A Non-Invasive Urinary Common Rejection Module (uCRM) Gene Expression Score Quantifies and Differentiates Kidney Transplant Injury.
1University of California San Francisco, San Francisco
2Immucor Inc, Atlanta
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 263
Keywords: Gene expression, Kidney transplantation, Rejection, Urinalysis
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Long Term Kidney Graft Survival I
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:54pm-3:06pm
Presentation Time: 2:54pm-3:06pm
Location: E450a
We sought to investigate the use of the common rejection module (CRM) genes in the discrimination of AR, BKVN, and stable transplant phenotypes in urine of kidney transplant patients. Kidney transplantation (tx)is preferred for treatment of ESRD by any cause. Despite short-term improvemnts, long-term kidney allograft outcomes have not improved as expected. The most plausible explanation for this unmet achievement relies on rather poor immune-risk assessment of transplant patients in current clinical practice.
Methods
A CRM consisting of 11 genes expressed on allograft biopsies was recently shown to be highly accurate to discriminate patients undergoing acute rejection (AR), correlate with the extent of graft injury, and predict future allograft damage. Cell pellet from 117 urine samples were evaluated for expression values of all 11 using qPCR. ROC analysis was performed to assess clinical utility of these CRM genes. Symbolic regression was used to create a urinary CRM (uCRM) score from a subset of these genes.
Results
The 5-gene uCRM score calculated from gene expression in the urine cell pellet was significantly higher in AR than in stable (STA) and in BK viral nephropathy (BKVN) (9.705 ± 1.018 vs. 0.4567 ± 0.1213 and 1.45 ± 0.3917 respectively, p<0.0001) and significantly discriminated AR from STA and BKVN patients with high accuracy (AUC=0.9723; 95% CI = 0.9426 – 1.0000, p<0.0001). In a validation set, a threshold of 1.896 showed 100% sensitivity and 85.7% specificity to discriminate high-risk from low-risk patients for AR. 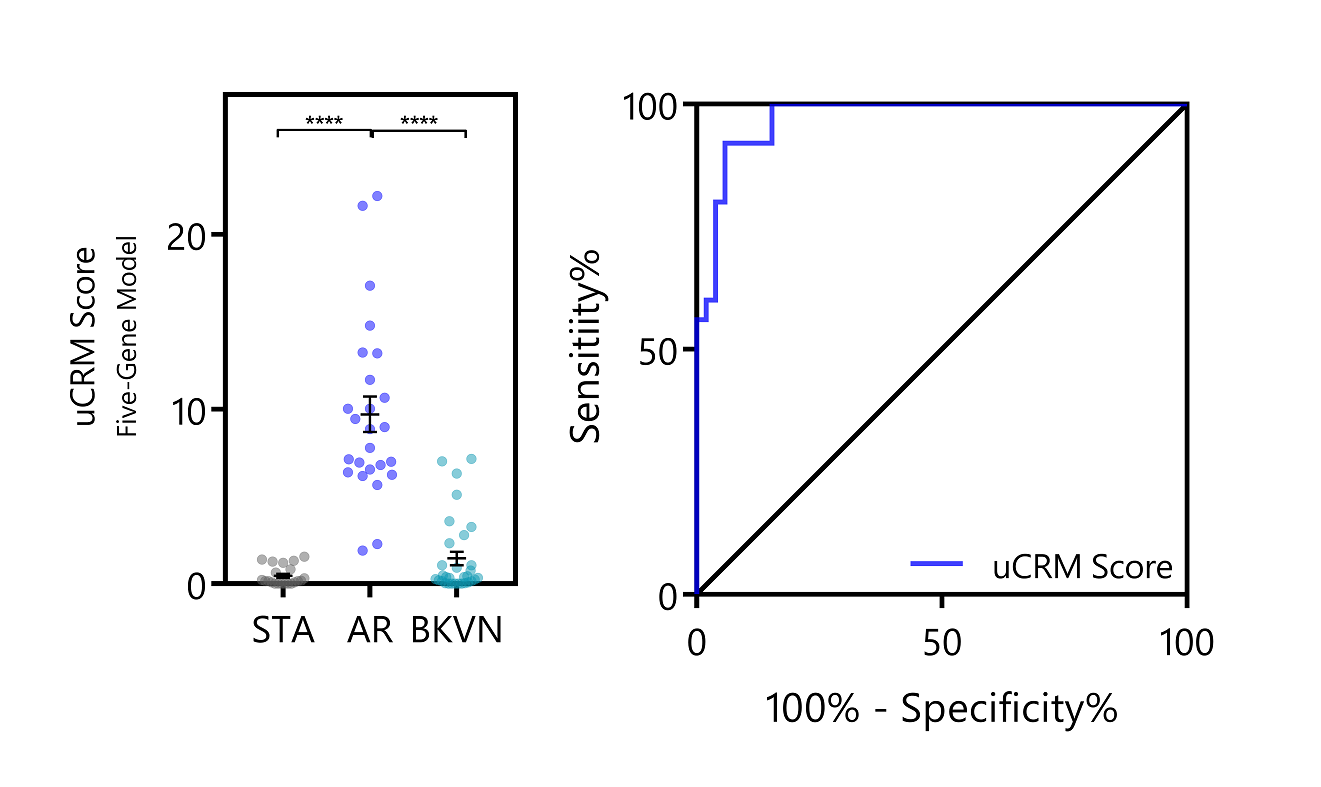 Conclusion
Conclusion
By using a previously published gene list, we investigated the role of this panel as a surrogate biomarker panel. The 5-gene uCRM score in urine samples is able to non-invasively detect kidney transplant patients at high risk of AR and could provide a tool for non-invasive, prospective AR and BKVN risk assessment, with implications on tx precision medicine.
CITATION INFORMATION: Sigdel T, Yang J, Bestard O, Hsieh S.-C, Roedder S, Damm I, Liberto J, Nandoe S, Sarwal M. A Non-Invasive Urinary Common Rejection Module (uCRM) Gene Expression Score Quantifies and Differentiates Kidney Transplant Injury. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sigdel T, Yang J, Bestard O, Hsieh S-C, Roedder S, Damm I, Liberto J, Nandoe S, Sarwal M. A Non-Invasive Urinary Common Rejection Module (uCRM) Gene Expression Score Quantifies and Differentiates Kidney Transplant Injury. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-non-invasive-urinary-common-rejection-module-ucrm-gene-expression-score-quantifies-and-differentiates-kidney-transplant-injury/. Accessed July 18, 2025.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
