Bespoke Immunosuppression: Prolonging Transplant Survival through Enhanced T-cell Activation Induced Cell Death
1WWIEM, QUB, Belfast, United Kingdom, 2CCRCB, QUB, Belfast, United Kingdom, 3Renal Transplantation, Belfast City Hospital, Belfast, United Kingdom
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C11
Keywords: Apoptosis, Immunosuppression, T cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Immunosuppression Preclinical Studies
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: We aim to develop donor-specific immunosuppression by inhibiting T-cell cellular FLICE like inhibitory protein (c-FLIP). Our current work focuses on clinically relevant pharmacological inhibitors of c-FLIP. Utilising Histone Deactylase Inhibitors (HDACis) and also more specific novel small molecule c-FLIP inhibitors, to selectively enhance apoptosis in allo-reactive T-cells.
*Methods: BALB/c T-cells were purified and transfected with siRNA to c-FLIP or scrambled control (SC). These T-cells were used to reconstitute T-cell deficient RAG BALB/c recipient mice. Skin grafts from C57BL/6 donors were then carried out (n=6) and survival of the allograft assessed.
In vitro experiments were designed to ascertain the ability of the HDACis, Vorinostat and Entinostat, to induce apoptosis within activated murine T-cells from total splenocytes. Murine splenocytes and purified T-cells were stimulated using anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies, in the presence or absence of c-FLIP inhibitor, for 72 hours. Flow cytometry was used, with markers of apoptosis and cell death, to ascertain the incidence of apoptosis within the T cell populations.
*Results:
Figure 1: c-FLIP knock-down in T-cells prolongs allograft survival.
Reconstitution with T-cells transfected with siRNA to c-FLIP resulted in significantly longer allograft survival compared to reconstitution with T-cells transfected with scrambled control.
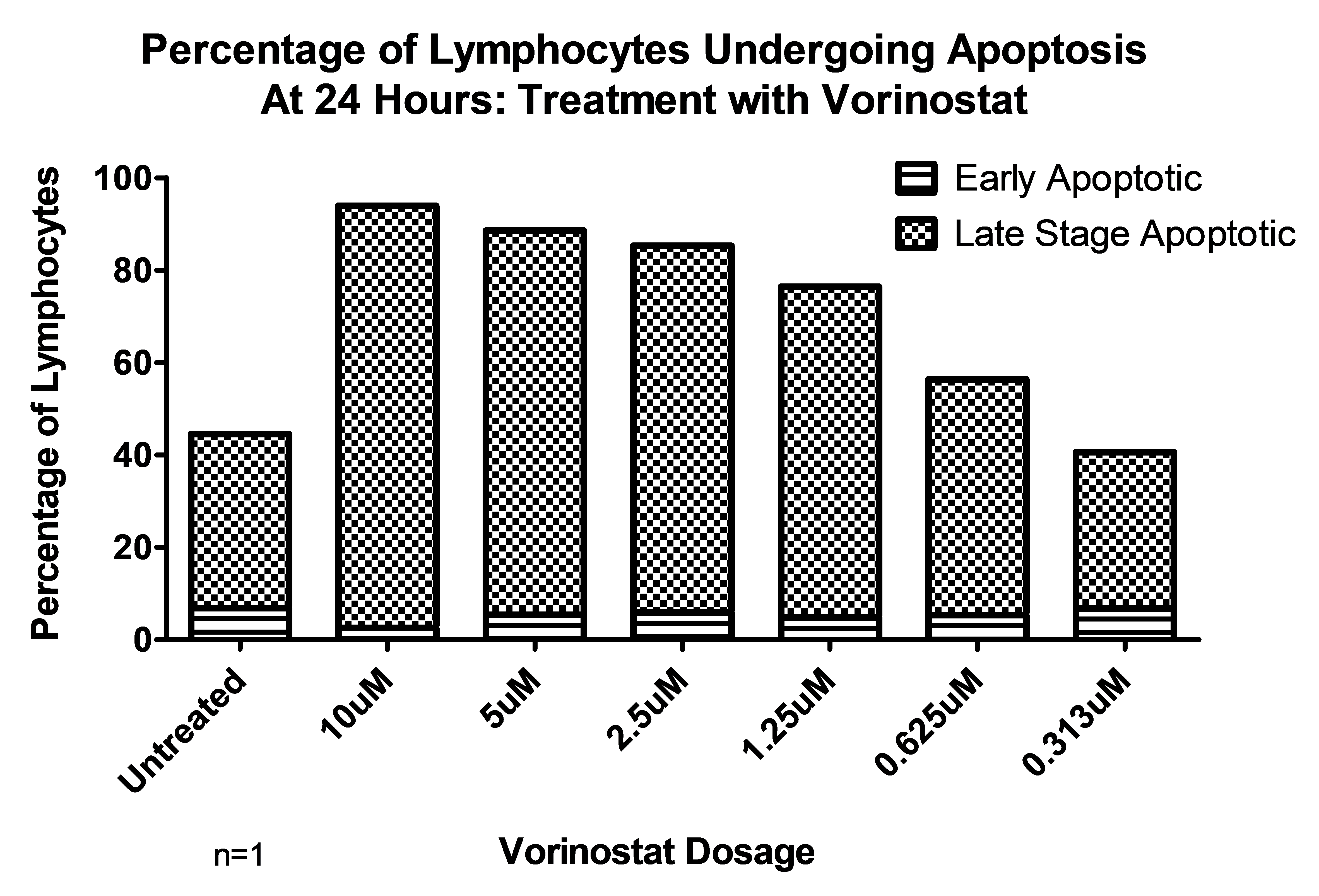
Figure 2: Populations of lymphocytes treated with Vorinostat have a greater incidence of apoptosis.
Vorinostat and Entinostat induce apoptosis within activated T-cells. A dose-response relationship exists, cells treated with higher doses of Vorinostat or Entinostat have a greater incidence of apoptosis (Fig.2). Preliminary data suggests Entinostat may more selectively induce apoptosis in activated T cells than Vorinostat.
*Conclusions: Vorinostat and Entinostat have potential as immunosuppressive therapies for transplantation. We plan to test these drugs as well as novel small molecule inhibitors in rodent heart transplant recipients shortly.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Costello R, Ingram RJ, Longley D, McDaid J. Bespoke Immunosuppression: Prolonging Transplant Survival through Enhanced T-cell Activation Induced Cell Death [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/bespoke-immunosuppression-prolonging-transplant-survival-through-enhanced-t-cell-activation-induced-cell-death/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress