Human Gingival Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Murine Acute GVHD Via Killing of Effector CD8+ Cells Through CD39/Adenosine A1R and A2BR Pathways
Liver Transplantation Center, First Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B59
Keywords: Graft-versus-host-disease, T helper cells
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Cell Transplantation and Cell Therapies
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Human gingival tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (GMSCs) are a convenient source of MSCs that have been shown to treat autoimmune disease. Here we use human GMSCs to prevent lethality in two distinct murine acute GVHD models. GMSCs infusion markedly suppressed donor CD8+ cells engraftment, Granzyme A and B expression and the production of inflammatory cytokines during acute GVHD. GMSCs prevents both CD4 and CD8 Tregs from converting to Th1 and/or Th17 cells and sustains their Foxp3 expression and suppressive function in vivo or in vitro following encounters with IL-1 and IL-6.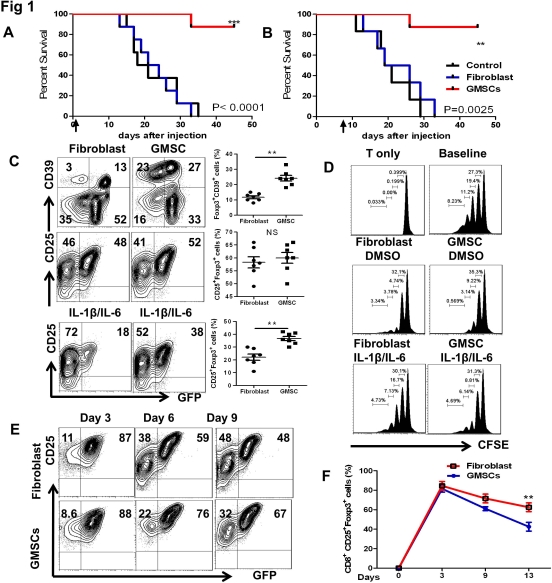 GMSCs inhibition of acute GVHD can be ablished by Anti-CD25, and GMSCs inhibition of acute GVHD is dependent on CD39 signaling in part via Adenosine receptors A1 and A2B.
GMSCs inhibition of acute GVHD can be ablished by Anti-CD25, and GMSCs inhibition of acute GVHD is dependent on CD39 signaling in part via Adenosine receptors A1 and A2B.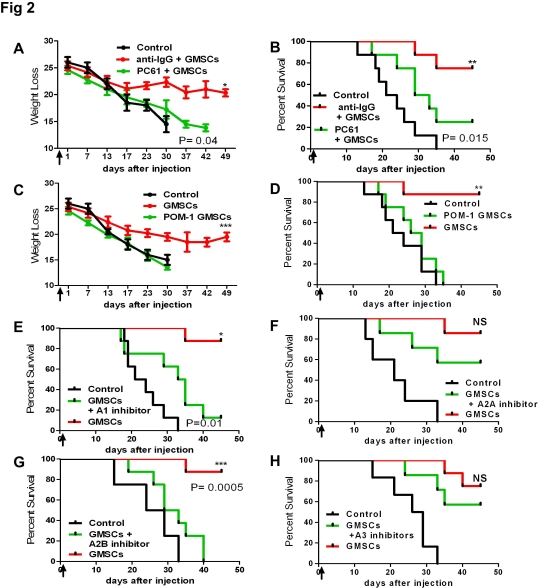 These data indicate the potential therapeutic effect of human GMSCs to treat acute GVHD.
These data indicate the potential therapeutic effect of human GMSCs to treat acute GVHD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gu J, Ling L. Human Gingival Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Murine Acute GVHD Via Killing of Effector CD8+ Cells Through CD39/Adenosine A1R and A2BR Pathways [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/human-gingival-tissue-derived-mesenchymal-stem-cells-reduce-murine-acute-gvhd-via-killing-of-effector-cd8-cells-through-cd39adenosine-a1r-and-a2br-pathways/. Accessed February 16, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
