Using Predictive Modeling to Manage Cardiovascular Risk and Improve Kidney Transplant Outcomes.
MUSC, Charleston.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 9
Keywords: Graft failure, Kidney transplantation, Mortality, Resource utilization
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Cardiovascular Complications in Kidney Transplantation
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:06pm-3:18pm
Presentation Time: 3:06pm-3:18pm
Location: Room 304
Objective: We aimed to improve post-kidney transplant (tx) outcomes through predictive analytics and natural language processing (NLP) integrated into the electronic health record (EHR). The goal is to reduce risk of graft loss (GL) and death by cueing Patient-centered Medical Home (PCMH) teams to support tx programs.
Methods: Daily, data from the modeling system are pushed to the EHR in a concise view. We generated predictive models for GL in yrs 1 and 3, and 3-yr mortality using baseline and follow up data (structured and unstructured). We included adult kidney tx recipients transplanted 2007-15. Structured data were directly used from electronic medical records (EHR,Txp database (Velos)) and NLP (IBM Watson) was applied to unstructured text to extract data (rejection, vitals). IBM SPSS Modeler and Essentials for R were used for analysis.We used backward selection at the 20% level for variables;statistical significance was set at 5%.
Results: Mutable factors associated with 1 and 3 year GL and death fell into 2 groups: tx associated risk, historically managed by tx nephrology, and patient-level risk factors not associated with tx. Salient patient-level factors (non-tx) associated with higher risk of GL at 1 yr (n=22/45) included cardiac/vascular events (OR=3.2) or active smoking (OR=3.5). Acute MI (OR=10.5) or cardiac/vascular events (OR=2.5) significantly associated with 3 yr GL (n=40/89))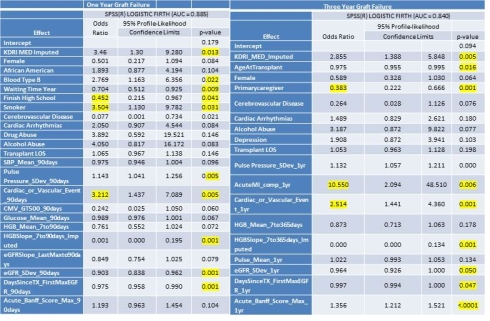 . Finally, cardiac/ vascular events significantly associated with 3 yr mortality (OR=2.6) with cardiovascular mortality rate of 21.6% at yr 3 (50.7% of overall death)
. Finally, cardiac/ vascular events significantly associated with 3 yr mortality (OR=2.6) with cardiovascular mortality rate of 21.6% at yr 3 (50.7% of overall death)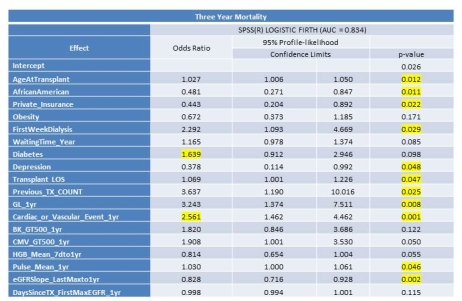 .
.
Conclusions: Non-tx associated cardiovascular risk factors and events strongly associate with 1 and 3 yr GL and 3 yr mortality. Reducing cardiovascular risk is historically a primary care responsibility. PCMHs could synergize with a tx team to reduce graft failure and mortality through EHR deployed predictive data interfaces.
CITATION INFORMATION: Moran W, Zhang J, Su Z, Taber D, Mauldin P, Srinivas T. Using Predictive Modeling to Manage Cardiovascular Risk and Improve Kidney Transplant Outcomes. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moran W, Zhang J, Su Z, Taber D, Mauldin P, Srinivas T. Using Predictive Modeling to Manage Cardiovascular Risk and Improve Kidney Transplant Outcomes. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/using-predictive-modeling-to-manage-cardiovascular-risk-and-improve-kidney-transplant-outcomes/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
