Bisphosphonates Effectively Improve the Long Term Renal Transplant Outcomes; A Single Center Retrospective Study
1Surgery, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 11
Keywords: Graft function, Graft survival, Kidney, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Complications: Late Graft Failure I
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Location: Veterans Auditorium
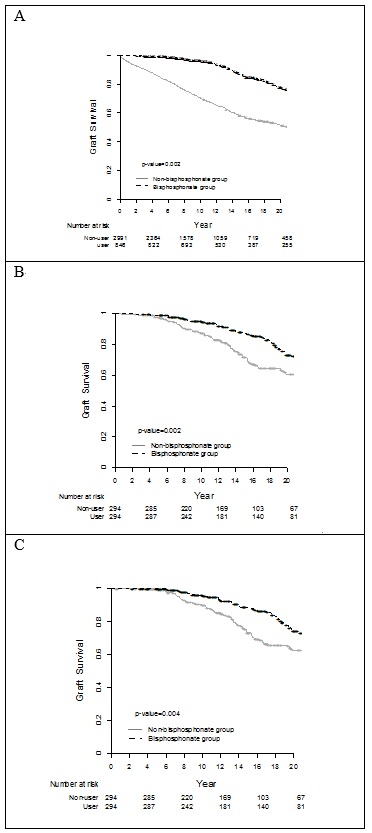
*Purpose: Kidney transplantation (KT) is a treatment of choice for patients with end-stage renal disease. Despite of remarkable improvement in short term graft survival, few effective strategies are available to increase long-term survival. Bisphosphonates are used in patients with mineral and bone disorders after KT, but it is not known how they affect the long-term graft survival. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of bisphosphonates on long-term graft outcome after KT.
*Methods: Among 3837 eligible patients from the single center cohort between April 1979 and June 2016, 294 patients who administrated bisphosphonates and 294 propensity score matched patients not treated with bisphosphonates were included in the analyses. We evaluate long term graft survival using propensity-score matching, landmark analysis, and nested case-control study.
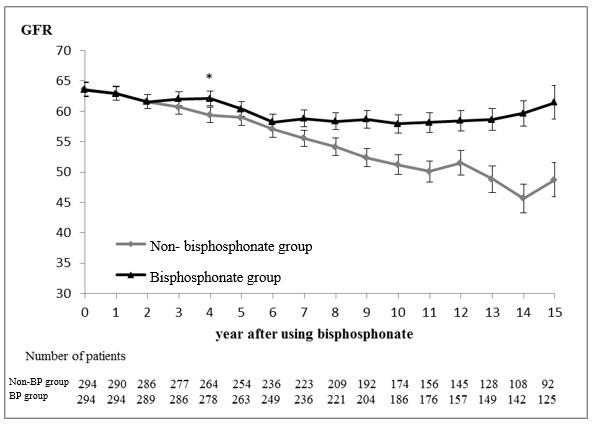
*Results: The demographic characteristics were not different significantly between bisphosphonate group (BP group) and non-bisphosphonate group (Non-BP group) except donor age in the matched study. Donor age, deceased donor, HLA mismatch, hypertension, vitamin D use, acute rejection, and bisphosphonates administration influenced the long-term survival of the renal allograft in multivariate analysis. Especially, BP group showed significantly increased long term graft survival in landmark analysis. Bisphosphonates significantly reduced the risks of graft failure (P<0.001), and improved graft renal function (P=0.017).
*Conclusions: Bisphosphonates may effectively improve long-term graft survival and renal function for kidney transplant recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Song S, Huh K, Choi H, Lee J, Kim D, Kim Y, Kim M, Kim S, Joo D, Kim B. Bisphosphonates Effectively Improve the Long Term Renal Transplant Outcomes; A Single Center Retrospective Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/bisphosphonates-effectively-improve-the-long-term-renal-transplant-outcomes-a-single-center-retrospective-study/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress