Additional Dose of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Increases Neutralization Capacity in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
Y. Yoo1, J. Husson2, T. Iraguha3, S. Niederhaus4, X. Wen5, A. Crane5, A. Carrier5, J. Avruch5, A. Ahuja6, M. Mathew7, S. Dahiya8, A. P. Rapoport8, D. Atanackovic8, K. K. Saharia2
1Inst of Human Virology, Baltimore, MD, 2Div of Infect Diseases, Univ of Maryland School of Med. and Inst of Human Virology, Baltimore, MD, 3Univ of Maryland School of Med. and Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center, Baltimore, MD, 4Dept of Surgery, Univ of Maryland School of Med., Baltimore, MD, 5Dept of Surgery, Univ of Maryland Med. Center, Baltimore, MD, 6Dept of Medicine, Univ of Maryland Med. Center, Baltimore, MD, 7Div of Infect. Diseases, Univ of Maryland Med. Center, Baltimore, MD, 8Dept of Medicine, Univ of Maryland School of Med. and Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 683
Keywords: Antibodies, COVID-19, Immunogenicity, Vaccination
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 24 - All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis) I
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 4, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Solid organ transplant recipients (SOTR) develop weak antibody responses after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. Published data on neutralizing activity of plasma, a better measure of protection, in SOTR following an additional dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is limited.
*Methods: Plasma was longitudinally collected from SOTR following initial COVID-19 vaccination. Neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 was assessed using the cPass Neutralization Antibody Detection Kit (GenScript, Biotech). ELISAs were performed against SARS-CoV-2 proteins (S1, N, RBD), CMV (glycoprotein B), Influenza A H1N1 (nucleoprotein), HSV-1, EBV glycoprotein (gp350), and tetanus toxoid for comparison.
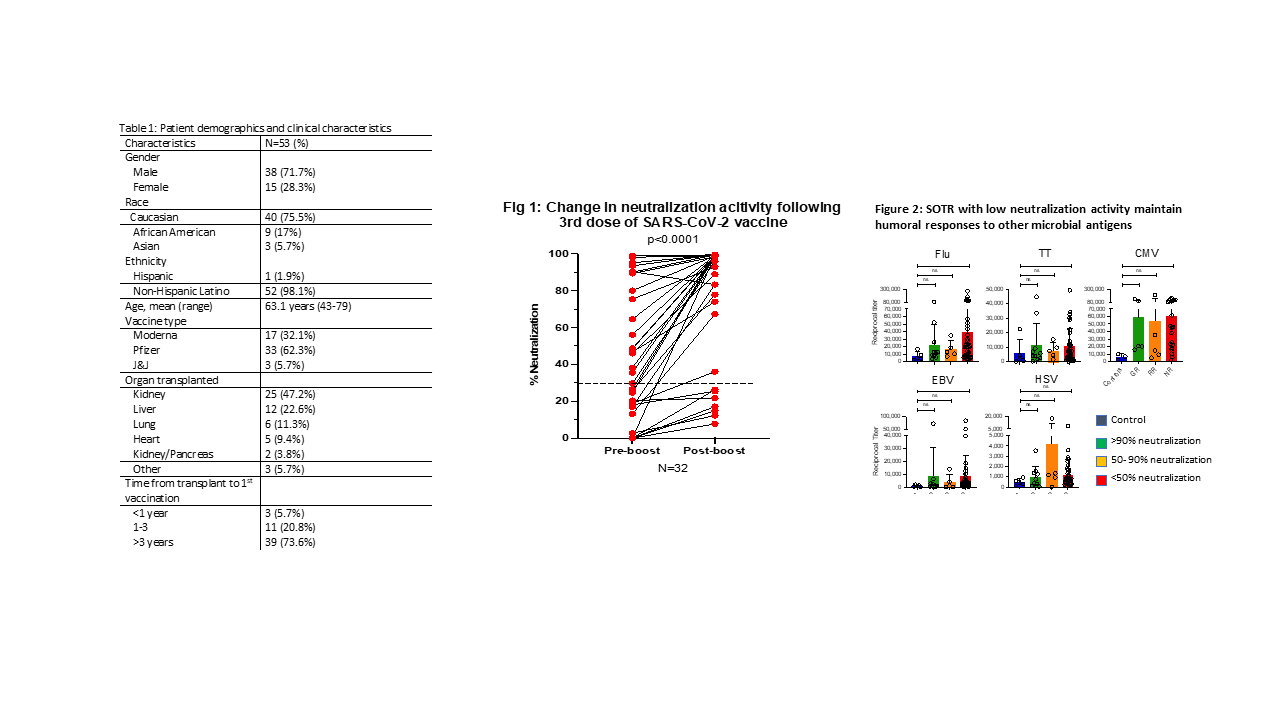
*Results: Demographic and clinical characteristics are summarized in table 1. No participants had evidence of COVID-19 infection as IgG titers to SARS-CoV-2 N protein were low. Neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 RBD was observed in 39.6% of individuals (N=21/53) ~93 days after initial vaccination. Participants with neutralizing activity were more likely to have received a liver transplant (47.6% vs 6.25%, p=0.001), and less likely to be on an anti-metabolite (52.4% vs. 87.5%, p=0.009) or triple immunosuppression (14.3% vs. 53.1%, p=0.008). After an additional vaccine dose, 78.1% (N=25/32) of participants developed neutralizing activity with significant increases in viral neutralization (figure 1, median 36.8% [95%CI 18.9-64.6] to 97.2% [95%CI 74.0-98.9], p<0.0001). Participants with low neutralizing activity demonstrated adequate antibody titers to other microbial antigens (figure 2).
*Conclusions: An additional dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine increased the number of SOTR with neutralizing activity and the magnitude of the seroresponse. SOTR with low neutralizing activity maintain humoral responses to other microbial antigens suggesting the diminished seroresponse might be related to inhibition of new B cell responses.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoo Y, Husson J, Iraguha T, Niederhaus S, Wen X, Crane A, Carrier A, Avruch J, Ahuja A, Mathew M, Dahiya S, Rapoport AP, Atanackovic D, Saharia KK. Additional Dose of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Increases Neutralization Capacity in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/additional-dose-of-sars-cov-2-vaccine-increases-neutralization-capacity-in-solid-organ-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress