CD209+ Macrophages-Mediated Immunosuppressive Effects in ADPKD Tissues
1Nanfang Hospital, Guangzhou, China, 2Departments of Urology and Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1289
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Kidney/liver transplantation, Polycystic kidney disease
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 12 - Immunosuppression & Tolerance: Preclinical & Translational Studies
Session Information
Session Name: Immunosuppression & Tolerance: Preclinical & Translational Studies
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: The intensity of maintenance immunosuppression required in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) patients after renal transplantation is lower than average, suggesting a reduced immune status in ADPKD patients. This study aims to explicit what underlies the immune suppressive status in ADPKD patients.
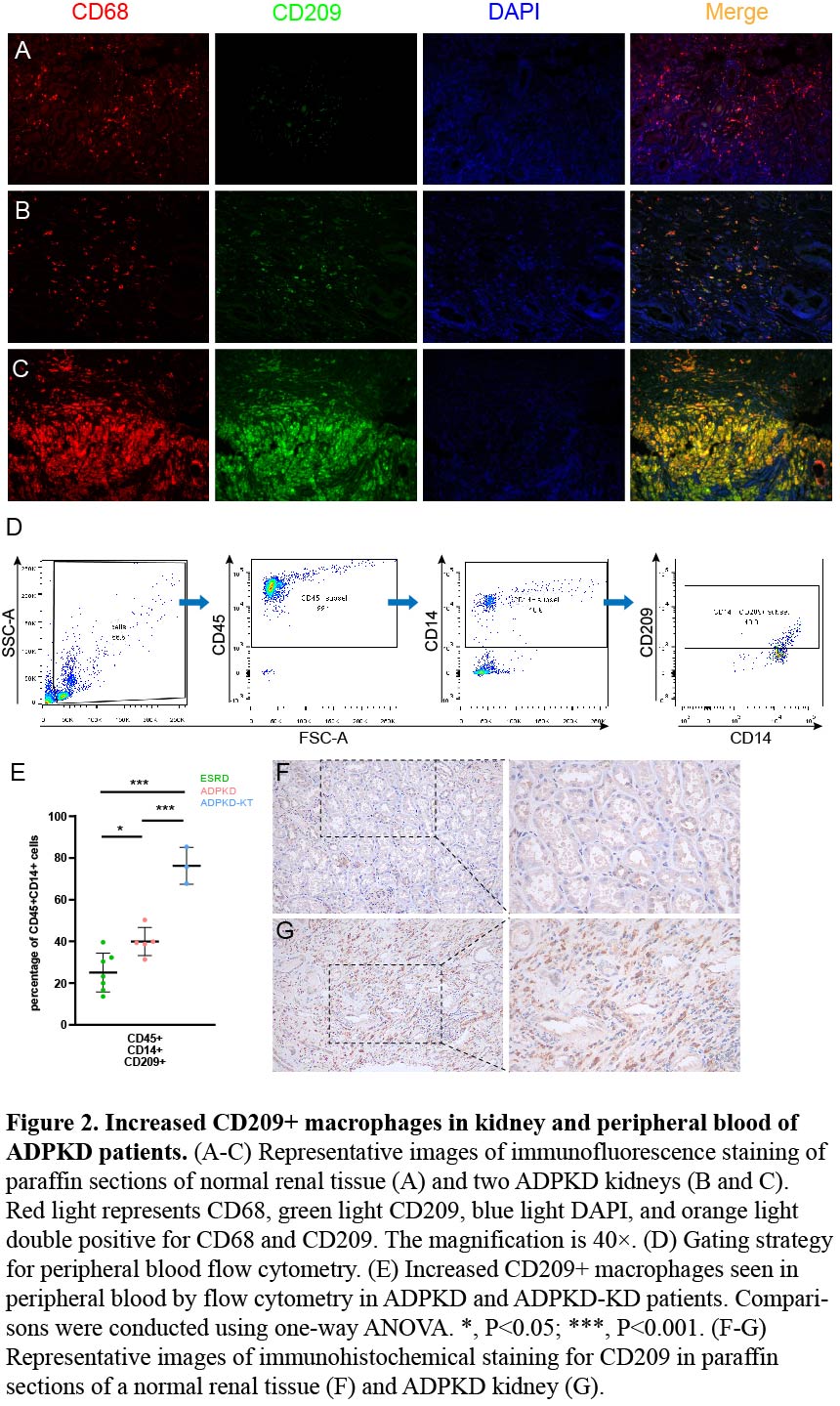
*Methods: We performed scRNA-seq of renal tissue samples from one patient with ADPKD progressed to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and two normal renal tissue obtained in nephrectomy for renal cancers. The findings were validated in four other cases of ADPKD with comorbid ESRD by immunohistochemical staining and in peripheral blood from fourteen patients with non-ADPKD ESRD, ADPKD, and renal transplantation recipients with ADPKD by flow cytometry.
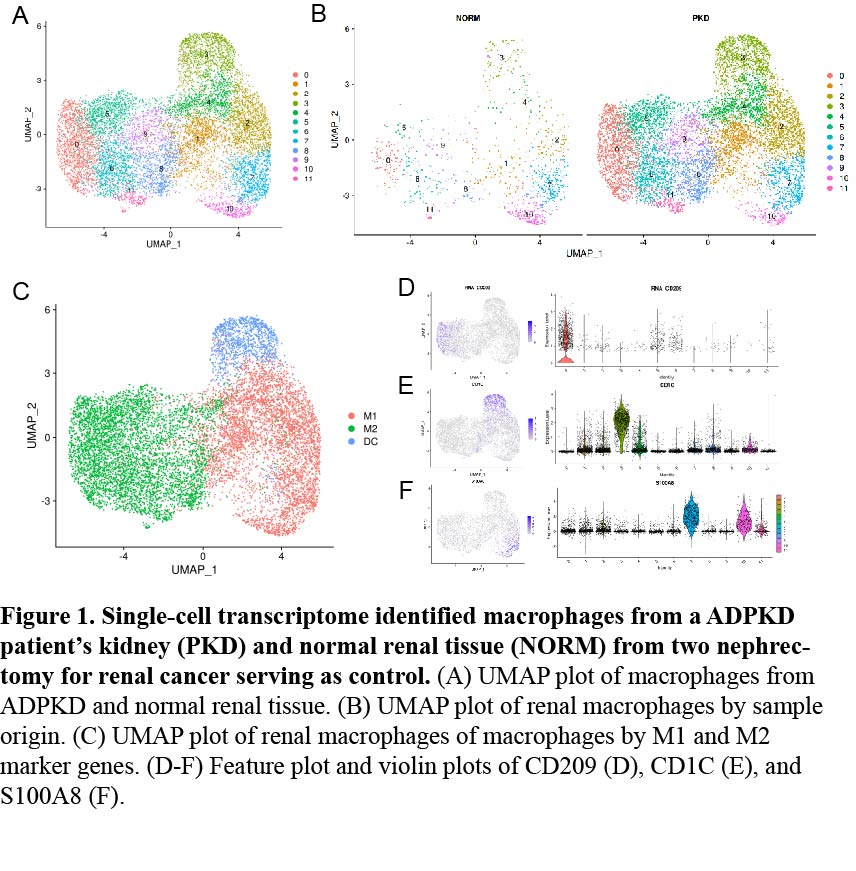
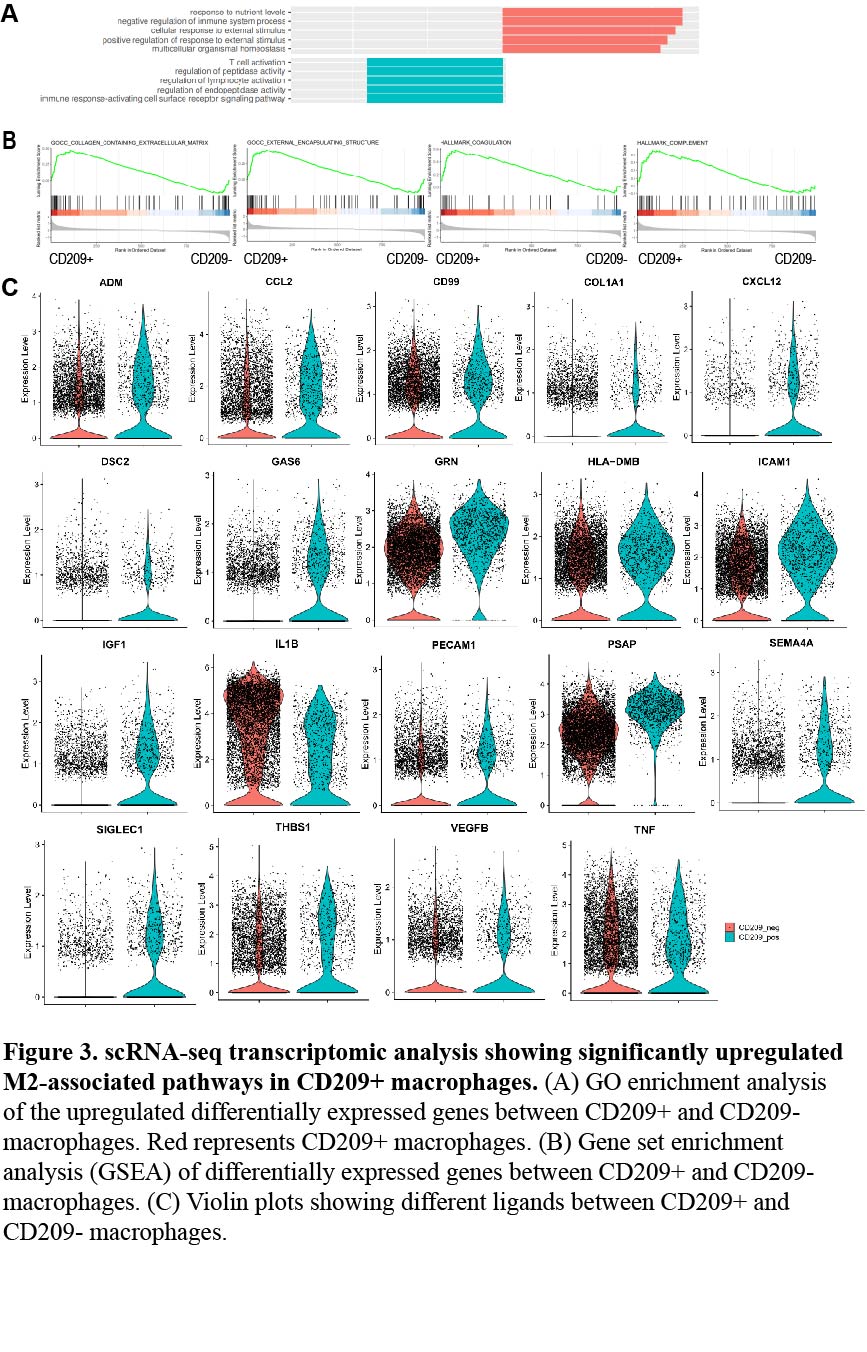
*Results: In ADPKD kidney samples, significantly increased CD209+ macrophages were observed. Besides, proportion of CD209+ macrophages in the peripheral blood of patients with ADPKD and ADPKD-post kidney transplant was higher than that in ESRD. scRNA-seq analysis revealed that CD209+ macrophages functionally resembled type M2 macrophages, which show high expression of M2 markers like CD163 and CD206. In addition, multiple M2-associated pathways were significantly upregulated. CD209+ macrophages mediated immunosuppression by expressing high levels of anti-inflammatory factors, some of which also mediate cell proliferation and fibrosis.
*Conclusions: The substantial CD209+ macrophage infiltration in the kidney and peripheral blood of ADPKD patients is closely associated with immunosuppression, which may explain the immunosuppressive environment in ADPKD patients after renal transplantation and help to determine the appropriate management of these patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ou Z, Wang Y, Yan Z, Liu Y, Li Q, Fang Y, Geng J, Deng W, Li Z, Xia R, Zeng W, Xu J, Wu C, Miao Y. CD209+ Macrophages-Mediated Immunosuppressive Effects in ADPKD Tissues [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cd209-macrophages-mediated-immunosuppressive-effects-in-adpkd-tissues/. Accessed July 5, 2025.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress