A Prognostic Model to Identify Deceased Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients at High Risk for Delayed Graft Function
Terasaki Research Institute, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A143
Keywords: Graft function, Kidney transplantation, Prediction models
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: We have previously identified pre-transplant risk factors for delayed graft function (DGF) in deceased donor kidney transplant (DDKT) recipients and built a machine learning (ML) model to predict the occurrence of DGF using a subpopulation of patients (Kawakita et al. 2018). To further support the model, we used additional data to re-train the model and conducted an external validation study.
*Methods: Development data were obtained from the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network/United Network of Organ Sharing on adult, deceased donor kidney transplant recipients transplanted between 1/1/2009 and 12/31/2013 (n = 47,612). This analysis included more patients than the previous study as the patients only needed to have complete data for the selected 30 variables versus the original pool of unscreened variables to be included in the analysis. Patients transplanted between 1/1/2014 and 6/30/2014 were selected as a validation cohort (n = 5,134). DGF was defined as the need for dialysis within one week post-transplant. The artificial neural network (ANN) model previously developed was re-trained with 10-fold cross-validation and evaluated for its performance via the receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve, area under the ROC curve (AUC) and Brier score. Decision curve analysis was performed to examine clinical utility of the final model calibrated with a logistic function.
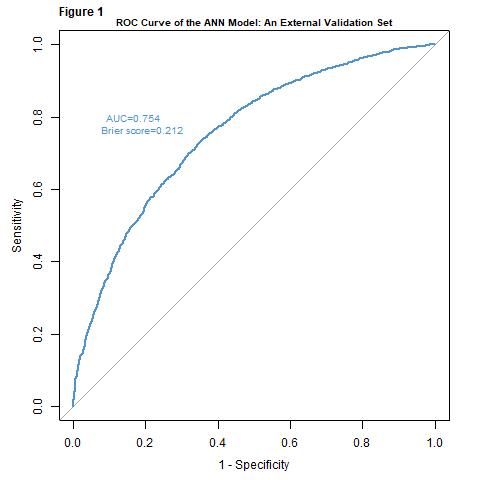
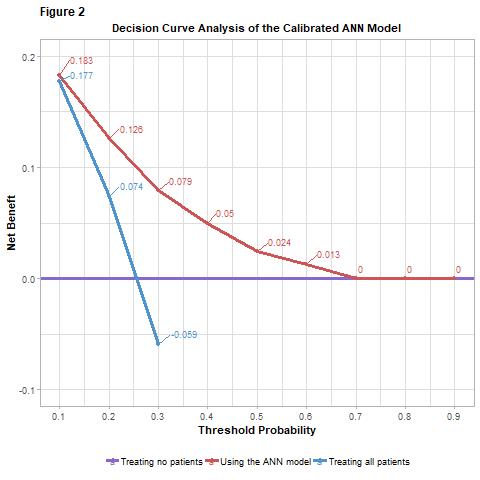
*Results: When tested in the validation set, the ANN model had an AUC of 0.754 and a Brier score of 0.212 (Figure 1). Decision curve analysis revealed that the predicted probabilities had greater net benefit compared to the two alternative options when threshold probabilities between 0.1 and 0.6 were used (Figure 2). For example, at a threshold value of 0.3, there is NB of 0.079, which is equivalent to identifying 7.9 DGF positive patients per 100 DDKT patients with no unnecessary treatment.
*Conclusions: We improved our previously developed prognostic model for early identification of DDKT patients at high risk for DGF and validated the model with an external dataset. The proposed model may be used as a tool to supplement enrichment strategies for clinical trials and also as a means to aid in clinical decision-making processes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kawakita S, Beaumont JL, Everly MJ. A Prognostic Model to Identify Deceased Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients at High Risk for Delayed Graft Function [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-prognostic-model-to-identify-deceased-donor-kidney-transplant-recipients-at-high-risk-for-delayed-graft-function/. Accessed February 13, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress