What Are Factors That Can Influence The High Immunological Graft Loss Rate In Young Pancreas Transplant Recipients
SUNY Downstate Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D271
Keywords: Age factors, Pancreas transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Pancreas and Islet: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
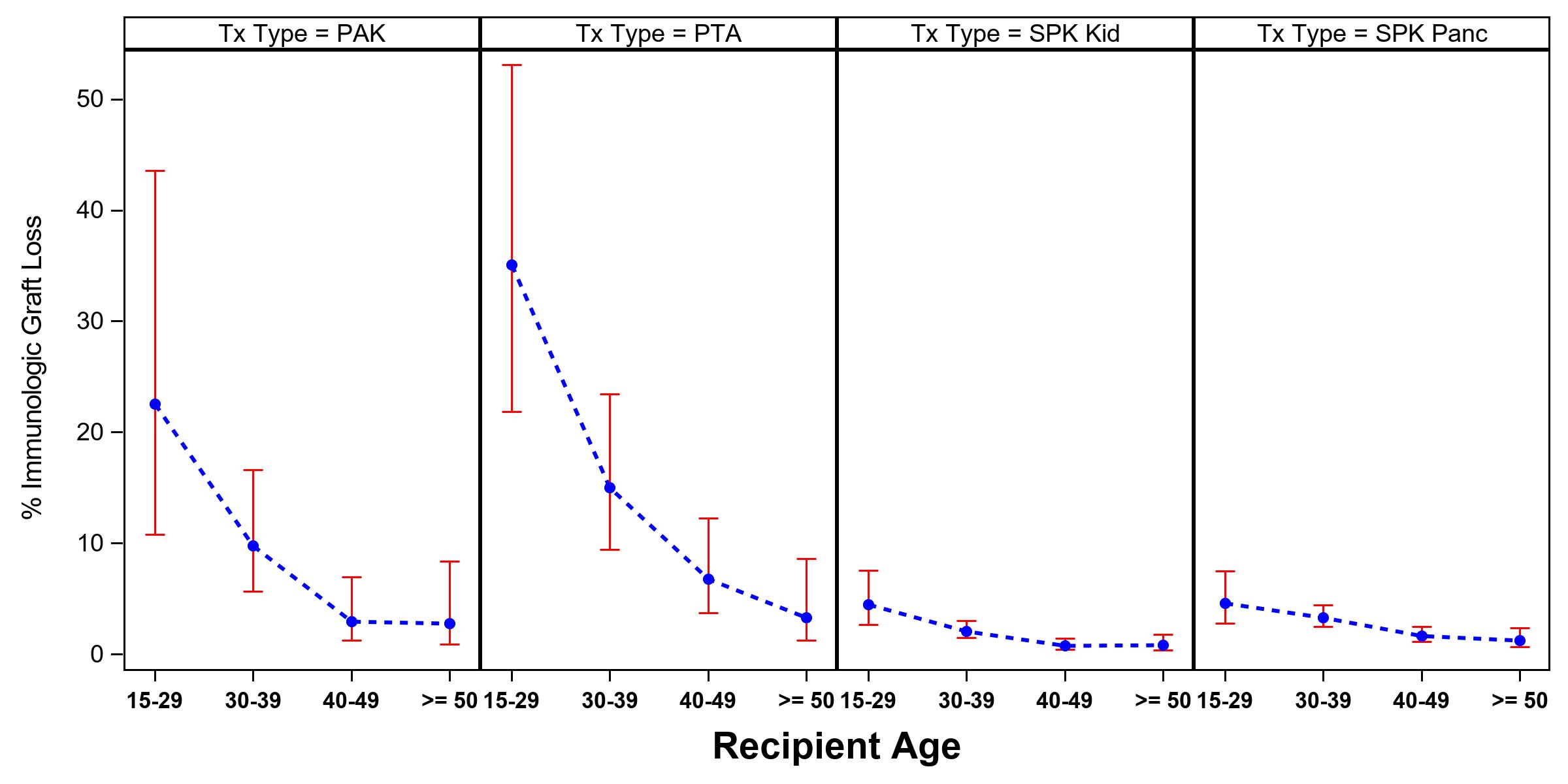
*Purpose: Pancreas transplants (tx) are increasingly performed in older patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. This trend may be explained by the significantly higher immunologic graft loss rate in patients 35 years of age or younger. The purpose of this study was to identify risk factors for pancreas transplants in younger recipients and the impact of different immunosuppressive protocols on graft outcome. Figure 1 shows the immunologic pancreas and kidney graft loss rates according to age at transplants in technically successful transplants 2 years post-tx.
*Methods: Using the IPTR/UNOS databases, we analyzed graft function and immunologic graft loss in 1671 primary pancreas transplant recipients under the age of 35 years with type 1 diabetes mellitus performed between 1/2010 and 12/2017. The follow-up time was at least 6 months. The majority of transplants were performed in SPK (86%), followed by PTA (8%) and PAK (6%). Using uni- and multivariate models we assessed the impact of various induction and maintenance protocols on outcome adjusted for donor and recipient risk factors.
*Results: Overall pancreas graft function in recipients 35 of age or younger at 3 years post-tx was 82% in SPK, 52% in PTA and 67% in PAK. In technically successful transplants, wthin the first 12 month posttx, 23% of PTA, 14 % of SPK and 15% of PAK recipients were treated for acute rejection episodes. At 3 year posttx, the immunologic graft loss rates were 7% for SPK pancreas, 38% for PTA and 21% for PAK. 80% of all patients received depleting antibody therapy, 87% Tacrolimus in combination with MMf, 52% of the solitary txs and 72% of SPK steroid maintenance. When adjusted for the standard donor and center specific factors the immunosuppressive protocol had the highest impact on graft outcome. In all 3 categories recipients under the age of 25 and treatment for rejection during the first year a significant increase in graft loss In PTA, also a very strong center effect was noted. centers performing .a higher number of transplants showed significantly better results.
*Conclusions: Pancreas transplants in recipients under the age of 36 are more prone to immunologic graft loss. It appears that potent induction therapy with depleting antibodies is strongly warranted in all 3 categories. The combination of depleting antibodies for induction and immunosuppression tailored to the specific recipient category may further improve outcome in young pancreas transplant recipients but more research is warranted to reduce the high loss rate in solitary pancreas transplants. .
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gruessner AC, Renz J, Saggi S, Gruessner RW. What Are Factors That Can Influence The High Immunological Graft Loss Rate In Young Pancreas Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/what-are-factors-that-can-influence-the-high-immunological-graft-loss-rate-in-young-pancreas-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress