Antibody-Suppressor CD8+ T Cells Ameliorate Antibody-Mediated Rejection Following Kidney Transplant in Mice
1Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, 2Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D-308
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Survival, T cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Cellular Therapies, Tissue Engineering / Regenerative Medicine
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: We previously reported the novel alloantibody suppressor activity of alloprimed CXCR5+IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells following hepatocellular transplant in mice. We utilized a murine kidney transplant (KTx) model and CCR5 KO recipient mice in order to investigate the role of these cells in suppression of alloantibody after a vascularized solid organ transplant. CCR5 KO KTx mice produce high titer alloantibody associated with severe antibody mediated rejection (AMR) that reproduces AMR histology observed in human KTx recipients. In the current studies, we investigated the biologic impact of adoptive cell transfer (ACT) of alloprimed CXCR5+IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells into high alloantibody producing CCR5 KO KTx recipients.
*Methods: CCR5 KO mice (H-2b) were transplanted with an allogeneic A/J (H-2a) kidney, and on postoperative day 5 underwent ACT of flow-sorted, alloprimed CXCR5+IFN-γ+CD8+ T cell subsets [retrieved from C57BL/6 mice alloprimed with A/J alloantigen (day 7)]. A second CCR5 KO KTx cohort received concomitant bilateral native nephrectomy in order to evaluate allograft survival by serial monitoring of serum creatinine (>100 μmol/L creatinine defines rejection). Untreated CCR5 KO recipients served as controls.
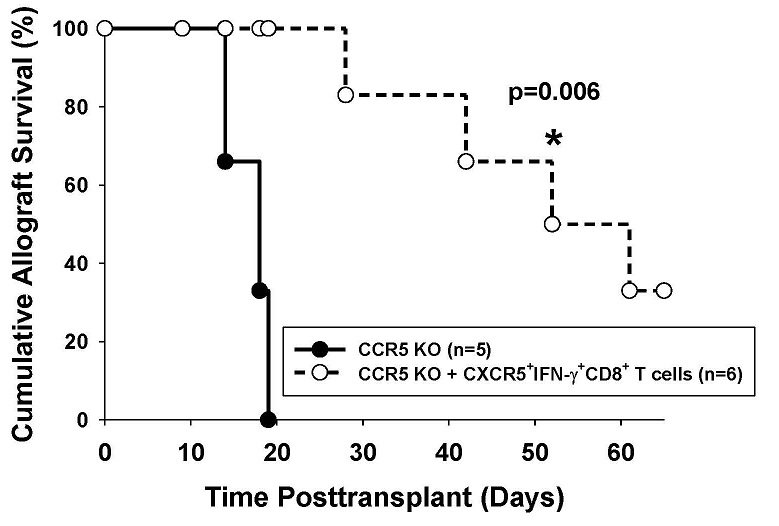
*Results: CCR5 KO KTx recipients developed high alloantibody titer (5,800±700, n=7) compared to wild-type recipients (1,200±100, n=9, p=0.0003). ACT of alloprimed CXCR5+IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells significantly inhibited alloantibody production in CCR5 KO recipients by 5-fold (1,200±200, p<0.0001). In addition, ACT of alloprimed CXCR5+IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells significantly inhibited day 14 AMR pathology (peritubular capillary margination and C4d deposition, arteritis) in CCR5 KO recipients (n=5) compared to untreated controls (n=5; composite histologic score 3.6±1.5 vs. 8.4±0.2, respectively; p=0.006). Alloantibody titer remained suppressed in treated mice greater than 30 days posttransplant, which correlated with a significant enhancement of allograft survival following ACT of alloprimed CXCR5+IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells (MST= 52 days, n=6) compared to untreated controls (MST= 14 days, n=5, p=0.006; see Figure).
*Conclusions: These data support the conclusion that ACT of antibody-suppressor CXCR5+IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells effectively inhibits alloantibody production and AMR not only after allogeneic hepatocellular transplant but also after vascularized solid organ transplant such as in CCR5 KO murine KTx recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zimmerer JM, Han JL, Zeng Q, Ringwald BA, Cassol C, Warren R, Abdel-Rasoul M, Breuer CK, Bumgardner GL. Antibody-Suppressor CD8+ T Cells Ameliorate Antibody-Mediated Rejection Following Kidney Transplant in Mice [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/antibody-suppressor-cd8-t-cells-ameliorate-antibody-mediated-rejection-following-kidney-transplant-in-mice/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress