Alemtuzumab versus Anti-Thymocyte Globulin Induction in the Setting of Immediate Post-Renal Transplant Acute Tubular Necrosis in an Urban, Minority Patient Population
University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B194
Keywords: Graft function, Induction therapy, Kidney
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Post-renal transplant (RTx) delayed graft function (DGF) or slow graft function (SGF) increase the risk of rejection and impair allograft function. Lymphocyte depleting induction agents reduce acute rejection and can be used to modulate maintenance immunosuppression in the setting of acute-tubular necrosis (ATN). There is currently insufficient evidence comparing alemtuzumab and rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin (rATG) in the setting of ATN immediately post-RTx in racially diverse, high-risk populations.
*Methods: Adult RTx recipients who received either rATG or alemtuzumab from 1/2015-10/2017 were assessed. High-immunologic risk patients received alemtuzumab if they met the following criteria (African American with panel-reactive antibody [PRA] of 0%). All other high-immunologic risk patients received rATG. In the setting of post-RTx ATN risk factors, rATG was utilized per protocol. The primary outcome was the incidence of DGF and SGF. DGF was defined as need for dialysis before post-operative day (POD) 7. SGF was defined by <50% decrease in serum creatinine (SCr) from pre-RTx SCr or SCr ≥ 3.00 mg/dL by POD7.
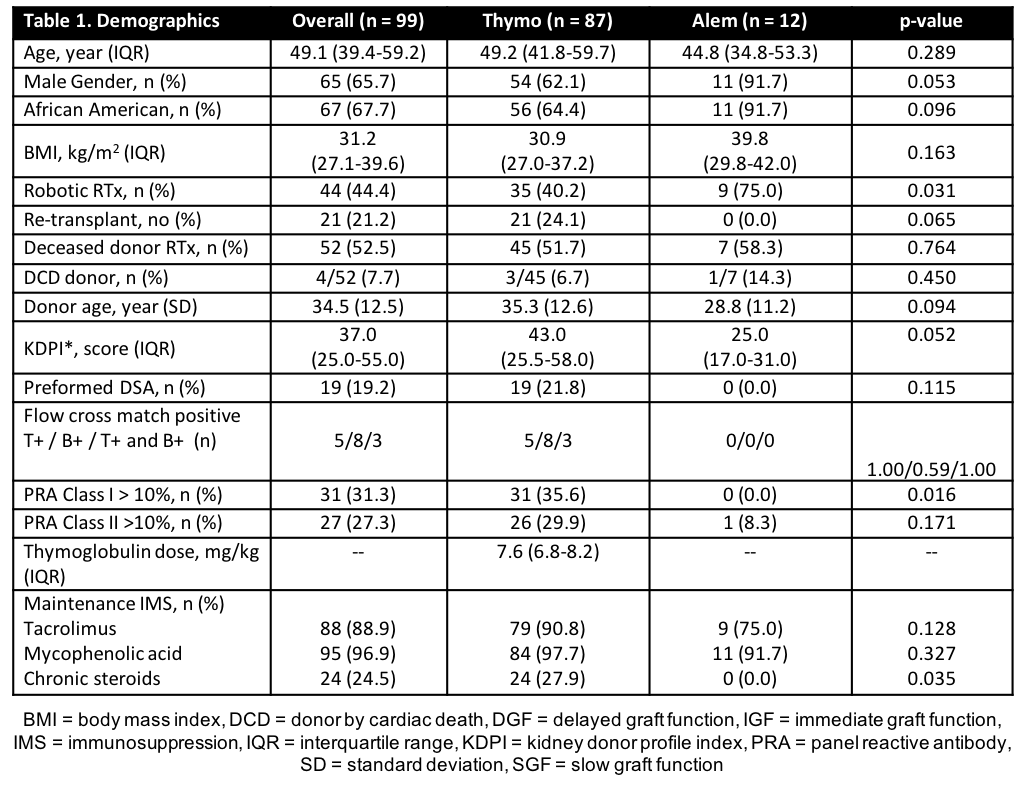
*Results: A total of 99 patients were analyzed. A majority of patients were male (65.7%), African American (67.7%), and received a deceased donor RTx (DDRT) (52.5%) (Table 1). Average rATG dose was 7.6 mg/kg (ideal body weight). No difference was seen in length of stay (p=0.862) or incidence of post-RTx ATN (p = 0.966). Patients receiving alemtuzumab had significantly higher eGFR at 12 months (p=0.044). Incidence of BPAR, empiric rejection, death-censored graft loss at 12 months was higher in rATG (Table 2).
*Conclusions: Patients has similar incidence of renal dysfunction post-RTx when receiving either alemtuzumab or thymoglobulin. Utilization of alemtuzumab did not increase the risk of ATN post-RTx and could potentially serve as an alternative in patients with pre-operative risk factors for ATN, pending other recipient immunologic criteria. Further prospective studies are warranted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tejani K, Benedetti E, Lichvar A. Alemtuzumab versus Anti-Thymocyte Globulin Induction in the Setting of Immediate Post-Renal Transplant Acute Tubular Necrosis in an Urban, Minority Patient Population [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/alemtuzumab-versus-anti-thymocyte-globulin-induction-in-the-setting-of-immediate-post-renal-transplant-acute-tubular-necrosis-in-an-urban-minority-patient-population/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress