Successful Prophylaxis of Antibody-Mediated Rejection by Downregulation of C5 Expression via RNA Interference in a Rat Kidney Transplant Model
1Urology, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo, Japan, 2KAN Research Institute, Inc., Kobe, Japan, 3Tsukuba Research Laboratories, Eisai, Co., Ltd., Ibaraki, Japan
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 503
Keywords: Antibodies, Efficacy, Sensitization, Survival
Topic: Basic Science » Acute Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Acute Rejection
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) is a major contributor towards poor prognosis in kidney transplantation. Circulating donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) cause AMR with complement activation. This study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of a lipid nanoparticle formulation of small interfering RNA against complement C5 (C5 siRNA-LNP) for AMR in a rat kidney transplantation model.
*Methods: Seven- to nine-week-old Lewis recipient rats were sensitized by skin grafting from Brown Norway donor rats, and kidney transplantation was performed at four weeks post-sensitization. Graft survival was followed up for 100 days post-transplantation. The grafts were histopathologically assessed using periodic acid-Schiff-stained images taken seven days after the transplantation. The serum levels of DSA-IgG were measured by flow cytometric crossmatch using molecules of equivalent soluble fluorochromosome. Suppression of C5 expression and complement activity was confirmed via Western blotting and hemolysis assays, respectively.
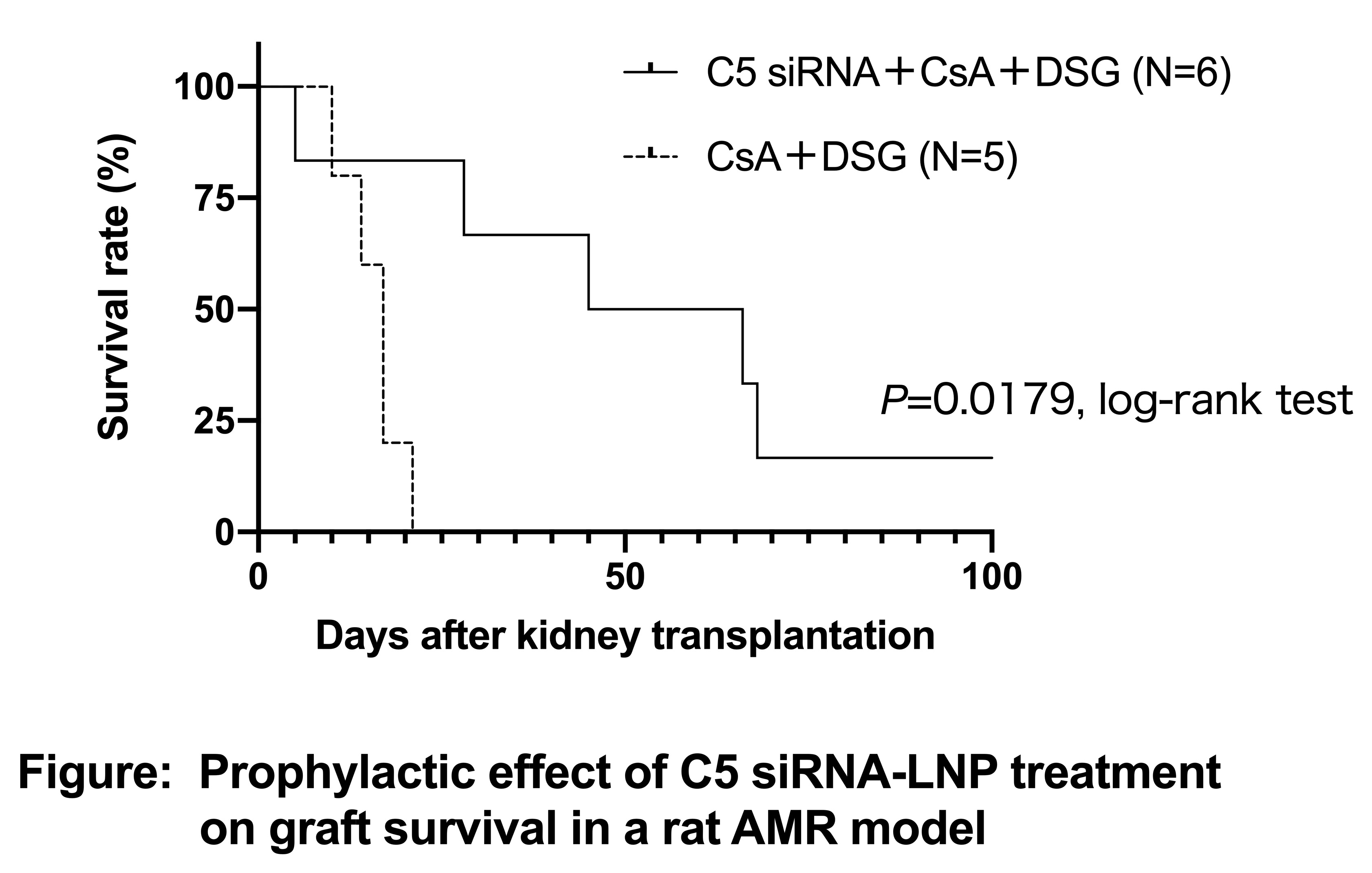
*Results: C5 siRNA-LNP completely suppressed C5 expression and complement activity (hemolysis ≦ 20%) one week after its administration, and the suppressive effect was maintained up to 2 weeks later. Its weekly administration continued to suppress complement activity. C5 siRNA-LNP monotherapy (median survival time, MST: 8 days), combined therapy with C5 siRNA-LNP and cyclosporine (C5 siRNA+CsA, MST: 14 days), and treatment with CsA and deoxyspergualin (CsA+DSG, MST: 17 days) failed to prolong graft survival, whereas combination treatment with the three compounds (C5 siRNA+CsA+DSG, MST: 55.5 days) significantly prolonged graft survival (P=0.179, vs. CsA+DSG, log-rank test) (Figure). DSA-IgG was persistently present in peripheral blood in the triple-drug combination group. Severe mononuclear cell interstitial inflammation and moderate to severe peritubular capillaritis were observed in the CsA+DSG group but not in the triple-drug combination group.
*Conclusions: AMR can be controlled by downregulating C5 expression along with the suppression of immune cell functions, such as T and B cells, even in the presence of DSAs without desensitization therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ishigooka H, Motoi S, Yamakawa T, Matsui C, Suzuki Y, Ishii R, Saiga K, Tokita D, Imai T, Tanabe K. Successful Prophylaxis of Antibody-Mediated Rejection by Downregulation of C5 Expression via RNA Interference in a Rat Kidney Transplant Model [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/successful-prophylaxis-of-antibody-mediated-rejection-by-downregulation-of-c5-expression-via-rna-interference-in-a-rat-kidney-transplant-model/. Accessed February 3, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress