Evaluation of a Risk-Stratified Induction Immunosuppression Protocol Utilizing Low-Dose Antithymocyte Globulin in Renal Transplantation.
Solid Organ Transplantation & Hepatobiliary Diseases, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Burlington, MA.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 225
Keywords: Dosage, Graft survival, Infection, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Induction Therapy 1
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-3:42pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-3:42pm
Location: Room 312
Lower doses of rabbit-derived antithymocyte globulin (rATG) may result in less infection and cost, but may increase the incidence of acute rejection. We compared the safety and efficacy of a risk-stratified rATG dosing protocol.
53 patients received renal transplants between January 2014 and September 2015. Low risk patients received 0.75 mg/kg x 3 doses and high risk patients received 1.25 mg/kg x 3 doses. 41 patients met inclusion criteria (23 low dose, 18 high dose). The primary outcome was biopsy-proven acute rejection (BPAR) at twelve months. Secondary outcomes include twelve month patient and graft survival, infectious complications, and delayed graft function. A cost analysis was also performed.
BPAR as well as patient and graft survival were similar between groups at twelve months. Donor and recipient characteristics, infectious complications, and graft function were also comparable. Average costs were reduced by approximately 40% in the low dose group. Additional information is in Table 1.
|
|
Low-Dose |
High-Dose |
p-value |
|
Recipient age at transplant, (years), mean |
56 |
51 |
NS |
|
Donor age (years), mean |
46 |
45 |
NS |
| Expanded criteria donor (%) | 9 | 11 | NS |
| Donor after cardiac death (%) | 9 | 17 | NS |
| Living donor (%) | 30 | 38 | NS |
|
Biopsy-proven acute rejection (%) |
26 |
20 |
NS |
|
Graft loss (%) |
8 |
5 |
NS |
|
Patient death (%) |
4 |
5 |
NS |
| Delayed graft function (%) | 30 | 17 | NS |
|
CMV viremia (%) |
13 |
17 |
NS |
| Urinary tract infection (%) | 39 | 33 | NS |
|
Cost per patient (USD), mean |
5,182 |
9,216 |
<0.001 |
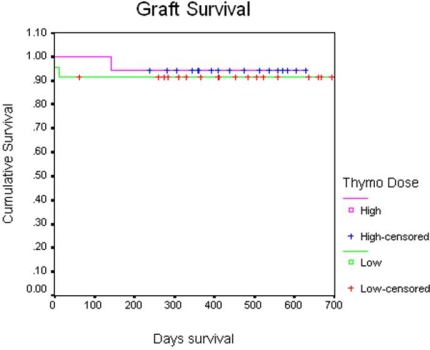
Our findings indicate that low risk patients achieve acceptable outcomes with low dose rATG. Initial analysis suggests that the use of low dose rATG provides a similar efficacy and safety profile. A cost savings of approximately $100,000 was achieved with this risk-stratified protocol in just 23 patients. Follow-up continues in order to determine the impacts on long-term outcomes.
CITATION INFORMATION: Diamond A, Khawaja Z, Simpson M, Kung S.-C, Akoad M, Pomposelli J, Pomfret E. Evaluation of a Risk-Stratified Induction Immunosuppression Protocol Utilizing Low-Dose Antithymocyte Globulin in Renal Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Diamond A, Khawaja Z, Simpson M, Kung S-C, Akoad M, Pomposelli J, Pomfret E. Evaluation of a Risk-Stratified Induction Immunosuppression Protocol Utilizing Low-Dose Antithymocyte Globulin in Renal Transplantation. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/evaluation-of-a-risk-stratified-induction-immunosuppression-protocol-utilizing-low-dose-antithymocyte-globulin-in-renal-transplantation/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
