Urinary Cell mRNA Sequencing Profiles of Kidney Allograft Recipients Mirror Intragraft Events and Demonstrate Enrichment for Immune Cells
1Division of Nephrology, Weill Cornell, New York, NY, 2Institute for Computational Biomedicine, Weill Cornell, New York, NY
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 487
Keywords: Gene expression, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Acute Rejection: Basic
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Location: Room 313
*Purpose: Urinary cell mRNA profiling to interrogate kidney allograft status is based on the premise that the allograft can function as an in-vivo flow cytometer and sort graft destructive/protective T cells into the urinary space. We sought direct proof that urinary cell mRNA profiles mirror intragraft events and urinary cells are enriched for immune cells during an episode of acute rejection.
*Methods: We performed global RNA sequencing and characterized mRNA transcriptomes of urinary cells from 49 kidney transplant recipients (Acute T Cell Mediated Rejection [ACR], n=22 and Normal, n=27), and allograft tissues from 32 kidney transplant recipients (ACR n=12 and Normal n=20). We did Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) to test whether the urine-based mRNA profile reflected the biopsy-based profile and used a gene-signature expression based cell-type deconvolution tool xCell.
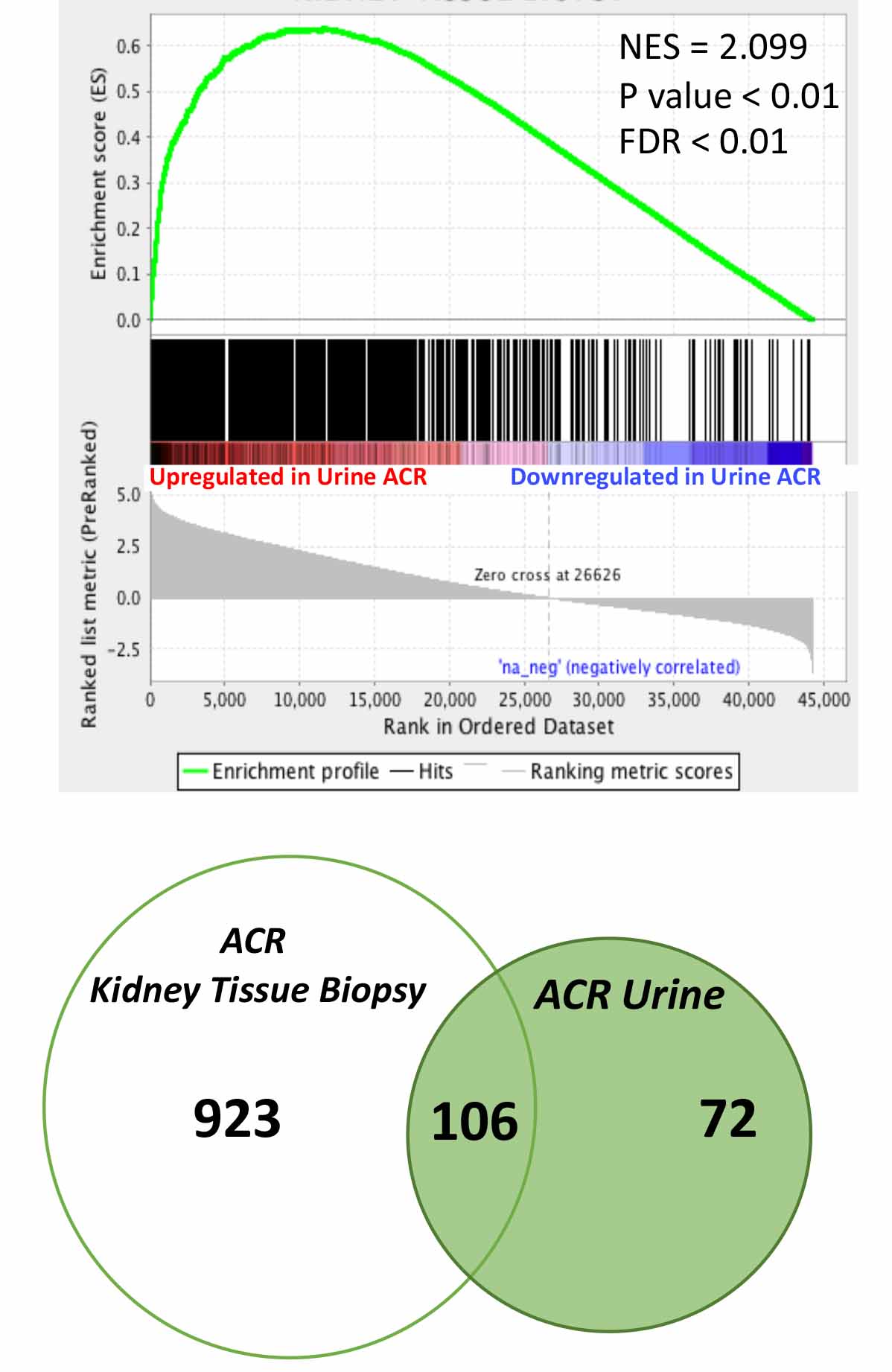
*Results: By GSEA analysis, genes upregulated in the kidney allograft biopsies with ACR were upregulated in the urinary cells with ACR (FDR-P<0.01). Similarly, genes downregulated in the biopsies with ACR were downregulated in the urinary cells with ACR (FDR-P<0.01). There were 106 differentially expressed (ACR vs. Normal) mRNAs that were shared between urine and biopsy profiles, including previously discovered biomarkers of ACR such as CD3E, Granzyme B, and IP-10/CXCL10 (Figure 1, GSEA analysis and Venn Diagram of shared genes).
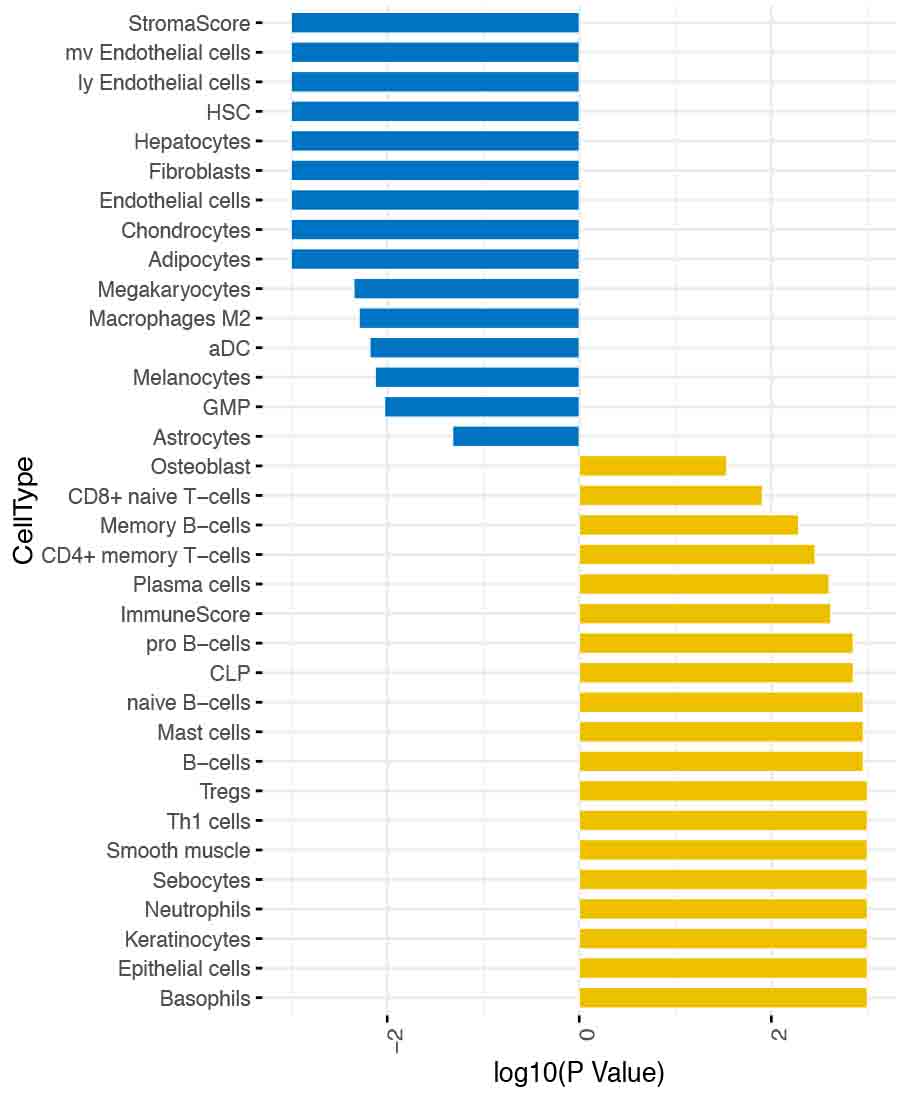
Deconvolution analysis revealed higher enrichment of stromal cell score in the biopsies compared to urine, whereas various immune cell types were enriched in the urine (Figure 2, Blue=Biopsy and Yellow=urine)
*Conclusions: Gene set enrichment analysis of RNA sequencing data from urinary cells and kidney allografts along with deconvolution demonstrate enrichment of genes related to immune cells in urine that is undiluted by the stromal component. Our data support urine as an excellent biospecimen for biomarker discovery and development as well as for deciphering the anti-allograft repertory.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lubetzky M, Verma A, Yang H, Muthukumar T, Salvatore S, Lee J, Dadhania D, Seshan S, Mueller F, Elemento O, Suthanthiran M. Urinary Cell mRNA Sequencing Profiles of Kidney Allograft Recipients Mirror Intragraft Events and Demonstrate Enrichment for Immune Cells [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/urinary-cell-mrna-sequencing-profiles-of-kidney-allograft-recipients-mirror-intragraft-events-and-demonstrate-enrichment-for-immune-cells/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress