Primary Hyperoxaluria Type-1 in Chinese Population: A Case Series and Review of Literature.
D. Du,1,2 Q. Li,1,2 H. Shi,1,2 S. Chen,1,2 B. Liu,1,2 Z. Lin,1,2 G. Chen,1,2 F. Zeng,1,2 W. Zhang,1,2 Z. Chen.1,2
1Institute of Organ Transplantation, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
2Key Laboratory of Organ Transplantation, Ministry of Health/Education, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D153
Keywords: Genomics, Metabolic disease
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 2, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Background: Primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (PH1) is rare but devastating autosomal recessive inherited disease and cause to graft failure after kidney transplant (KT). We report a case series and a comprehensive review of literature in order to review the AGXT mutations in Chinese population and discuss the genotype-outcome correlation of PH1.
Methods and Results: First we scanned the AGXT, GRHPR and HOGA1 genes for 6 Chinese families with PHs. Four novel variants in AGXT gene including p.Ala186Val, p.Gly41Trp, p.Lys12Gln fs and p.Leu33Met were identified and subsequent Western Blotting analysis showed the variants affected the function of AGT protein on different levels. 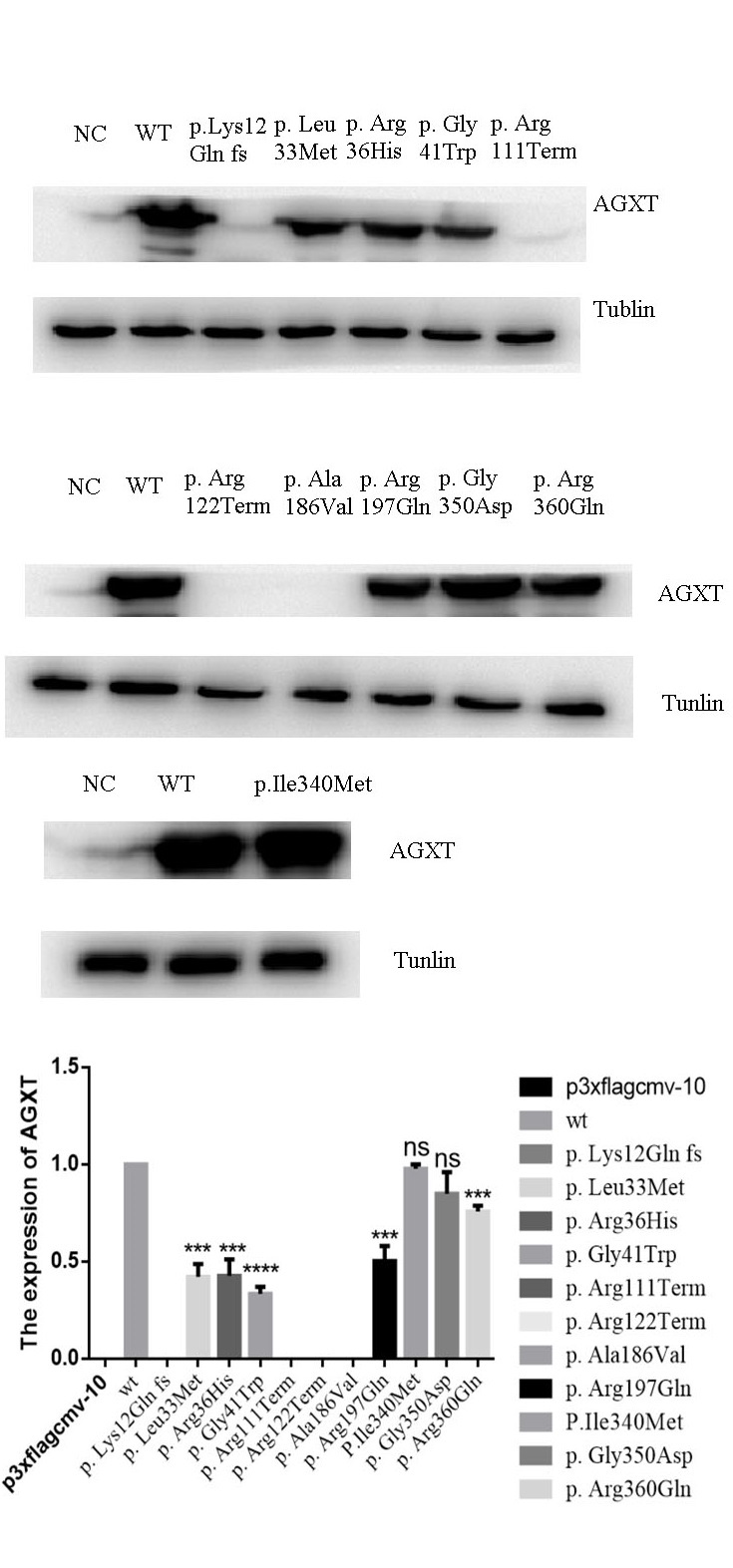 With review of literature, AGXT mutations are significantly different in Chinese Han population (53.3% of mutations detected from Chinese population were particular). Furthermore, we used the new published M-CAP classifier to classify total 104 missense variants and evaluate the genotype-outcome correlation in PH1.
With review of literature, AGXT mutations are significantly different in Chinese Han population (53.3% of mutations detected from Chinese population were particular). Furthermore, we used the new published M-CAP classifier to classify total 104 missense variants and evaluate the genotype-outcome correlation in PH1.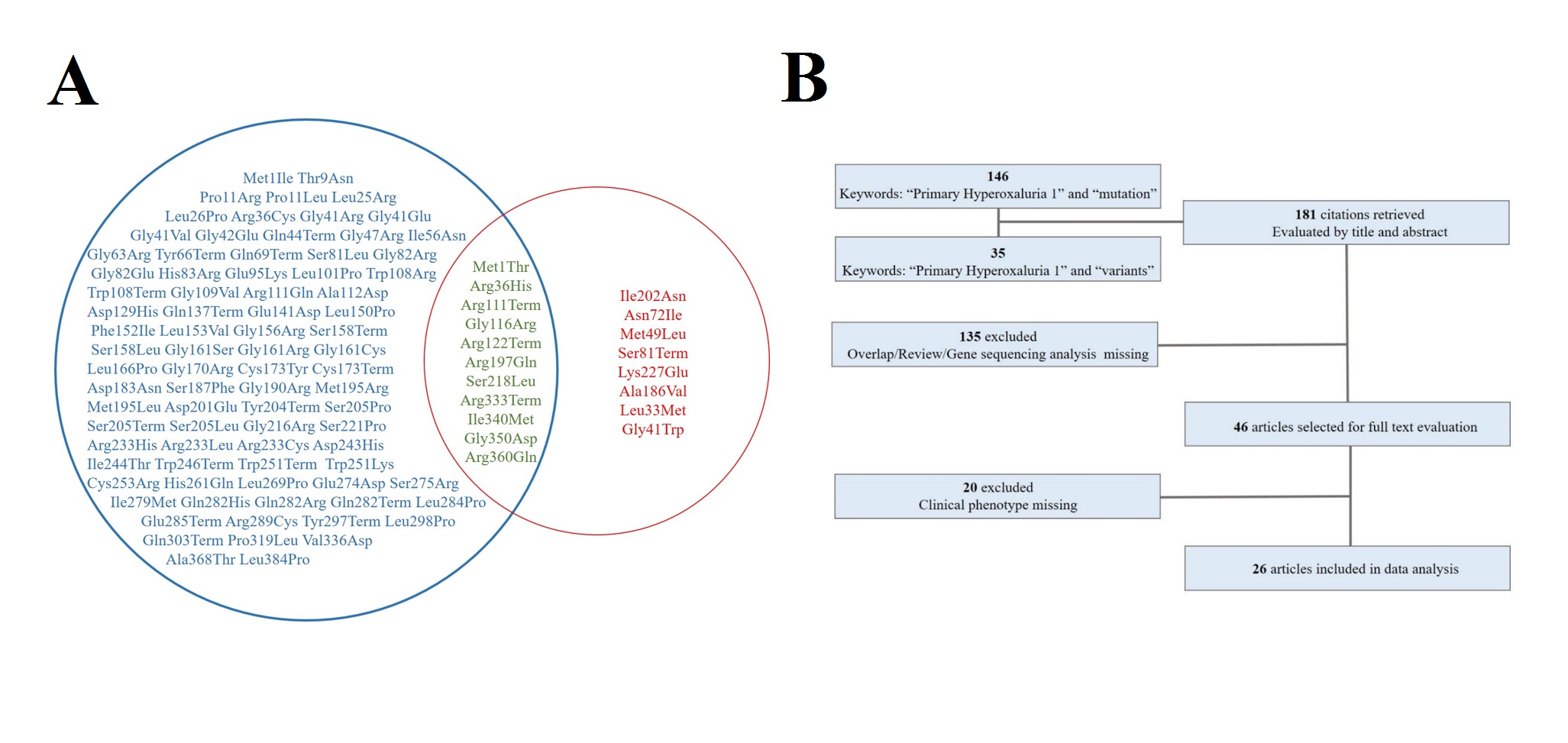 Conclusions: Our results underscore the extreme necessity to perform sequencing analysis for patients with bilateral stubborn kidney stones before KT to avoid PH1 related graft failure. Because of significantly inherited heterogeneity in Chinese Han population, it seems more appropriate for complete direct sequencing of all exons of AGXT.
Conclusions: Our results underscore the extreme necessity to perform sequencing analysis for patients with bilateral stubborn kidney stones before KT to avoid PH1 related graft failure. Because of significantly inherited heterogeneity in Chinese Han population, it seems more appropriate for complete direct sequencing of all exons of AGXT.
CITATION INFORMATION: Du D, Li Q, Shi H, Chen S, Liu B, Lin Z, Chen G, Zeng F, Zhang W, Chen Z. Primary Hyperoxaluria Type-1 in Chinese Population: A Case Series and Review of Literature. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Du D, Li Q, Shi H, Chen S, Liu B, Lin Z, Chen G, Zeng F, Zhang W, Chen Z. Primary Hyperoxaluria Type-1 in Chinese Population: A Case Series and Review of Literature. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/primary-hyperoxaluria-type-1-in-chinese-population-a-case-series-and-review-of-literature/. Accessed January 27, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
