic A-Tg and xenogeneic hu-O RBC did not induce anti-A; b) after CD4+ T-cell depletion, xenogeneic cells failed to elicit anti-A (figure) .
Conclusions: Exposure to non-self A-Ag in syngeneic cells is insufficient to induce anti-A production; stimulation of antibody depends not only on exposure to the foreign carbohydrate but co-engagement with allogeneic or xenogeneic protein, and requires CD4 T cell help. These results are consistent with our previous data showing a requirement for chemical/physical linkage of non-self A-antigen and foreign protein.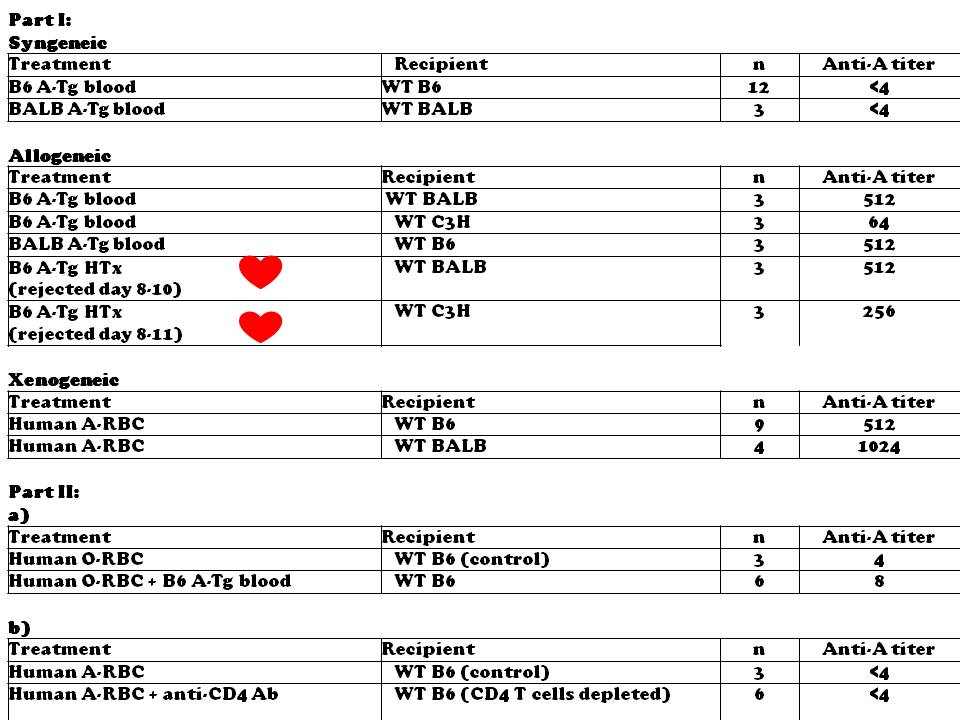
CITATION INFORMATION: Adam I, Motyka B, West L. CD4 T Cells and Co-Engagement with Foreign Protein Are Required in Antibody Response to Non-Self Blood Group A-Antigen. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Adam I, Motyka B, West L. CD4 T Cells and Co-Engagement with Foreign Protein Are Required in Antibody Response to Non-Self Blood Group A-Antigen. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cd4-t-cells-and-co-engagement-with-foreign-protein-are-required-in-antibody-response-to-non-self-blood-group-a-antigen/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
