Basiliximab vs. Low-Dose Thymoglobulin Induction Therapy in Low Risk Kidney Transplant Patients: Prospective Randomized Study in Southeastern Mexico
Organ Transplantation & Research, IMSS UMAE HE 14, Veracruz, Mexico
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B203
Keywords: Graft function, Induction therapy, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Demonstrate that low dose Thymoglobulin (3 mg/kg total ) has similar efficacy (DGF, SGF, BPAR, hospitalizations, adverse events, graft loss and death) than Basiliximab induction.
*Methods: Prospective randomized study of patients undergoing renal transplantation (NCT03006419). Inclusion Criteria: Graft recipients >18 years, first living donor kidney transplant. Exclusion Criteria: 2nd kidney transplant, multiple organ recipients, ABO incompatibility, positive cross-match test prior to transplantation, PRA > 30%, positive DSA, HIV, HBsAg or HCV positive patients, leukocyte count <2000 / mm3, platelet count <75,000 / mm3, history of malignancy. 100 patients were randomized from 12/2016-05/2018. Group A: Induction with Basiliximab 20 mg IV day 0 and day 4. Group B: rATG (Thymoglobulin) 1 mg/kg body weight per day for days 0, 1 and 2 up to a total dose of 3 mg/kg day. If WBC<2000 / mm3 and/or platelets <75,000 / mm3), administration may be postponed until day 7 posttransplant. Posttransplant immunosuppression: TAC, MMF and steroids. Outcome measures (12 months): DGF, SGF, BPAR, infections, adverse events, graft loss, death. eGFR was measured by MDRD.
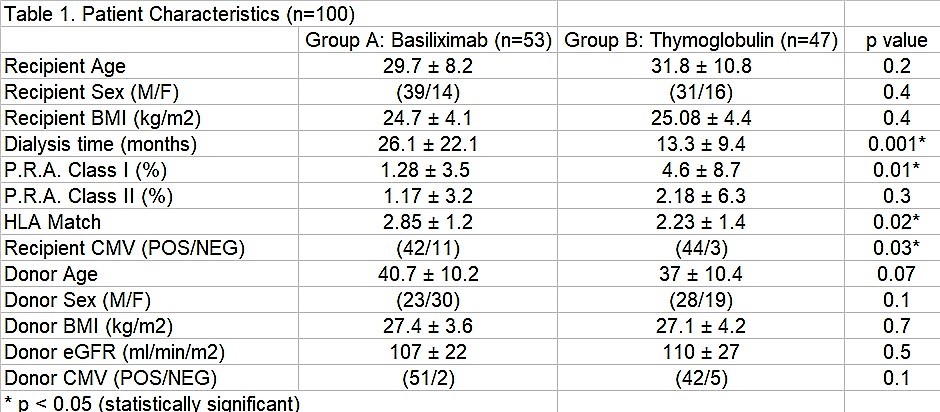
*Results: Group A (Basiliximab) (n=53) had longer dialysis time than group B (Thymoglobulin) (n=47) (p<0.05). ESRD etiology were similar in both groups. Both PRA were < 5% in both clases but class I was higher (s.s) in group B. Donor characteristics were similar between groups.
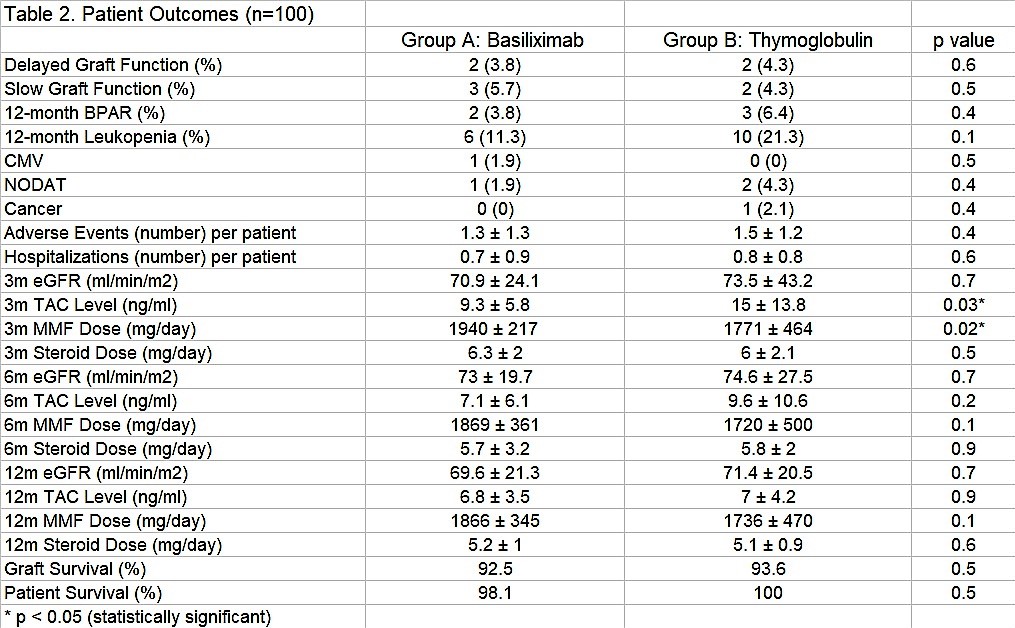
Mean Thymoglobulin dose was 3.1 ± 0.44 mg/kg. Initial TAC dose was 0.07 ± 0.07 mg/kg. All patients have completed six months follow-up minimum. There were no differences in DGF, SGF and BPAR between groups. All BPAR were Banff IB. 3-month TAC level and MMF dose was higher (s.s.) in Thymoglobulin group. No differences in eGFR, AE, hospitalizations, patient and graft survival were noted between groups.
*Conclusions: Our results suggest that 3mg/kg Thymoglobulin induction therapy has similar efficacy and safety outcomes than Basiliximab in low-risk living donor kidney transplantation during follow-up.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martinez-Mier G, Moreno-Ley PI, Budar-Fernandez LF, Mendez-Lopez MT, Barrera-Amoros DA, Paz-Roman MDela, Jimenez-López LA, Aguilar-Sandoval EG, Allende-Castellanos CA. Basiliximab vs. Low-Dose Thymoglobulin Induction Therapy in Low Risk Kidney Transplant Patients: Prospective Randomized Study in Southeastern Mexico [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/basiliximab-vs-low-dose-thymoglobulin-induction-therapy-in-low-risk-kidney-transplant-patients-prospective-randomized-study-in-southeastern-mexico/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress