Association between Sarcopenia and Nutritional Factors in Kidney Transplant Recipients
1Urology, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan, 2Innovative and Clinical Research Promotion Center, Gifu University Hospital, Gihu, Japan
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D-251
Keywords: Age factors, Area-under-curve (AUC), Kidney transplantation, Multivariate analysis
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
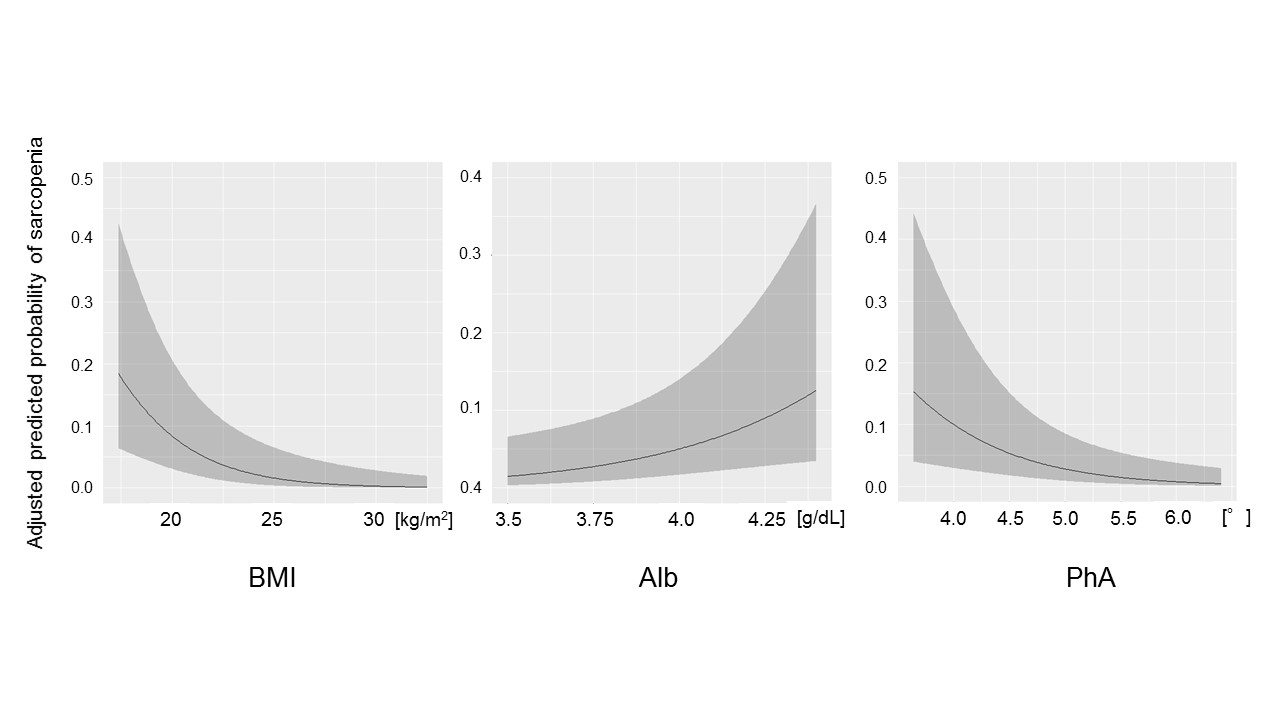
*Purpose: Malnutrition is an important risk factor for the development of sarcopenia. Several methods are used for the assessment of nutritional status including serum albumin (Alb) and body mass index (BMI), which are often used in clinical practice. Recently, phase angle (PhA) is increasingly becoming known as a nutritional status indicator. PhA is a parameter obtained from the bioelectrical impedance analysis and is associated with mortality, muscle mass, and muscle function. However, indicators associated with sarcopenia in kidney transplant patients remain unknown. The aim of the present study is twofold: firstly, to investigate the relationship between sarcopenia and PhA as well as other nutritional indicators such as BMI and Alb, and secondly, to evaluate the discrimination performance of these nutritional indicators for sarcopenia in kidney transplant recipients.
*Methods: A single-center cross-sectional study was conducted among kidney transplant recipients at Osaka City University Hospital between October 2018 and February 2019. We used the multivariable logistic regression model was used with adjustment for age, sex, C-reactive protein, dialysis vintage, time after transplant, diabetes mellitus, hemoglobin, and estimated glemerular filtration rate to assess the relationship between sarcopenia and PhA as well as the other nutritional markers including BMI and Alb and assessed the discrimination performance for sarcopenia by the area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) and the precision-recall curve (AUC-PR).
*Results: A total of 210 kidney transplant recipients were enrolled in this study. The median age was 55 years and 11% had sarcopenia. PhA as well as BMI was negatively and Alb was positively correlated with sarcopenia. The AUC-ROC and optimal cutoff values were 0.73 and 4.46 ° for PhA, were 0.83 and 20.5 kg/m2 for BMI, and were 0.67 and 3.91 g/L for Alb, respectively. The AUC-PR was 0.97 for BMI, 0.96 for PhA, and 0.16 for Alb. Figure shows the predicted probability of sarcopenia based on BMI, Alb and PhA after adjustment using multivariable logistic regression model.
*Conclusions: BMI and PhA were negatively correlated, whereas Alb was positively correlated with sarcopenia. PhA and BMI had enough power to detect sarcopenia. PhA < 4.46° may therefore be used to increase the pretest probability of sarcopenia in kidney transplant recipients, as well as BMI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kosoku A, Uchida J, Ishihara T, Iwai T, Shimada H, Kabei K, Nishide S, Naganuma T, Nakatani T. Association between Sarcopenia and Nutritional Factors in Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/association-between-sarcopenia-and-nutritional-factors-in-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress