Validation of an Integrative and Dynamic Prognostic Score for Response to Therapy in Solid Organ Transplants
Paris Translational Center for Organ Transplantation, Paris, France.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 318
Keywords: Graft survival, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Complications: Late Graft Failure
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Location: Room 6E
Drug development in transplantation has diminished due to the lack of suitable endpoints for predicting graft failure. We sought to validate the performance of an integrative scoring system to predict long-term kidney allograft loss in the setting of therapeutic interventions.
We used an integrative risk-scoring system, previously derived and validated in 5,125 KTR and based on readily-accessible parameters measured after transplant. We included patients who underwent standardized protocols for antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR), T-cell mediated rejection (TCMR) and CNI toxicity. ABMR patients received SOC treatment by PP, IVIg and anti-CD-20 (n=224). Patients with TCMR received steroid pulses (n=143). The last group included patients with CNI toxicity converted to belatacept (n=117). All patients underwent risk score measurement at the time of treatment and 3 months after. The outcome measure was the performance of the score to predict allograft failure as compared with the actual events observed.
484 patients were included. The mean time follow-up was 4.0±3.1 years. The risk score was significantly modified by the therapeutic interventions (mean risk score of 3.0±0.8 at the time of treatment vs 2.7±0.8 after treatment, p<0.001). 2 groups of patients were identified by the risk score: i) Group 1 showing decreasing predicted probability of graft loss after treatment (blue lines, responders, 68%); ii) Group 2 showing stable or increased predicted probability of graft loss after treatment (red lines, non-responders, 32%). The risk score prediction capability of individual patient long-term allograft loss was highly accurate (C-index 0.84). The calibration plot showed an optimal agreement between the risk score prediction model after therapeutic intervention and the actual allograft loss.
This integrative risk scoring system showed high performance in the setting of therapeutic interventions after kidney transplant, correlated well with the true clinical outcome and captured the net effect of treatment on the clinical outcome. The risk score could be used as a valid surrogate endpoint for next-generation trials and in the approval of drugs. 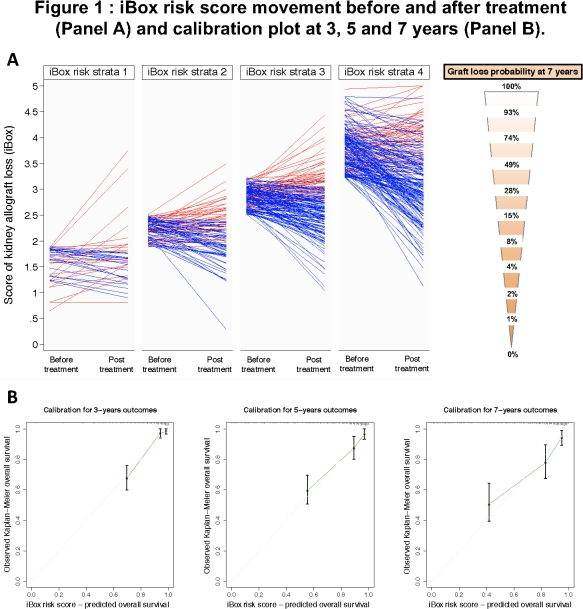
CITATION INFORMATION: Loupy A., Aubert O., Viglietti D., Legendre C., Glotz D., Lefaucheur C. Validation of an Integrative and Dynamic Prognostic Score for Response to Therapy in Solid Organ Transplants Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Loupy A, Aubert O, Viglietti D, Legendre C, Glotz D, Lefaucheur C. Validation of an Integrative and Dynamic Prognostic Score for Response to Therapy in Solid Organ Transplants [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/validation-of-an-integrative-and-dynamic-prognostic-score-for-response-to-therapy-in-solid-organ-transplants/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
