Results of Litmus (nct 02541916): The Liver Immune Tolerance Bio Marker Utilization Study
1Multi-Organ Transplantation, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 682
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Reverse transcriptase PCR, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Tolerance: Clinical Studies
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
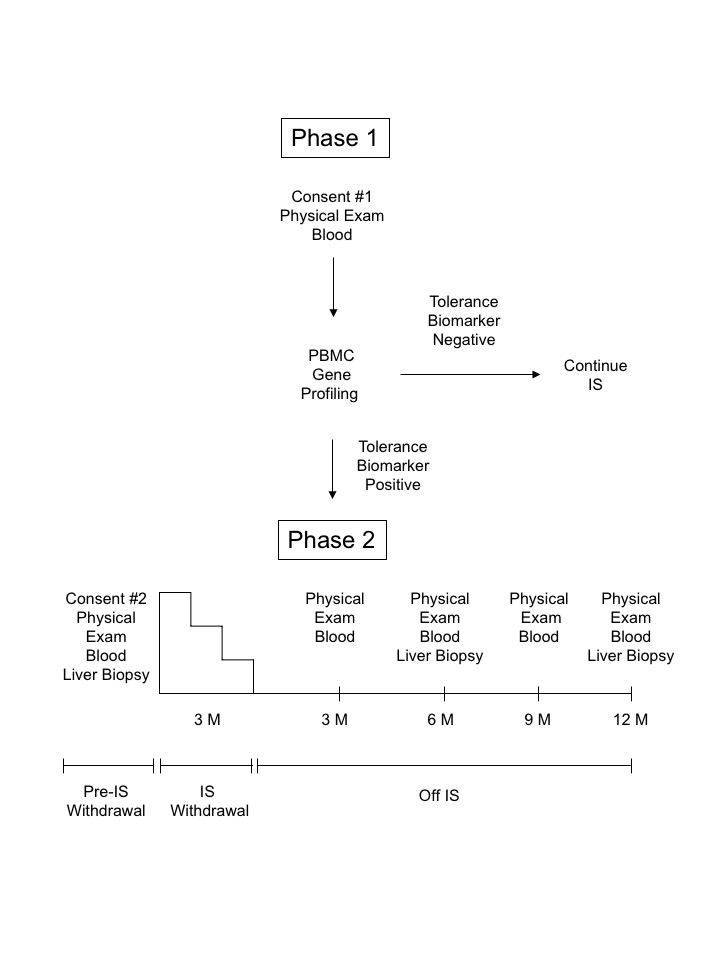
*Purpose: Although it is known that some liver transplant recipients are operationally tolerant and can be weaned off immunosuppression (IS), there is not currently a validated biomarker platform to identify these patients. Here we investigated if a gene biomarker profile predictive of tolerance in preclinical studies could identify operationally tolerant recipients.
*Methods: We developed GeXP RT-PCR assay to monitor expression of eight target genes (FGL2, FOXP3, TGF-β1, LAG3, TIGIT, IL-10, IFN-γ, and GZMB) previously identified to corelate with tolerance in pre-clinical models. Gene expression was measured in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from adult liver transplant recipients who were a minimum of six months post-transplant and had no biochemical evidence of rejection. Patients who positive for a putative tolerance biomarker (FGL2/IFN-γ ≥1) underwent a liver biopsy. If the liver biopsy was normal, patients underwent IS withdrawal over a three-month period. The primary aim of the study was the development of operational tolerance. Secondary endpoints were mortality, graft loss and changes in adverse effects associated with cessation of immunosuppression.
*Results: Sixty-nine patients enrolled in the study, and 28 (41%) were positive for the tolerance biomarker. Of these 28 patients, 23 had evaluable outcomes including 8 patients who were successfully withdrawn from IS, 6 patients who developed rejection during IS withdrawal, and 9 patients who had abnormal baseline liver biopsies. Six of eight of the patients successfully withdrawn from IS are now designated as operationally tolerant as they are off IS greater than one year. GeXP analysis of baseline liver biopsies revealed that 8/8 (100%) of patients in the successful withdrawal group had a liver gene ratio of FOXP3/IFN-γ ≥1, whereas only 1/6 (17%) patient in the rejector group had this gene ratio. Additional immunologic studies demonstrated increased regulatory T cells (Treg) in the peripheral blood and in the liver allograft of operationally tolerant patients post-IS withdrawal.
*Conclusions: These data suggest that a combination of gene expression monitoring in PBMC and in the liver allograft may identify operationally tolerant liver transplant recipients, allowing for successful withdrawal of immunosuppression.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chruscinski A, Rojas-Luengas V, Issacher A, Lilly L, Renner E, Epstein M, Adeyi O, Fischer S, Galvin Z, Moshkelgosha S, Jaeckel E, Juvet S, Selzner N, Levy G. Results of Litmus (nct 02541916): The Liver Immune Tolerance Bio Marker Utilization Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/results-of-litmus-nct-02541916-the-liver-immune-tolerance-bio-marker-utilization-study-3/. Accessed February 19, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress