A Three-gene Peripheral Blood Potential Diagnosis Signature Associated With Autophagy For Antibody-mediated Rejection In Renal Transplantation
Department of Urology, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 9081
Keywords: Genomic markers, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Clinical Science » 17 - Biomarkers: Clinical Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers: Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) is emerging as a major cause of graft loss in renal transplantation. Nowadays, non-invasive diagnosis of AMR with high accuracy is urgently needed as the early screening guide for clinical renal biopsy. To change this status, we sought to apply machine learning methods to develop and validate a non-invasive diagnostic gene signature for AMR using peripheral blood.
*Methods: Two independent renal transplantation cohorts with peripheral blood gene expression profiles of AMR and stable functioning (STA) and T-cell mediated rejection (TCMR) patients were collected from the Gene Expression Omnibus database as training and validation cohorts. Based on differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in AMR, we performed functional enrichment analysis and gene set enrichment analysis to identify primary mechanisms. Then, we utilized boruta algorithm to screen specific genes and applied LASSO-logistic algorithm to build a diagnostic model which was then evaluated and validated.
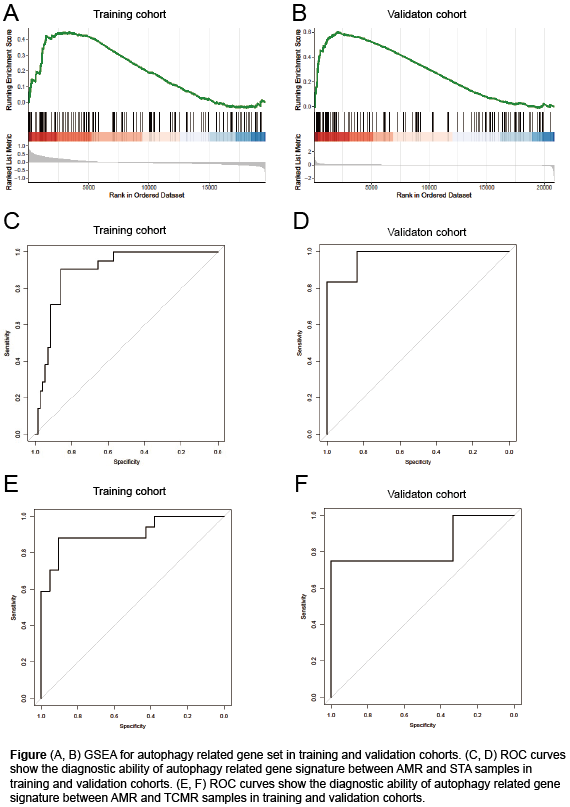
*Results: According to functional enrichment analysis, autophagy was found to be the primary biological process in AMR and selected for further analysis. Subsequently, a diagnostic model, consisting of three genes associated with autophagy, was established based on the training cohort in distinguishing AMR from STA blood samples (AUC = 0.879), while it demonstrated a higher accuracy (AUC = 0.917) in validation cohort. Besides, our model also showed high accuracy (89.5% and 90.0%) when distinguishing AMR from TCMR in training and validation cohorts, respectively.
*Conclusions: We identified and validated a three-gene diagnostic model with high accuracy for AMR state in renal transplant patients. As far as we know, this is the first study that reported a molecular diagnostic model derived from peripheral blood samples for AMR in renal transplantation. Our study provided a feasible and convenient tool for noninvasive diagnosis of AMR in clinical practice and highlighted the importance of autophagy in AMR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang Y, Xu Y, Zhang H, Hu X. A Three-gene Peripheral Blood Potential Diagnosis Signature Associated With Autophagy For Antibody-mediated Rejection In Renal Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-three-gene-peripheral-blood-potential-diagnosis-signature-associated-with-autophagy-for-antibody-mediated-rejection-in-renal-transplantation/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress