Assessment of the Relationship between Inflammation and Glomerular Filtration Rate
1Faculty of Medicine, Public Health Department, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico, Mexico, 2Department of Nephrology, Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición Salvador Zubirán, Mexico, Mexico, 3Department of Transplantation, Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición Salvador Zubirán, Mexico, Mexico, 4Department of Transplantation, Hospital General de México Doctor Eduardo Liceaga, Mexico, Mexico, 5Faculty of Medicine, Department of Public Health, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Mexico, Mexico, 6Department of Public Health Sciences, Loyola University Chicago, Chicago, IL, 7Department of Cardiology, Instituto Nacional de Cardiología Ignacio Chávez, Mexico, Mexico
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A147
Keywords: Donation, Kidney, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
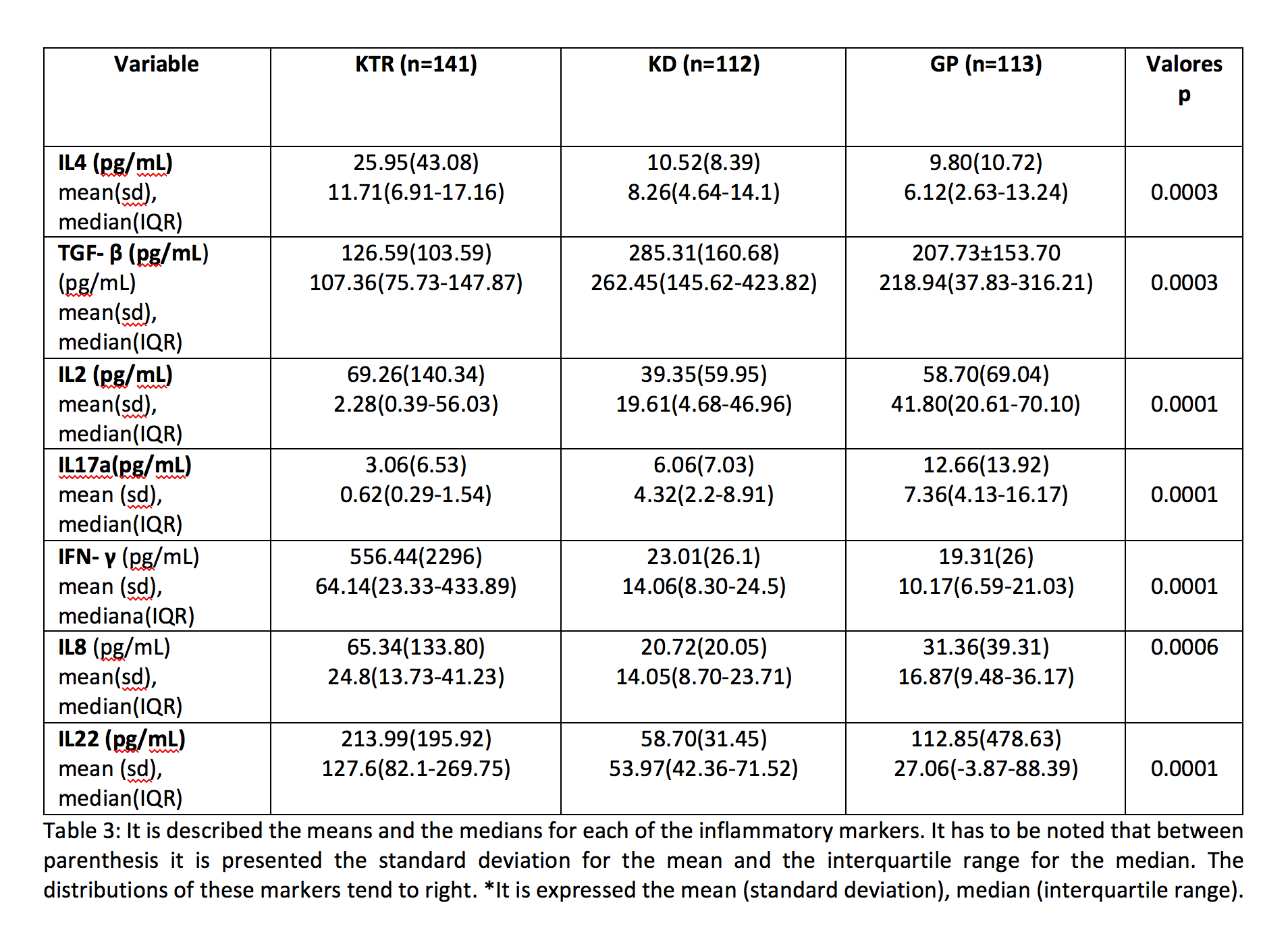
*Purpose: Since the inflammatory phenomena that occur after transplantation are decisive factors for developing renal rejection, we decided to study how the elevation of some cytokines levels, such as IL-2, IL-8 IL-17a, IL-22, IFN-γ, IL-4 and TGF-β, could impact to renal function.
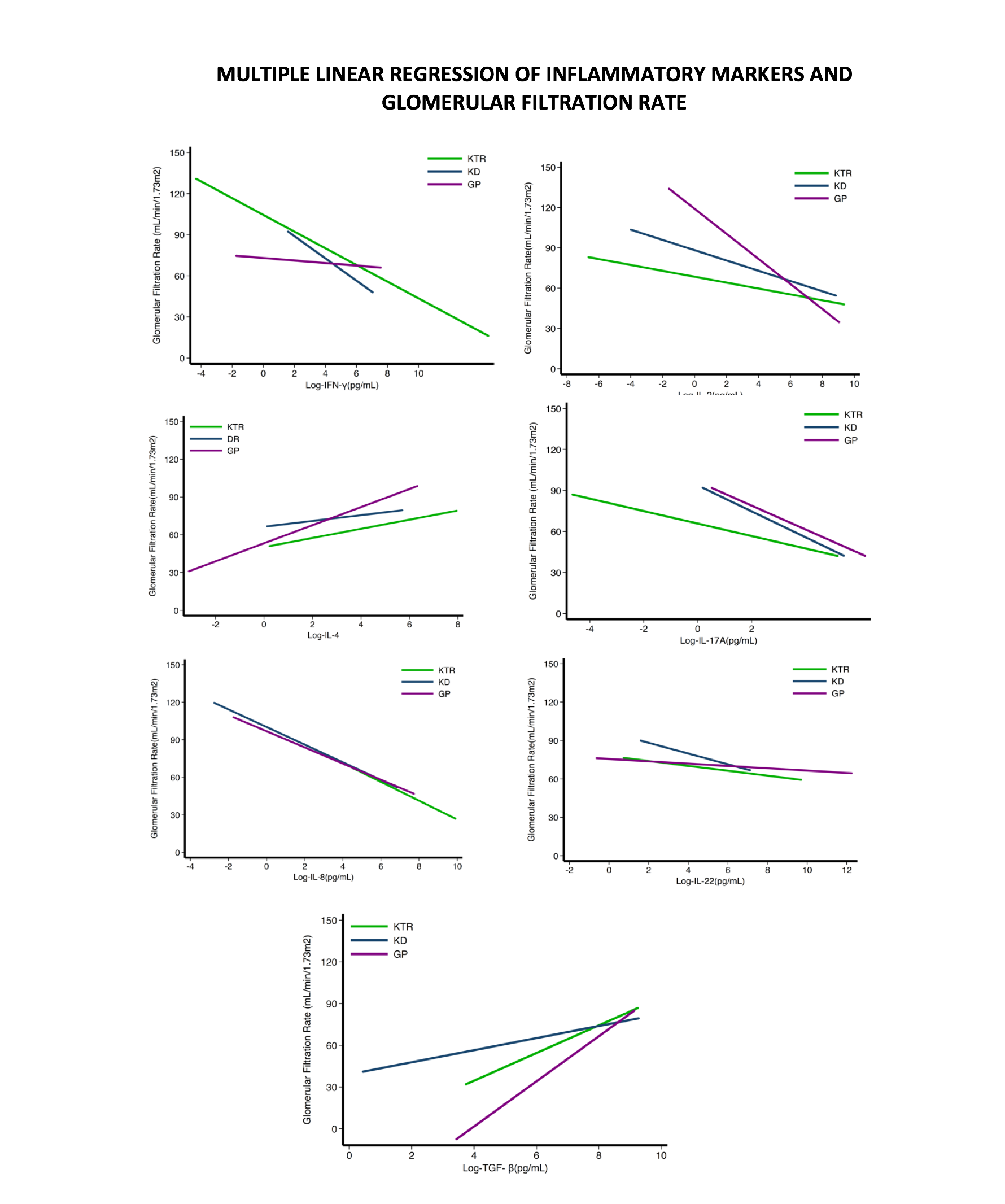
*Methods: The subjects’ age was between 18 and 75 years and none of the individuals had evidence of infection, chronic liver disease, cancer, autoimmunity, IMC ≥ 30 kg / m2, being pregnant, having had a hospitalization or a surgical procedure in the previous month, being recipient of multiple organ transplantation, and having had an event of acute rejection during the previous three months. We recruited, as well, 112 kidney donors (KD) with the same criteria, and also, 113 individuals from general population (GP) in the same age group from a community at the state of Michoacán, Mexico. We estimated the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of the individuals and then we obtained serum samples from everyone. We grouped the subjects according to their GFR and quantified the levels of such cytokines. Later, we did two statistical analyzes: first we realized a correlation probe to see if there was a relation between the kind of population and the levels of these cytokines and after we made a lineal regression to see how every cytokine modifies the GFR.
*Results: We found that IL-4, IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-8 and IL-22 levels are higher in KTR than in KD and GP. TGF-β levels were higher in KD and IL-17a levels were higher in PG. We found, also, that IL-4 and TGF-β were correlated with an increment in the GFR, the rest of them were correlated with a decrement in GFR.
*Conclusions: We concluded that IL-8 and TGF-β, as their relevance in correlation, could be studied as indicators of failure or success of renal function after transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ramirez-Gonzalez JB, Morales-BuenRostro LE, Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Garcia-Covarrubias L, Pacheco-Domínguez RL, Durazo-Arvizu R, Alberu J, Cuevas-Medina EN, López-Cervantes M, Osorio-Juárez RA. Assessment of the Relationship between Inflammation and Glomerular Filtration Rate [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/assessment-of-the-relationship-between-inflammation-and-glomerular-filtration-rate/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress