A Comparison of Cell-Mediated Immune Responses among Organ Transplant Recipients Receiving High-Dose vs Standard-Dose Influenza Vaccine
University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 174
Keywords: Immunogenicity, Infection, Vaccination
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Vaccines and Viruses
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:42pm-4:54pm
Presentation Time: 4:42pm-4:54pm
Location: Room 313
*Purpose: The High-dose (HD) influenza vaccine has been shown to induce better humoral immunity than the standard-dose (SD) vaccine in solid organ transplant (SOT) patients. We aimed to evaluate whether the HD vaccine also induced better cell-mediated immunity (CMI) than the SD vaccine.
*Methods: A subset of patients enrolled in a randomized trial of the HD vs. SD influenza vaccine were enrolled in CMI analysis substudy during the 2016-17 influenza season. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were collected pre- and 4 weeks post-immunization. PBMCs were stimulated with 1µg of vaccine antigens corresponding to seasonal influenza A/H1N1, A/H3N2 or B viruses. CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell populations were analyzed using flow cytometry with intracellular cytokine staining for IFNγ, TNFα, IL2 and IL4.
*Results: We enrolled 55 patients in the CMI substudy, of which 30 and 25 received the HD and SD vaccine, respectively. Median age was 57 years and median time since SOT was 4.8 years. The most frequent organ transplant was kidney (40%), followed by liver (16%), lung (15%) and heart (13%) and combined (16%).
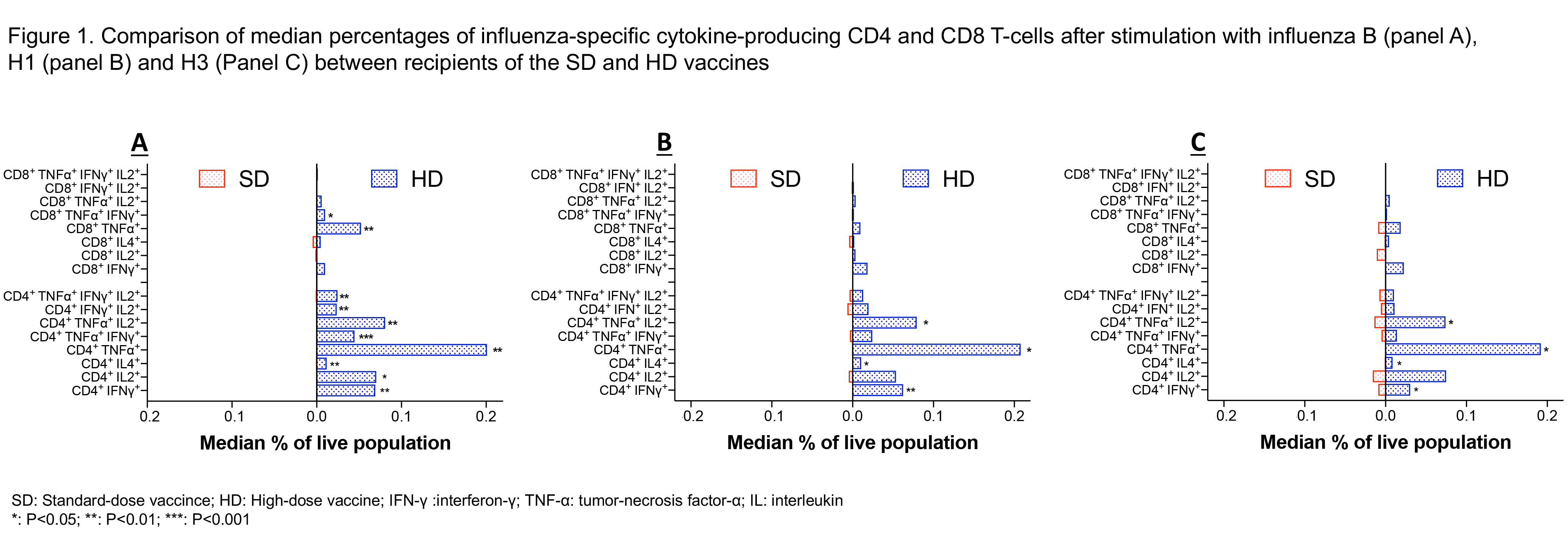
CD4+. Following stimulation with influenza B, patients who received the HD vaccine had a higher proportion of influenza-specific IFNγ+(p=0.009), IL4+(p=0.001), IL2+(p=0.017), TNFα+(p=0.003), IFNγ+TNFα+(p<0.001), TNFα+IL2+(p=0.003), IFNγ+IL2+ (p=0.006), and IFNγ+TNFα+IL2+(p=0.002) CD4+T-cells (Fig. 1A). Following stimulation with influenza A/H1N1, patients who received the HD vaccine had a higher proportion of influenza-specific IFNγ+(p=0.003), IL4+(p=0.049), TNFα+(p=0.016) and TNFα+IL2+(p=0.014) CD4+T-cells (Fig. 1B). Following stimulation with A/H3N2, patients who received the HD vaccine had a higher proportion of influenza-specific IFNγ+(p=0.043), IL4+(p=0.035), TNFα+(p=0.014) and TNFα+IL2+(p=0.025) CD4+T-cells (Fig. 1C). CD8+. Following stimulation with influenza B, patients who received the HD vaccine had a higher proportion of influenza-specific TNFα+(p=0.007) and IFNγ+TNFα+(p=0.022) CD8+T-cells (Fig. 1A). Following stimulation with A/H1N1, patients who received the HD vaccine had a higher proportion of influenza-specific IFNγ+(p=0.047] and TNFα+ CD8+T-cells (p=0.047) (Fig. 1B). Following stimulation with A/H3N2, CMI between HD and SD was similar (Fig. 1C).
*Conclusions: The HD vaccine displayed enhanced CMI when compared to the SD vaccine, and this was especially evident for CD4+ T-cell immunity. For optimal CMI, our study suggests that HD vaccine may be the preferred vaccine for SOT patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
L'Huillier AG, Ferreira VH, Natori Y, Ku T, Hirzel C, Ierullo M, Humar A, Kumar D. A Comparison of Cell-Mediated Immune Responses among Organ Transplant Recipients Receiving High-Dose vs Standard-Dose Influenza Vaccine [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-comparison-of-cell-mediated-immune-responses-among-organ-transplant-recipients-receiving-high-dose-vs-standard-dose-influenza-vaccine/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress