Clinical Outcomes of Kidney Allograft Recipients with Apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) Risk Alleles from Living Kidney Donors.
1Minneapolis Medical Research Foundation, Minneapolis
2University of Minnesota, Minneapolis
3Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis
4University of Alabama, Birmingham.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C141
Keywords: Biopsy, Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, Lipoproteins
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Donor Evaluation and Donor Nephrectomy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background:
Apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) alleles G1 and G2 in deceased donors are associated with poor kidney allograft survival. However, the effect of these alleles in living donor transplants is unknown. We investigated clinical outcomes of 58 allograft recipients that received kidneys from living donors.
Methods:
58 African American living donors provided blood samples for DNA at the time of transplant via the Deterioration of Kidney Allograft Function (DeKAF) genomics cohort. The DNA was genotyped using Taqman and confirmed by Sanger DNA sequencing.
Results:
Of the living donor kidneys, 28 (48%), 23 (40%) and 7 (12%) had 0, 1 or 2 APOL1 renal-risk alleles, respectively; which is consistent with the reported frequency of this allele in individuals of African Ancestry.
Median subject follow-up time was 3.2 years. Of the 58 recipients, 2 subjects had graft failure with 1 having a donor with at least one risk allele, (HR for graft failure = 0.64, p = 0.75). 5 recipients died, 4 of whom had a donor with at least one risk allele (HR for death = 3.0, p = 0.33).
Acute Rejection (AR) data was available for 37 subjects, 20 of whom had a donor with at least one risk allele. Subjects with 1 or more risk allele trended towards more AR; 7 (35%) of the subjects had a donor with at least one risk allele developed AR, while only 3 (18%) subjects with no donor risk alleles developed AR (HR = 2.2, p = 0.26).
For those subjects who underwent biopsy, the first biopsy scores post-transplant are described in Table 1. 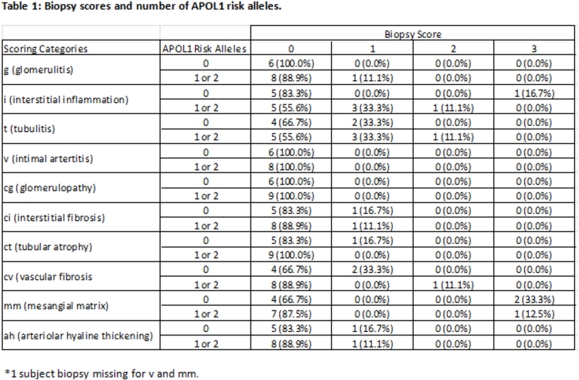
Conclusions:
Although the analysis was limited by small sample size, we found no significant association between APOL1 risk alleles in living donors and poor allograft outcomes. We did detect a trend toward increased risk of AR with an APOL1 risk allele, but additional follow up study, with more subjects and statistical power is needed to determine whether an association exists between APOL1 risk alleles with kidney allograft outcomes.
CITATION INFORMATION: Dorr C, Hart A, Schladt D, Muthusamy A, Mannon R, Oetting W, Matas A, Jacobson P, Israni A. Clinical Outcomes of Kidney Allograft Recipients with Apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) Risk Alleles from Living Kidney Donors. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dorr C, Hart A, Schladt D, Muthusamy A, Mannon R, Oetting W, Matas A, Jacobson P, Israni A. Clinical Outcomes of Kidney Allograft Recipients with Apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) Risk Alleles from Living Kidney Donors. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/clinical-outcomes-of-kidney-allograft-recipients-with-apolipoprotein-l1-apol1-risk-alleles-from-living-kidney-donors/. Accessed January 25, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
