Belatacept-Based Maintenance Immunosuppression Promoted Long-Term Antibody-Mediated Rejection Free Graft Survival After Desensitization in Sensitized Multiparous Female Recipients
Duke Transplant Center, Durham, NC
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 170
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Kidney transplantation, Sensitization
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 12 - Immunosuppression & Tolerance: Preclinical & Translational Studies
Session Information
Session Name: Immunosuppression and Tolerance: Preclinical and Translational Studies
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-6:10pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-6:10pm
Location: Hynes Ballroom A
*Purpose: Amongst sensitized patients awaiting a transplant, females are disproportionately represented. To date, nonhuman primate (NHP) models of transplantation have relied on male animals, sensitized by skin transplantation to model the sensitization. Using female NHPs sensitized by pregnancy, we sought to examine the desensitization strategy using costimulation blockade and proteasome inhibition on graft survival.
*Methods: 10 multiparous animals were allocated to three different treatment groups. Donors were allocated following screening to ensure greatest flow crossmatch positivity and repeated mismatch based on offspring MHC typing. Three (3) animals received no desensitization (control) and three (3) animals received weekly Carfilzomib (CFZ, 27mg/m2) and belatacept (Bela, 20mg/kg) for desensitization prior to kidney transplantation. All animals received tacrolimus-based maintenance immunosuppression (tacrolimus/mmf/steroid). Four (4) animals received desensitization with CFZ and Bela followed by the addition of belatacept (20mg/kg monthly) to the triple immunosuppression. Comparison was made with skin sensitized control male animals who did not receive desensitization, n=5).
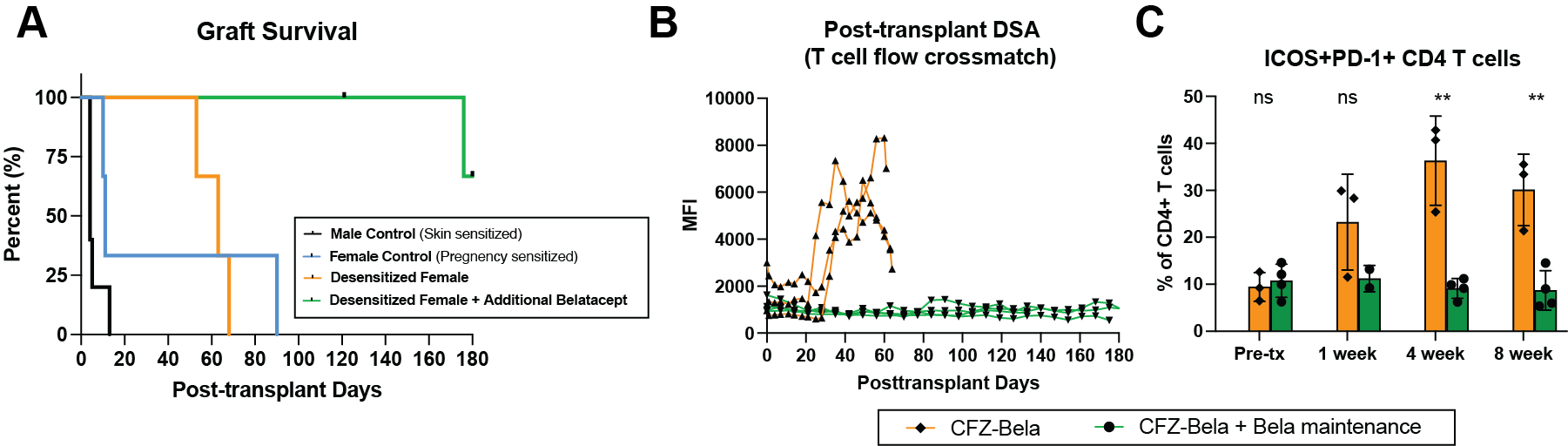
*Results: Multiparous female controls demonstrated heterogeneously prolonged survival compared to male skin sensitized animals, while multiparous animals receiving desensitization with CFZ-Bela showed significantly prolonged graft survival (MST= 4d vs. 63, p=0.01), but did not show a survival benefit over pregnancy sensitized controls (MST= 11d vs. 63d, p=0.98). The addition of belatacept in the maintenance immunosuppression allowed 2 animals to reach the end of study timepoint (6 month) and significantly prolonged graft survival (Fig A), although, 1 animal was lost due to PTLD. Desensitized multiparous animals showed better control of early post-transplant DSA compared to controls, while the addition of belatacept resulted in persistently suppressed DSA and post-transplant follicular helper T (Tfh) cells in the lymph nodes. (Fig B and C)
*Conclusions: Real life pregnancy-induced MAMU sensitization results in reduced transplant survival with a DSA rise. Desensitization with CFZ and Bela prolongs survival and suppresses DSA production during the initial 3 weeks post-transplant. The addition of belatacept to triple maintenance immunosuppression results in a sustained reduction of DSA, lymph node Tfh cells and AMR development.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Manook M, Anwar I, Schmitz R, Fitch Z, Yoon J, Jackson A, Kwun J, Knechtle S. Belatacept-Based Maintenance Immunosuppression Promoted Long-Term Antibody-Mediated Rejection Free Graft Survival After Desensitization in Sensitized Multiparous Female Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/belatacept-based-maintenance-immunosuppression-promoted-long-term-antibody-mediated-rejection-free-graft-survival-after-desensitization-in-sensitized-multiparous-female-recipients/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress