Generation of Insulin-Producing Cells via Multiplex Epigenetic Engineering of Human Somatic Cells in 2 Weeks
1Division of Transplant Surgery, Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN, 2Diabetes Research Center, Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 428
Session Information
Session Name: Islet/Cell Transplantation
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:51pm-4:03pm
Presentation Time: 3:51pm-4:03pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Stem cell-derived β-cells not only promise a renewable supply of insulin-producing cells with negligible immunosuppression but may also provide a substrate for the identification of personalized therapies for individuals with type-1 or 2 diabetes. Though innovative, the development of stem cell-derived β-cells is cumbersome and requires a seven-step protocol with very meticulous procedures. We designed a simple and single-shot approach to generate insulin-producing cells directly from somatic cells via targeted epigenetic activation of β-cells signature genes leveraging CRISPR/Cas9 technology.
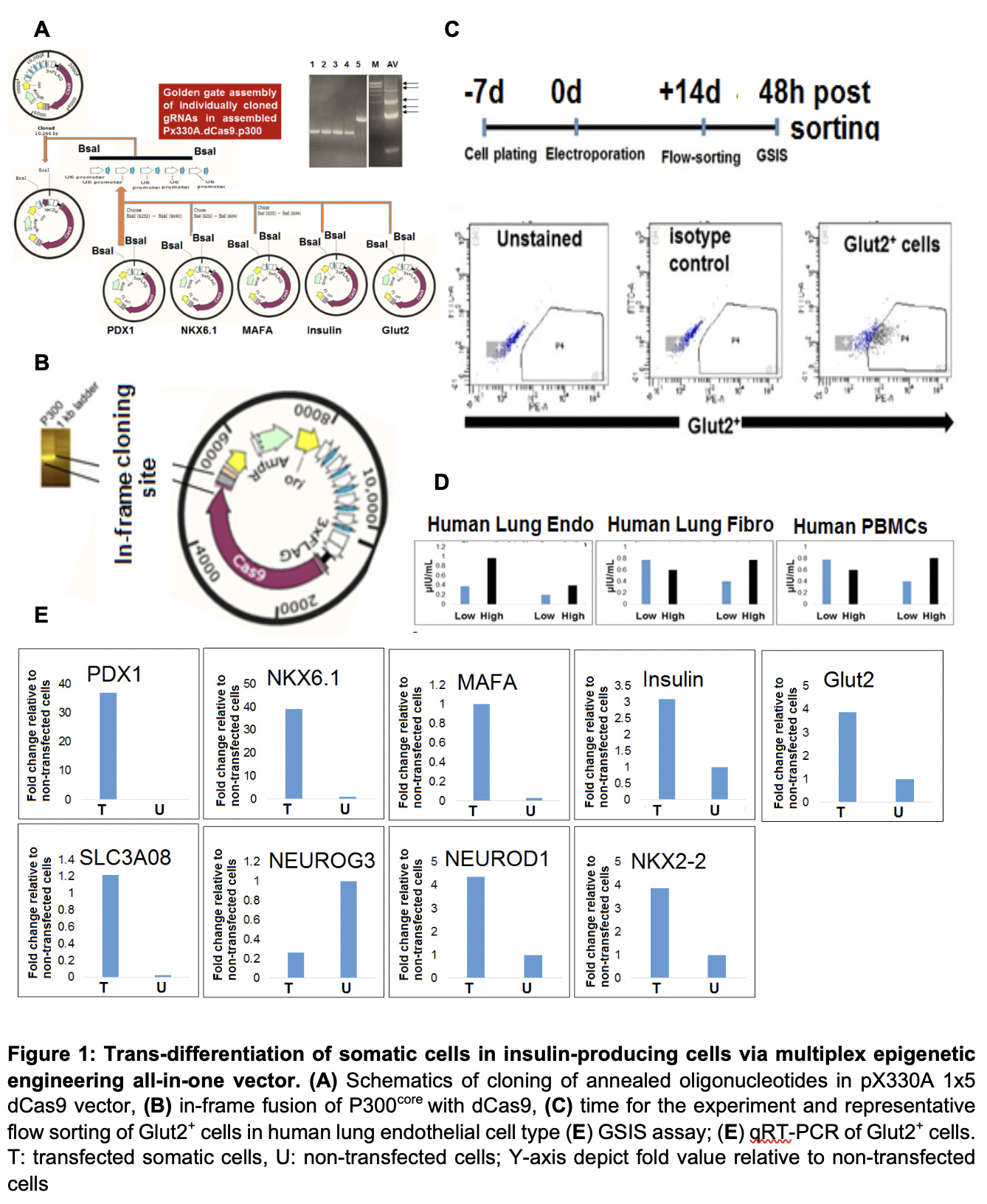
*Methods: We have developed multiplex epigenetic engineering vector (MEE-β) with fusion protein (dCas9.P300core domain of histone acetyl transferase). MEE-β contains 5 cloned oligonucleotides under separate U6 promoter targeting the DNase I hypersensitive sites of PDX1, NKX6.1, MAFA, Insulin, and Glut2 genes (Figure 1A). Human somatic cells (lung endothelial cells, lung fibroblasts and PBMCs, 1x 106) were transfected in triplicate with MEE-β and Glut2+ cells were flow-sorted after 14 days post-transfection. Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) was measured in Glut2+cells following stimulation with 2.8mM (low) and 28 mM (high) glucose and measurement of insulin was done using an ultrasensitive ELISA platform. Glut2+ cells were evaluated for expression of β-cell-specific genes using SYBR-green based qRT-PCR.
*Results: Cloning of aforementioned oligonucleotides and correct fusion of P300core in MEE-β vector was confirmed by PCR and Sanger’s sequencing (Fig.1B). Total of 2×104, 2.8×104 , 4.7x 104 and 1.7×104 Glut2+ cells were recovered after flow sorting of human lung endothelial cells, human lung fibroblasts and PHA activated human PBMCs, respectively (Fig.1C). These cells responded to high and low concentration glucose challenge and produced insulin (Fig.1D). In addition, Glut2+ cells not only demonstrated expression of targeted genes by MEE-β (PDX1, NKX6.1. MAFA, Insulin, Glut2), but also upregulation of other downstream β-cell genes, including NUROD1, NKX2.2, SLC03A08 (Fig.1E).
*Conclusions: This is a proof-of-concept study to demonstrate the conversion of somatic cells into insulin-secreting cells by a user-friendly, less cumbersome, and less expensive strategy. The activation of other downstream genes related with β-cell development besides targeted genes by MEE-β suggests the triggering of β-cell-specific cascades.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Naqvi RA, Zhang W, Isidan A, Evans-Molina C, Fridell JA, Li P, Ekser B. Generation of Insulin-Producing Cells via Multiplex Epigenetic Engineering of Human Somatic Cells in 2 Weeks [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/generation-of-insulin-producing-cells-via-multiplex-epigenetic-engineering-of-human-somatic-cells-in-2-weeks/. Accessed February 9, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress