Assessment of Renal Function in Kidney Transplant Recipients Through Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Vancomycin
Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B24
Keywords: Dosage, Graft function, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Bacterial/Fungal/Other Infections
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Background: Determining the dose of renally eliminated drugs such as vancomycin in kidney transplant recipients is often challenging due to unclear tools to assess renal function. The objective of this study is to determine factors that may predict optimized vancomycin dosing.
Methods: A retrospective chart review of kidney transplant patients between 2011 and 2014 who received vancomycin was performed. Recipients' demographics such as age, gender, weight, height, and serum creatinine were collected along with donor's demographics. Donor types such as living donor, deceased donor, standard criteria donor, expanded criteria donor, donation after cardiac death vs brain death were collected. Dosing of vancomycin received, dosing of calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) received, CNI serum levels and vancomycin levels were assessed.
Results: The average daily vancomycin dose increase to reach target levels was 12.2 ± 6.6 mg/kg/day. Patients with tacrolimus level < 5 ng/mL required an increase of 13.9 ± 7.2. Those with SCD have an average dose increase of 10.5 ± 5.6
| Number of patients required dose increase | Number of patients required dose decrease | |
| Tacrolimus < 5 ng/ml | 18 | 1 |
| Tacrolimus > 7 ng/ml | 2 | 6 |
| Donation after brain death | 4 | 3 |
| Donation after cardiac death | 4 | 0 |
| Living donor | 14 | 6 |
| Deceased donor | 14 | 6 |
| Standard criteria donor | 4 | 0 |
| Expanded criteria donor | 2 | 3 |
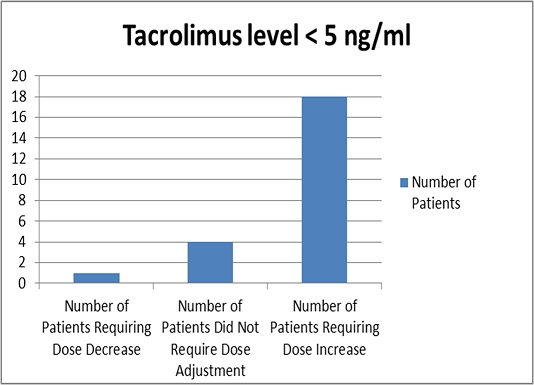
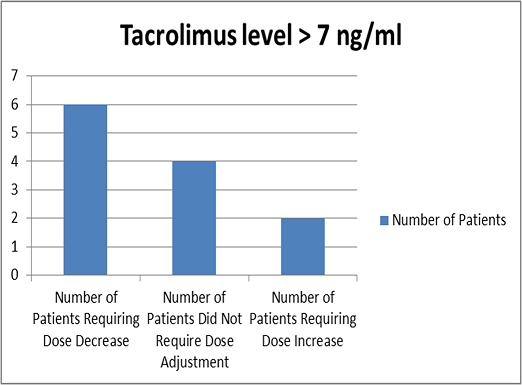
Conclusion: Renal function, as suggested by increased vancomycin requirements, appears higher in patients with an average tacrolimus trough level less than 5ng/mL and those who received a transplant from a standard criteria donors. Higher empiric vancomycin dosing in kidney transplant patients with these characteristics may be warranted, however further studies are needed to confirm this finding.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Thamer A, Elias N, Varughese C, Gift T, Fishman J, Shao S. Assessment of Renal Function in Kidney Transplant Recipients Through Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Vancomycin [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/assessment-of-renal-function-in-kidney-transplant-recipients-through-therapeutic-drug-monitoring-of-vancomycin/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
