Variable Course of Hepatitis A Virus Infection in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
A. Vostal1, J. Husson2, A. Shishido1, N. Jakhete3, E. Moore4, X. Wen5, A. Amoroso2, R. Meier6, E. Wilson2, K. K. Saharia2
1Div. of Infectious Diseases, Univ. of Maryland Medical Center, Baltimore, MD, 2Div. of Infectious Diseases, Univ. of Maryland School of Medicine and Institute of Human Virology, Baltimore, MD, 3Div. of Hepatology, Univ. of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, 4Dept of Surgery, Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY, 5Dept. of Surgery, Univ. of Florida, Gainesville, FL, 6Dept. of Surgery, Univ. of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 559
Keywords: Hepatitis, Immunosuppression, IVIG, Outcome
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 27 - Non-Organ Specific: Viral Hepatitis
Session Information
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:30pm-6:40pm
Presentation Time: 6:30pm-6:40pm
Location: Hynes Room 312
*Purpose: Although Hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection is typically a self-limited disease in immunocompetent individuals, the natural history and viral kinetics of HAV in solid organ transplant recipients (SOTR) is not well described. In this case series, we describe the variable nature of HAV infection in SOTR and demonstrate that HAV RNAemia can be prolonged in immunocompromised hosts.
*Methods: We describe 3 cases of acute HAV infection in SOTR at a single center occurring between November 2020 and July 2021. Diagnosis of acute HAV infection was made by Hepatitis A IgM and confirmed by detection of HAV RNA in serum (quantitative viral PCR performed by CDC Division of Viral Hepatitis Laboratory, Atlanta, GA).
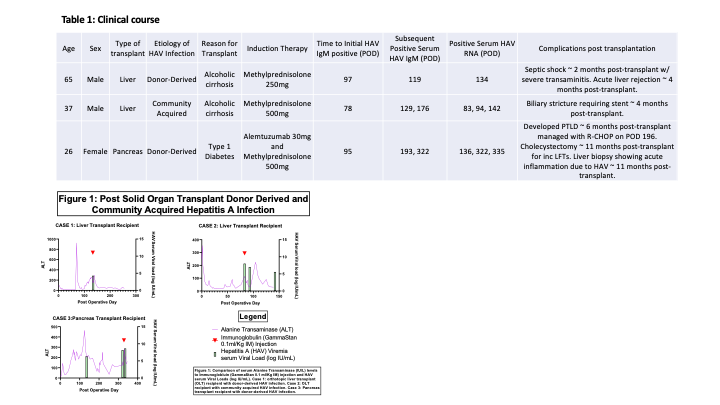
*Results: Two cases of acute HAV infection were due to donor-derived infection (case 1, liver transplant and case 3, pancreas transplant). One case was community-acquired (case 2, liver transplant). Acute HAV infection was diagnosed a median of 95 days (range 78 to 97 days) following organ transplantation. None of the patients had known prior exposure to HAV infection or evidence of natural or vaccine induced immunity to HAV prior to transplant. The clinical course and changes in lab values are detailed in Table 1 and Figure 1. All 3 patients received HAV immunoglobulin. Follow up HAV RNA testing was available for 2 patients (case 1 and case 3) and demonstrated persistence of HAV RNA in serum. Despite persistent viral RNAemia, case 1 demonstrated improvement in transaminases while case 3 continues to have elevated transaminases more than 1 year from time of HAV acquisition.
*Conclusions: HAV infection in SOTR can have a variable clinical course including prolonged HAV viremia and transaminitis. The prolonged course of HAV infection in our pancreas transplant recipient (case 3) in comparison to the two liver transplant recipients (cases 1 and 2) suggests that the net state of immunosuppression has a significant impact on the natural course of HAV infection following organ transplantation. The significance of persistent HAV RNA in the setting of improved biochemical liver function markers is uncertain.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vostal A, Husson J, Shishido A, Jakhete N, Moore E, Wen X, Amoroso A, Meier R, Wilson E, Saharia KK. Variable Course of Hepatitis A Virus Infection in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/variable-course-of-hepatitis-a-virus-infection-in-solid-organ-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress