Effect of Induction Therapy on Outcomes of De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients Receiving Everolimus with Reduced-Dose Calcineurin Inhibitor: 24-Month Results from the TRANSFORM Study
1TRANSFORM Study Group, Basel, Switzerland, 2Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 557
Keywords: Efficacy, Induction therapy, Kidney transplantation, Safety
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: Room 304
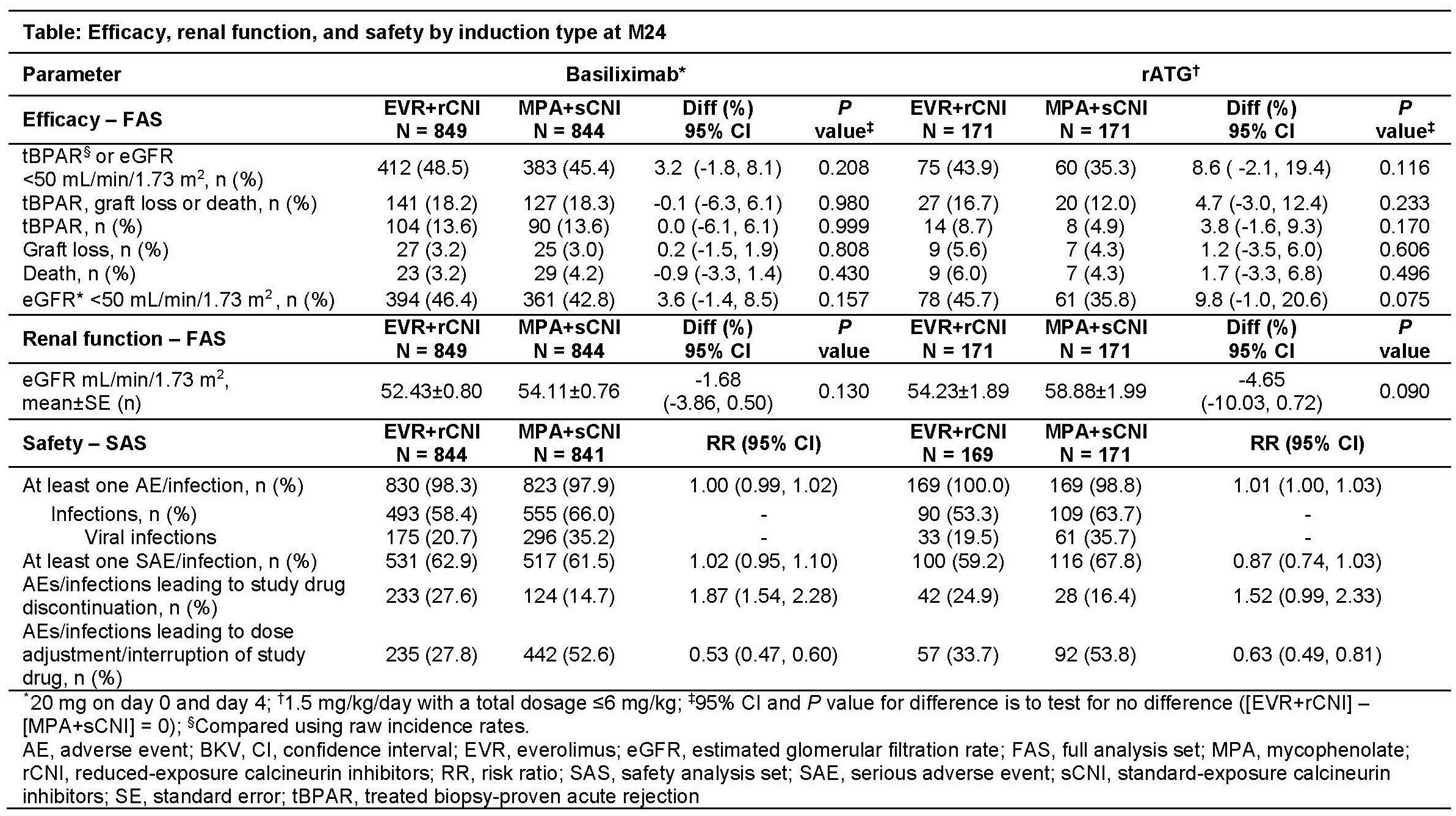
*Purpose: To assess the effect of induction therapy on efficacy and safety outcomes of de novo renal transplant recipients (RTxR) receiving everolimus with reduced calcineurin inhibitor (EVR+rCNI) vs mycophenolate with standard CNI (MPA+sCNI) in the TRANSFORM (NCT01950819) study.
*Methods: In this 24-month (M), phase IV, multicenter, open-label study, adult RTxR stratified by induction type (basiliximab [Bax] or rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin [rATG]) were randomized (RND) to receive EVR+rCNI or MPA+sCNI with steroids. Efficacy assessments were incidence of binary composite of tBPAR or eGFR <50 mL/min/1.73 m2, incidence of tBPAR, graft loss (GL), or death, and evolution of eGFR up to M24; safety assessments were incidence of adverse events (AE) and infections.
*Results: Of 2037 RND patients,1693 received Bax and 342 received rATG. Consistent with previous findings, the EVR+rCNI regimen was noninferior (P<0.001) to MPA+sCNI for the binary endpoint at M24 for both induction groups. At M24, incidences of tBPAR, GL, and death were comparable between EVR+rCNI and MPA+sCNI arms regardless of induction type (Table). Compared to Bax group, incidence of tBPAR was lower in both arms of rATG group. Mean eGFR was stable from Week 4 to M24 and comparable between arms at M24. Though the incidence of AE leading to study drug discontinuation was higher in EVR+rCNI arm, the incidence of AE leading to dose adjustment/interruption was higher in MPA+sCNI arm. Incidence of viral infections was lower in EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI arm in both induction groups. Consistent with previous reports, incidence of CMV (Bax:8.4% vs 22.6%; rATG:10.1% vs 20.5%) and BKV (Bax:10.1% vs 14.1%; rATG:10.7% vs 20.5%) infections was lower in EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI arm in both induction groups.
*Conclusions: Irrespective of the induction type, EVR+rCNI regimen offers comparable efficacy and safety and stable renal function to that of MPA+sCNI regimen up to M24 post-RTx.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Oberbauer R, Vincenti F, Viklicky O, Huynh-Do U, Kim D, Cruzado JM, Qazi Y, Kim MS, Narvekar P, Gutierrez MPHernandez, Bernhardt P, Kuypers D. Effect of Induction Therapy on Outcomes of De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients Receiving Everolimus with Reduced-Dose Calcineurin Inhibitor: 24-Month Results from the TRANSFORM Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/effect-of-induction-therapy-on-outcomes-of-de-novo-renal-transplant-recipients-receiving-everolimus-with-reduced-dose-calcineurin-inhibitor-24-month-results-from-the-transform-study/. Accessed February 15, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress