High-Risk Pharmacogenetic (PGx) Variants in Kidney Transplant (tx) Recipients.
1UofMN, Mpls
2MMRF, Mpls
3HCMC, Mpls
4UAB, Birmingham.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 334
Keywords: Adverse effects, Gene polymorphism, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Medication Errors, Variability and Adherence
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Location: Room 302
Kidney tx recipients carry a high burden of comorbidities, and some of the medications for these conditions have genetic predictors of efficacy and toxicity. These genes may be associated with subtherapeutic treatment, predisposition to side-effects and, in rare cases, death. However, these genetic variants are not commonly used to personalize therapy in clinical tx practice.
Recipients (n=3043) undergoing kidney tx between 2005-2011 were enrolled and followed prospectively in the DeKAF genomics multicenter study. DNA was genotyped using the Affymetrix Tx Array GWAS chip (exome panel with approx 782,000 variants) which included PGx variants. The Clinical PGx Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines were reviewed and medications with genetic recommendations that may be relevant to tx recips were selected. We then evaluated our subjects for the presence of these risk gene variants.
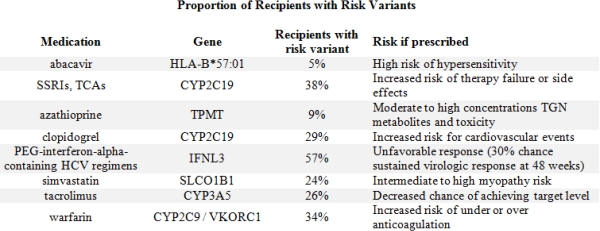
The mean age at tx was 49±14 yrs; 62% male; 75% White, 18% African American, 4% Asian. We identified 8 relevant high-risk PGx genotypes on our chip (Table 1). These genotypes occurred in 5-57% of recips. High risk clopidogrel CYP2C19 variants were present in 29% of recips. Clopidogrel was actively prescribed at time of tx in 111 of which 24% had a high risk genotype that would confer risk for lack of efficacy. 38% of recips had a CYP2C19 risk genotype that would place them at risk for antidepressant therapy failure. 24% carried the SLCO1B1 variant which placed them at higher risk for development of simvastatin related myopathy. The genotype conveying rapid clearance of tacrolimus was present in 26%.
We found a high proportion of recipients carried high risk PGx genotypes. The CYP2C19 risk variant was present in nearly a third of our >3,000 recips and may be at risk for therapeutic failure should they receive clopidgrel or antidepressants. Genetic testing is increasingly accessible and knowing this information prior to starting these medications may improve efficacy and reduce unnecessary side effects in an already complex patient.
CITATION INFORMATION: Berglund D, Schladt D, Sanghavi K, Guan W, Wu B, Dorr C, Remmel R, Mannon R, Matas A, Oetting W, Israni A, Jacobson P, DeKAF Genomics Investigators High-Risk Pharmacogenetic (PGx) Variants in Kidney Transplant (tx) Recipients. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Berglund D, Schladt D, Sanghavi K, Guan W, Wu B, Dorr C, Remmel R, Mannon R, Matas A, Oetting W, Israni A, Jacobson P, Investigators DeKAFGenomics. High-Risk Pharmacogenetic (PGx) Variants in Kidney Transplant (tx) Recipients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/high-risk-pharmacogenetic-pgx-variants-in-kidney-transplant-tx-recipients/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
