Viral Integration In BK Polyomavirus-Associated Urothelial Carcinoma in Renal-Transplant Recipients: Multistage Carcinogenesis Revealed by Next Generation Virome Capture Sequencing
1Department of Organ Transplantation, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 2State Key Laboratory of Virology, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Wuhan, China, 3Mygenostics Co., Beijing, China, 4Department of Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 5Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 6Department of Urology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 7Department of Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 497
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Polyma virus
Session Information
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:27pm-4:39pm
Presentation Time: 4:27pm-4:39pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: To elucidate the mechanism of carcinogenesis by BK Polyomavirus (BKV) integration in immunocompromised patients.
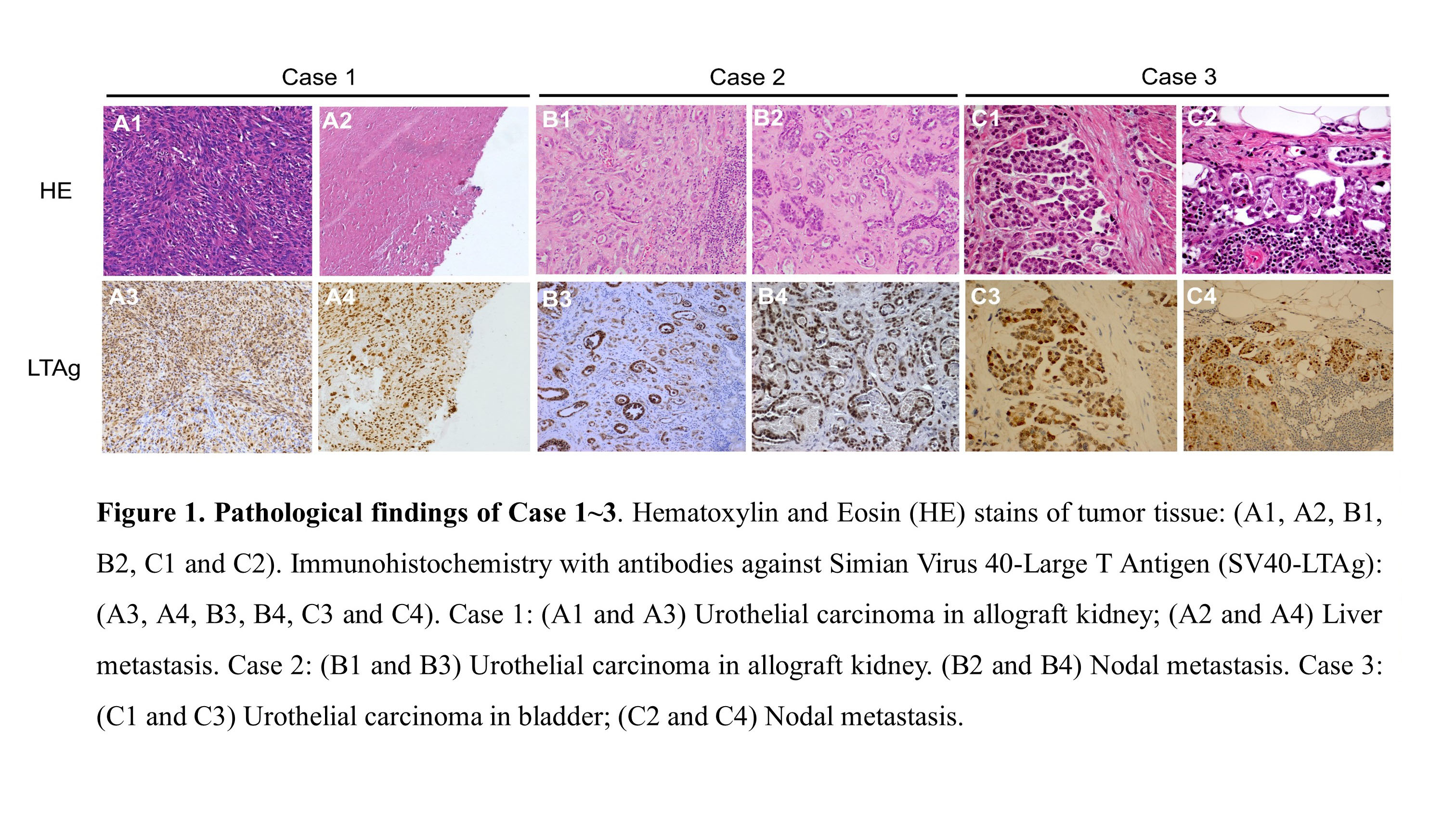
*Methods: Virome capture sequencing and whole genome sequencing were performed on both primary and metastatic tumors of three patients with BKV-associated urothelial carcinoma (UC) after renal transplantation (Figure 1).
*Results: Microhomologies between human and BKV genomes were significantly enriched in the flanking regions of over 80% of the integration sites. The distribution of viral DNA breakpoints was not random (χ2 test, p<0.01). Primary and metastatic tumors shared consensus integration sites whose supporting reads were higher than the sum of those of the other non-consensus sites in the same case, affecting LINC01924, eIF3c and NEIL2 genes in the three cases respectively.
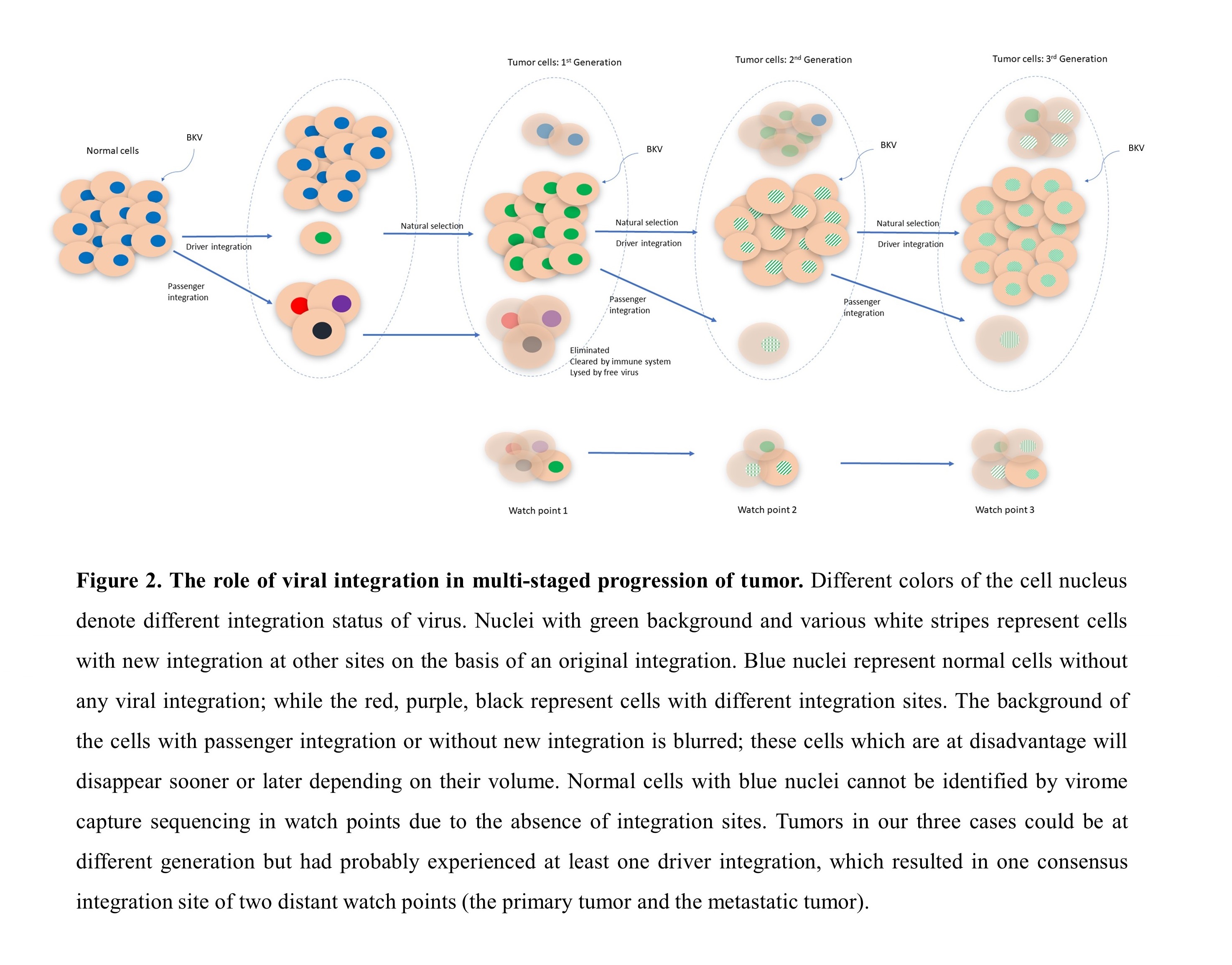
*Conclusions: The integration of BKV in both primary and metastatic tumors follows the mechanism of microhomology-mediated end joining or non-homologous end joining. The integration of BKV is a continuous process occurring in both primary and metastatic tumors, generating heterogenous tumor cell populations in relationship to viral integration. Through this ongoing process, certain cell populations might have gained growth advantage or metastatic potential, as a result of viral integration either affecting the cellular genes where the viral DNA integrated to or altering the expression or function of the viral genes (Figure 2).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang Y, Liu Y, Deng W, Fu F, Yan S, Yang H, Luo M, Liu R, Geng J, Xu J, Wu Y, Ma J, Zhou J, Liu N, Jin Y, Xia R, Elias N, Lee RJ, Feldman AS, Blute ML, Colvin RB, Wu C, Miao Y. Viral Integration In BK Polyomavirus-Associated Urothelial Carcinoma in Renal-Transplant Recipients: Multistage Carcinogenesis Revealed by Next Generation Virome Capture Sequencing [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/viral-integration-in-bk-polyomavirus-associated-urothelial-carcinoma-in-renal-transplant-recipients-multistage-carcinogenesis-revealed-by-next-generation-virome-capture-sequencing/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress