B2-Adrenergic Receptor Activation in Donor Cells Inhibits T Cell Trafficking in Vascularized Composite Tissue Allotransplants
1Surgical Oncology, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, NY, 2Pathology, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, NY, 3Cardiology, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, 4Immunology, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, NY
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D-238
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Interferon (IFN), T cells
Session Information
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Transplantation of faces, hands, and limbs using vascularized composite allotransplantation (VCA) has faced significant challenges hindering its routine implementation in the clinic. One critical hurdle is the scarcity of adequately matched HLA donors, requiring high doses of immunosuppressants which prevent rejection, but also present significant risks to the patient. New methods of controlling rejection are desperately needed. One possibility could be in exploiting the links between the nervous and immune systems that regulate host defense. The neurotransmitter norepinephrine acts through the β2-adrenergic receptors (β2-AR) to regulate immune cells resulting in immunosuppression. We hypothesize that β2-AR activation suppresses immune cell function after VCA.
*Methods: Heterotopic hind limb transplantation mouse model was used with C57BL/6 (H-2b) as recipients and BALB/c (H-2d) mice as donors. Graft survival was measured with and without treatment with the β2-agonist terbutaline, and the contribution to graft survival of β2-AR signaling in donor and recipient tissue was investigated.
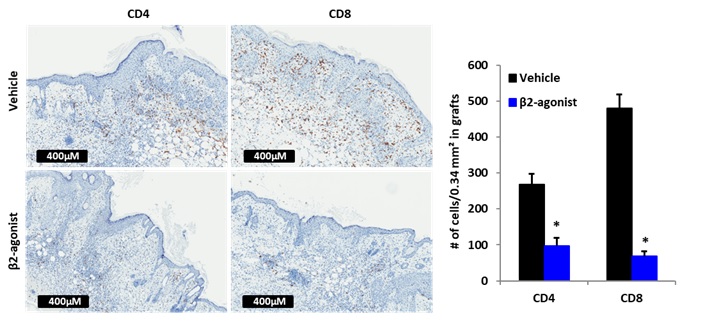
*Results: Induced β2-AR signaling significantly inhibited CD4+/8+ T cell infiltration in the graft with delayed graft rejection without severe side effects (Figure; brown color with Rabbit horseradish peroxidase). The β2-AR agonist significantly decreased the proportion of CD4+/8+ central/effector memory T cell populations in allotransplanted mice. Additionally, a significant reduction was noted in IFNγ secreting CD4+ T cells as well as IFNγ and IL-6 levels in the terbutaline group compared to the vehicle group. Graft rejection was delayed when β2-AR was activated in either recipient or donor cells, however β2-AR signaling in donor cells was requited for inhibition of T cell infiltration into transplanted grafts.
*Conclusions: A selective β2-AR agonist, terbutaline, was safe and effective to delay immune activation and graft rejection after VCA. Encouragingly, β2-AR agonists could be used clinically to decrease doses of toxic immunosuppressive drugs used to maintain healthy grafts and may serve as a bridging therapy while recipients cannot take immunosuppressive drugs due to toxicities. Further investigation is needed to maximize the efficacy of β2-AR agonist in transplant immunosuppression.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim M, Fisher D, Loo J, Bogner P, Sharma U, Skitzki J, Repasky E. B2-Adrenergic Receptor Activation in Donor Cells Inhibits T Cell Trafficking in Vascularized Composite Tissue Allotransplants [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/b2-adrenergic-receptor-activation-in-donor-cells-inhibits-t-cell-trafficking-in-vascularized-composite-tissue-allotransplants/. Accessed July 14, 2025.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress