Molecular Diagnosis and Risk Prediction in BK Virus Nephropathy: Discovery and Multicenter Validation of Novel Intragraft Gene Expression Signatures
1University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 3Paris Transplant Group, Paris, France
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 495
Keywords: Biopsy, Kidney transplantation, Polyma virus, Rejection
Session Information
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:03pm-4:15pm
Presentation Time: 4:03pm-4:15pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Novel tools are needed to improve diagnosis and risk prediction in BK virus nephropathy (BKVN). This study aimed to assess the utility of intragraft gene expression for this purpose.
*Methods: NanoString was used to assess differential gene expression between native kidney biopsies with BKVN (n=5) and renal allograft biopsies with pure T-cell mediated rejection (TCMR, n=10). Candidate gene sets were then evaluated in a cohort representing a spectrum of BK infection (n=25), followed by a separate multicenter validation cohort of renal allograft biopsies with BKVN (n=60) or TCMR (n=10). Diagnostic performance and correlation between gene set expression, histology and clinical outcome were assessed.
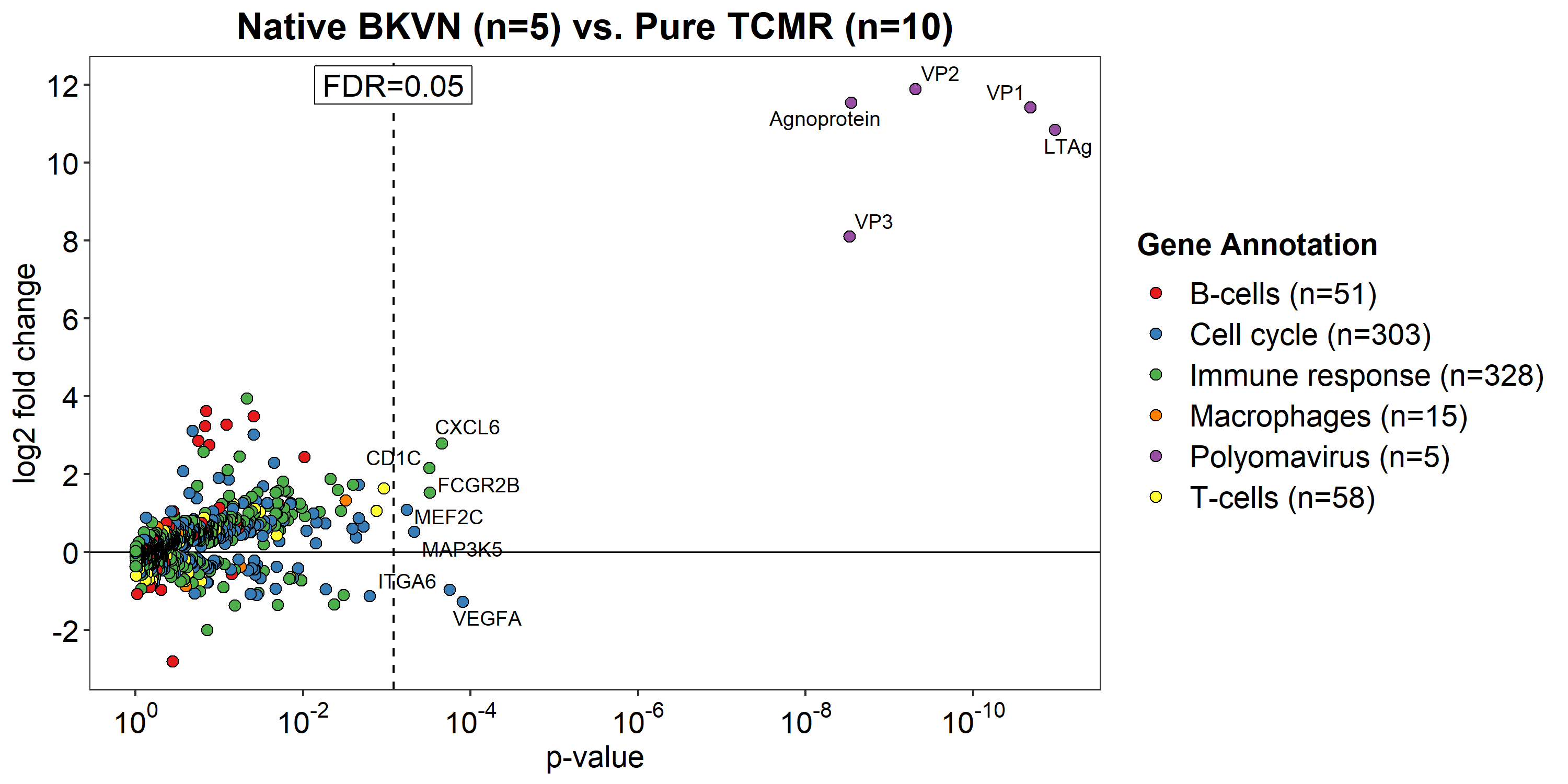
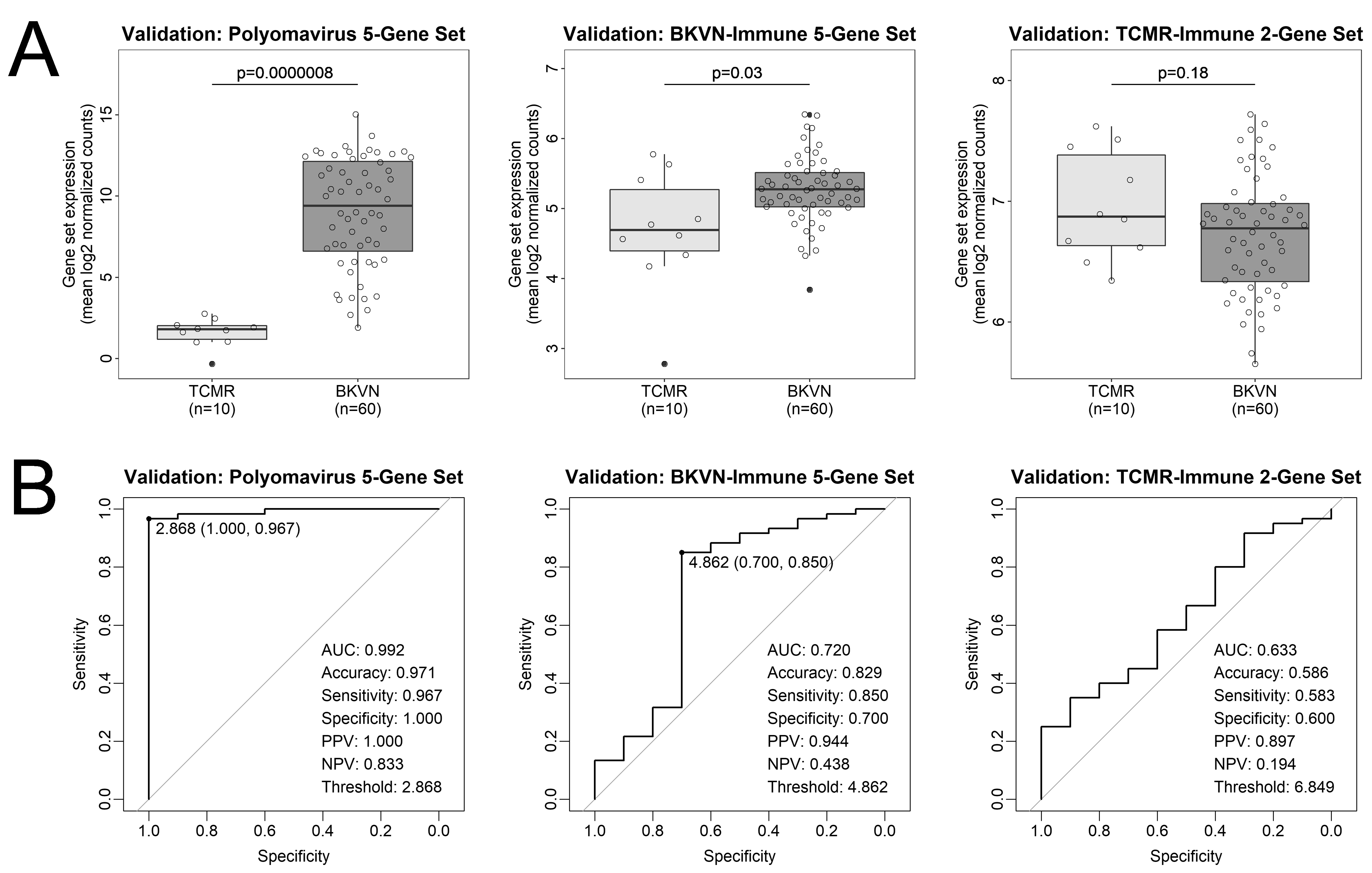
*Results: Five polyomavirus (PV) genes and 7 immune genes were significantly differentially expressed between native BKVN and pure TCMR (Fig. 1). PV 5-gene set expression demonstrated excellent distinction between BKVN and TCMR (validation cohort ROC AUC=0.992, p<0.0001) (Fig. 2) and correlated with Banff pvl-score (rho=0.443, p=0.0004) and PVN class (rho=0.345, p=0.007). Immune genes (5 associated with BKVN and 2 with TCMR) had inferior diagnostic performance (validation AUC=0.720 and 0.633, respectively). Within the validation cohort, no significant differential expression was identified between BKVN patients with resolution (n=35), persistence (n=14) and de novo rejection (n=11) at 6 months post-biopsy (Fig. 3). However, TCMR-immune 2-gene set showed higher expression in persistence vs. resolution (p=0.0005) and rejection (p=0.001).
*Conclusions: These data suggest that intragraft gene expression can improve diagnosis and risk prediction in BKVN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Adam B, Kikic Z, Bouatou Y, Gueguen J, Robin B, Reid G, Regele H, Rabant M, Loupy A, Mengel M. Molecular Diagnosis and Risk Prediction in BK Virus Nephropathy: Discovery and Multicenter Validation of Novel Intragraft Gene Expression Signatures [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/molecular-diagnosis-and-risk-prediction-in-bk-virus-nephropathy-discovery-and-multicenter-validation-of-novel-intragraft-gene-expression-signatures/. Accessed February 21, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress