Autoantibodies Against Ro/SS-A, CENP-B, and La/SS-B are Increased in Patients with Kidney Allograft Antibody-mediated Rejection
1Toronto General Hospital Research Institute, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2Krembil Research Institute, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada, 3Centre de Recherche du Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal, Montreal, QC, Canada, 4Department of Medicine, Division of Nephrology, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 515
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Autoimmunity, Immunoglobulins (Ig), Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: B-cell / Antibody /Autoimmunity
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
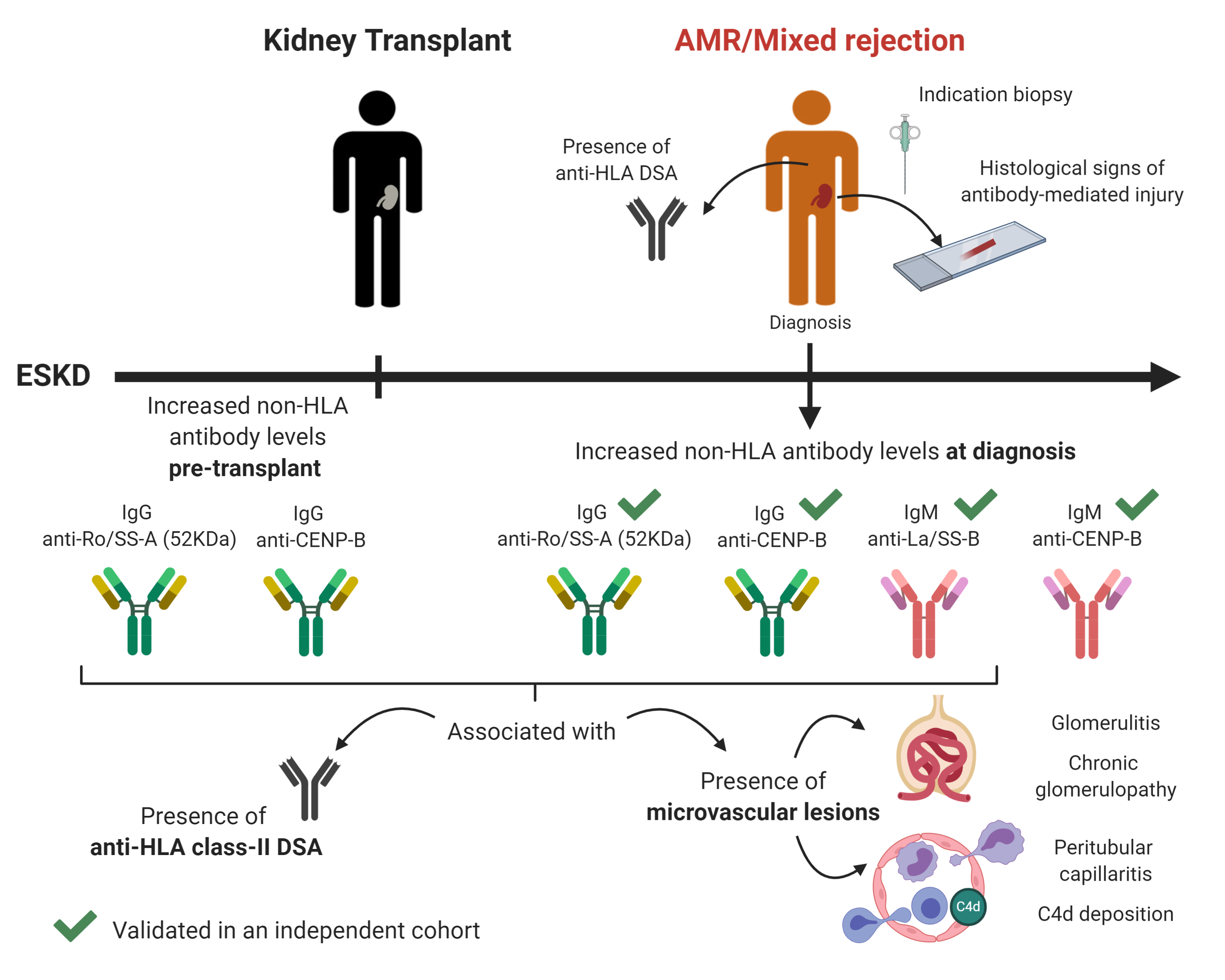
*Purpose: Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) causes >50% of late kidney graft losses. Although donor-specific antibodies (DSA) against HLA cause AMR, antibodies against non-HLA antigens are also linked to rejection. Identifying key non-HLA antibodies will improve our understanding of antibody-mediated injury.
*Methods: We analyzed non-HLA antibodies using protein arrays in sera from 91 kidney transplant patients with AMR, mixed rejection, acute cellular rejection (ACR), or acute tubular necrosis (ATN). IgM and IgG antibodies against 134 non-HLA antigens were measured pre-transplant and at the time of biopsy-proven diagnosis. Findings were validated in 60 kidney transplant patients from an independent cohort.
*Results: Seventeen non-HLA antibodies were significantly increased (P<0.05) in AMR/mixed rejection compared to ACR or ATN pre-transplant, and 9 at diagnosis. AMR/mixed cases showed significantly increased pre-transplant levels of IgG anti-Ro/SS-A and anti-CENP-B, compared to ACR. Together with IgM anti-CENP-B and anti-La/SS-B, these antibodies were also significantly increased in AMR/mixed rejection at diagnosis. Increased IgG anti-Ro/SS-A and anti-CENP-B pre-transplant and at diagnosis, and IgM anti-La/SS-B at diagnosis, were associated with the presence of microvascular lesions and class-II DSA (P<0.05). Significantly increased IgG anti-Ro/SS-A in AMR/mixed compared to ACR (P=0.01), and numerically increased IgM anti-CENP-B (P=0.05) and anti-La/SS-B (P=0.06), were validated in the independent cohort.
*Conclusions: This is the first study that implicates autoantibodies against Ro/SS-A and CENP-B in AMR. These non-HLA antibodies may participate in the crosstalk between autoimmunity and alloimmunity in kidney AMR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Clotet-Freixas S, Kotlyar M, McEvoy CM, Pastrello C, Rodríguez-Ramírez S, Farkona S, Cardinal H, Dieudé M, Hébert M, Li Y, Famure O, Chen P, Kim S, Chan E, Jurisica I, John R, Chruscinski A, Konvalinka A. Autoantibodies Against Ro/SS-A, CENP-B, and La/SS-B are Increased in Patients with Kidney Allograft Antibody-mediated Rejection [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/autoantibodies-against-ro-ss-a-cenp-b-and-la-ss-b-are-increased-in-patients-with-kidney-allograft-antibody-mediated-rejection/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress