A Simple HLA Class II Matching Strategy for the Prediction of De Novo Donor-Specific HLA Antibodies
1Surgery, University of Wisconsin - Madison, Madison, WI, 2Nephrology, Hospital Angeles Pedregal, Mexico City, Mexico, 3Nephrology, Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Medicas y Nutricion, Mexico City, Mexico, 4Medicine, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 108
Keywords: HLA antibodies, HLA matching, Immunogenicity, Prediction models
Session Information
Session Name: Histocompatibility and Immunogenetics
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:15pm-4:27pm
Presentation Time: 4:15pm-4:27pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: In kidney transplantation, degree of HLA Class II mismatch (MM) between donor and recipient drives the risk to develop de novo DSA (dnDSA). New methods to gauge HLA MM focus on specific amino acid differences rather than conventional HLA MM. We sought to examine whether a modified serology-based matching strategy could also assess alloimmune risk.
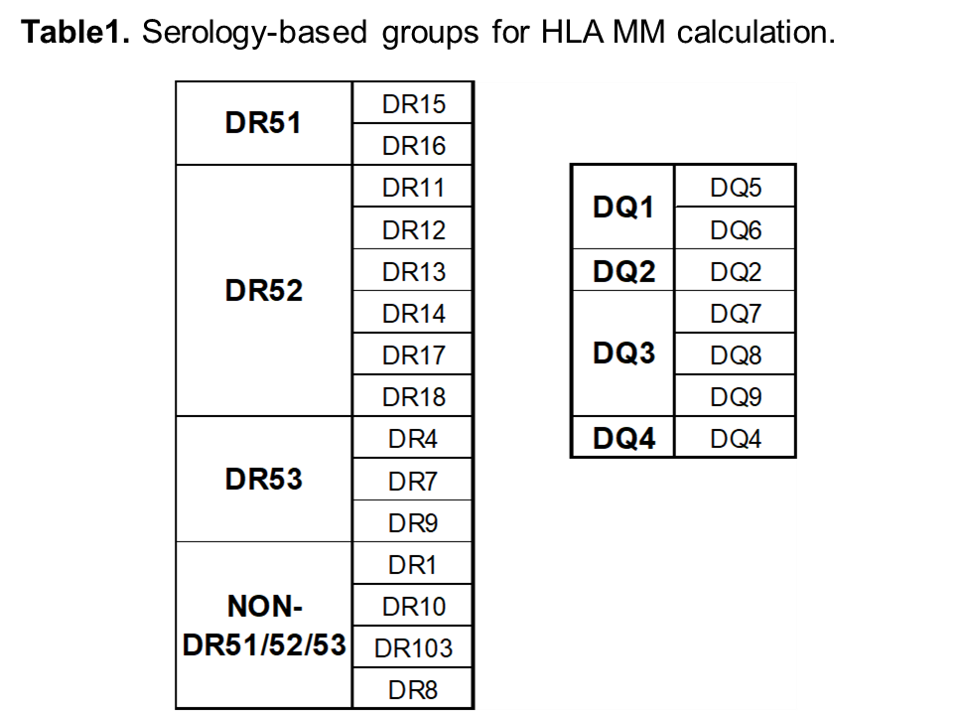
*Methods: We devised an HLA Class II MM strategy that groups Class II antigens based on serologic relation (Table1) and examined the rates of dnDSA formation in 349 kidney transplant recipients with negative DSA at time of transplant. This strategy was compared to eplet calculations and conventional HLA MM for the risk to develop dnDSA.
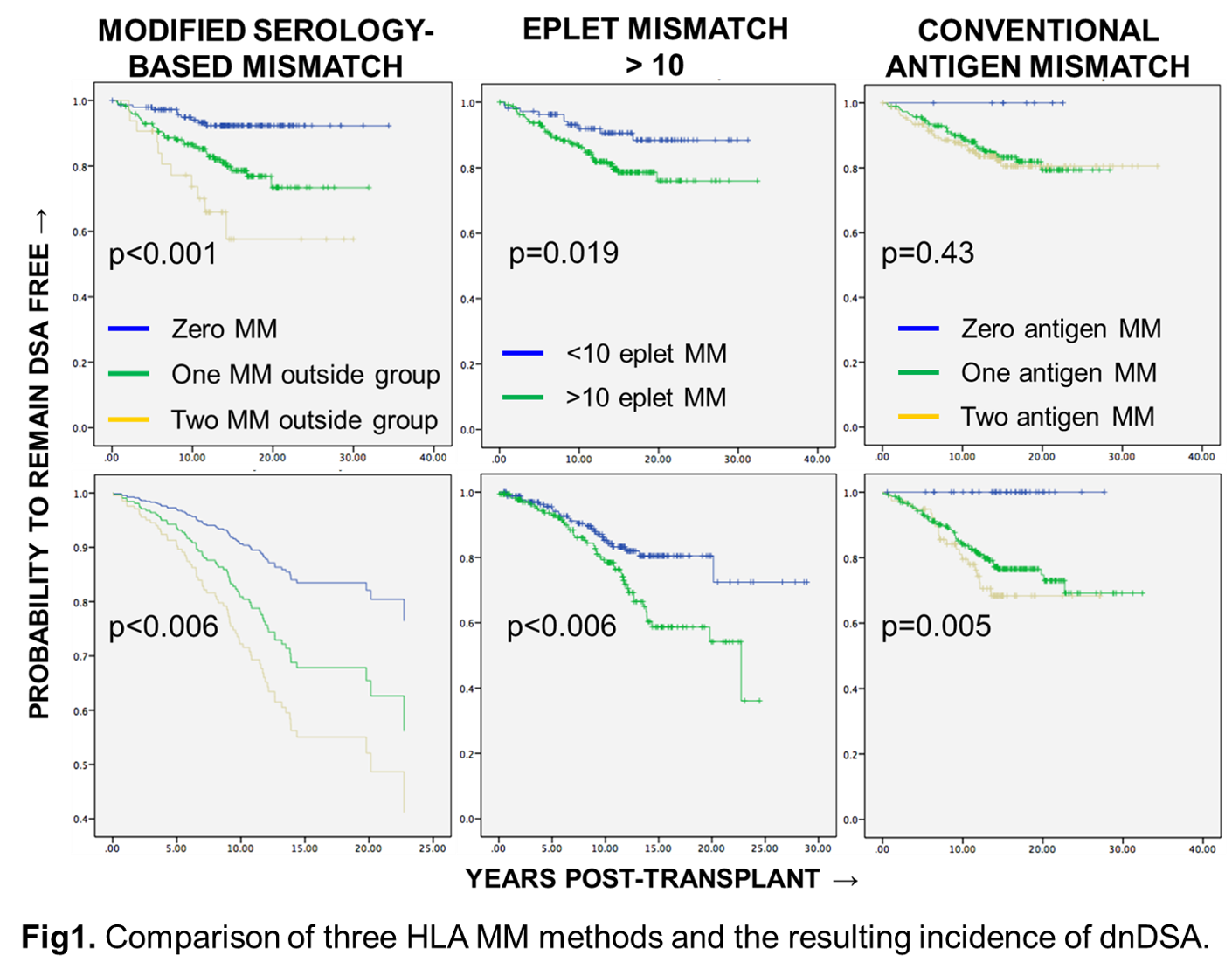
*Results: 95 patients developed Class II dnDSA between 0.5-32 years post-transplant. The incidence of dnDSA against HLA-DR gradually increased with the number of MMs outside of the serology-based groupings (p<0.001, Fig1). Using a published DR eplet MM threshold of 10 showed a subtler increased risk for dnDSA (p=0.019). The risk for dnDSA with DQ MMs outside serology-based groups also increased with number of MMs (p<0.006). Published DQ eplet MM threshold of 17 was unable to clearly stratify the risk (p<0.105) but a calculated threshold of 10 eplet MMs was best able to assess DQ dnDSA risk (p<0.006). Conventional antigen MM was unable to stratify dnDSA risk for DR but could stratify for DQ (p=0.005).
*Conclusions: Our data suggest that this modified matching strategy performs as well as eplet calculations and better than conventional MM calculations in risk prediction for the development of dnDSA. The simplicity of our matching strategy does not require imputations or actual high resolution HLA typing and may be an option for programs with limited access to imputation models and limited HLA typing resources.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hidalgo LG, Juarez IAMartinez, Morales-Buenrostro L, Shojai S, Campbell P. A Simple HLA Class II Matching Strategy for the Prediction of De Novo Donor-Specific HLA Antibodies [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-simple-hla-class-ii-matching-strategy-for-the-prediction-of-de-novo-donor-specific-hla-antibodies/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress