Unravelling the Stage-Shift of Acute Rejection by Urine QSant
1Nephrosant, Brisbane, CA, 2NephroSant, Brisbane, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1062
Keywords: Biopsy, Kidney, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 44 - Kidney Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Acute Antibody Mediated Rejection
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
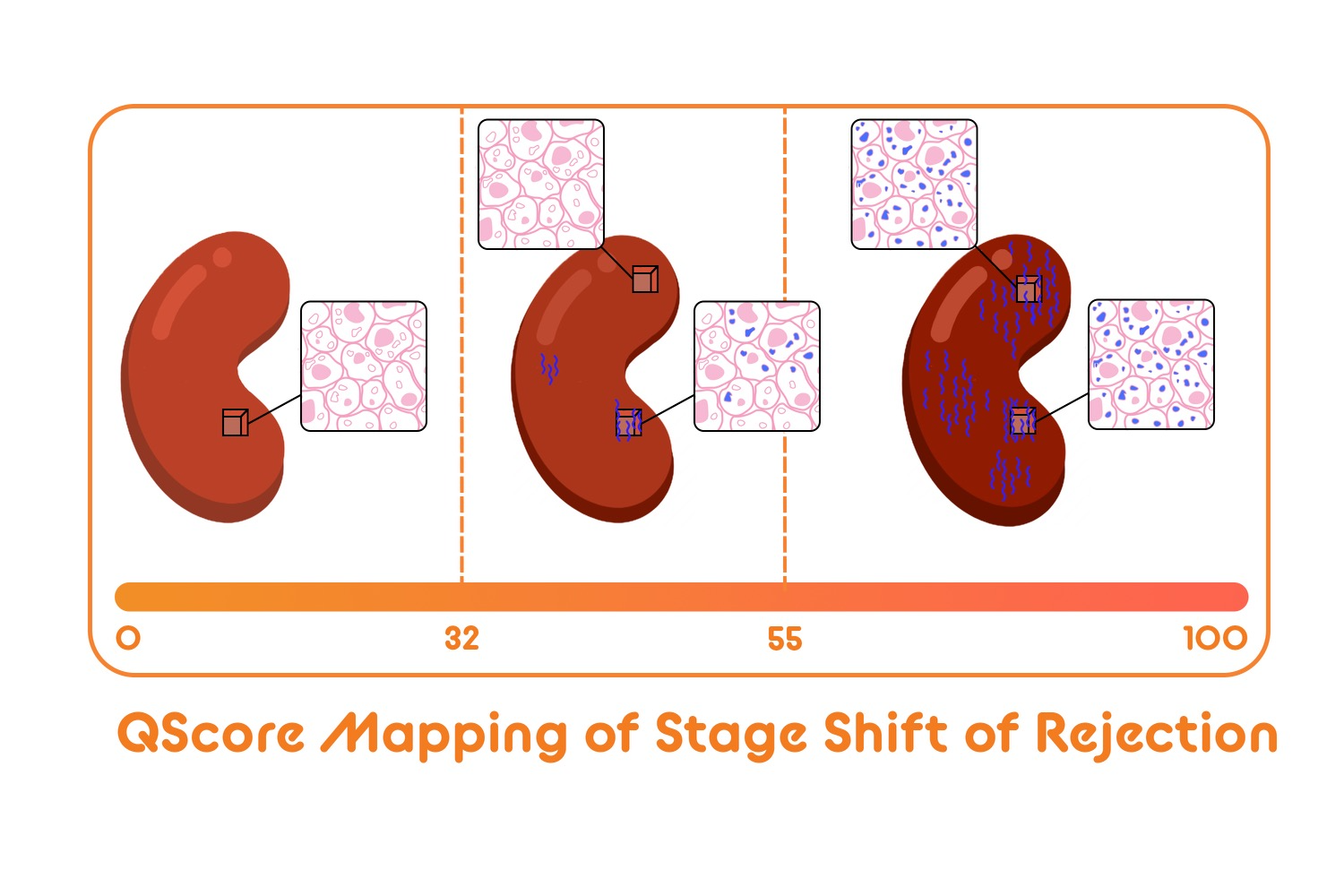
*Purpose: Suboptimal performance in current methods for allograft monitoring underscores the unmet need for enhanced immunosurveillance accuracy, to uncover the alloimmunity flux. QSant[Yang et al, STM 2020] – a multi-analyte urinary diagnostic assay was developed to profile overall renal transplant health and prognosticate the risk of acute rejection(AR). QScore – A ML-based scaled(0-100) score across measurements of DNA, protein and metabolic biomarkers, enables this prognostication.
*Methods: We analyzed a real-world-data cohort, comprising of 235 urine samples collected from renal transplant patients – between 4/1 and 10/1, 2021 – across 11 US transplant centers. Fresh samples, self-collected by patients in urine-cups with proprietary preservatives were shipped to our CLIA lab and assayed by QSant and QScores reported. Increasing QScore reflects progression in allograft damage post transplantation(figure). A 3-state model is hypothesized informed by the fact that evolution and resolution of rejection is a patchy process and the gold standard biopsy could miss histological signs of rejection depending on the site of the tissue sample. QScore <32 classifies allograft stability/immunoquiescence; QScore between 32-55 exposes a state of alloimmunity flux; and QScore >55 identifies AR presenting high concordance with biopsy-backed histological instability.
*Results: The patients span the entire QScore spectrum. 37.9% of the samples enrich for immunequiescence (QScore<32); 49.8% enrich for the alloimmune flux domain with QScore 32-55 and 12.3% enrich the higher-grade AR domain with a QScore ≥55. Serial QSant monitoring, across a subset of 32 patients, over a period of two consecutive quarters, captures the essence of the alloimmunity flux (p-value: 0.086,Wilcoxon test). 53% [17/32] of the patients encompass the alloimmune injury domain and follow three primary trajectories: i) a planar gradient in QScore across time, showing persistence of alloimmunity(53% [9/17]); ii) a decreasing gradient, delineating patients moving into the immunoquiescent domain, putatively in response to immunomodulation following assessment of active rejection (41%); iii) an increasing gradient, delineating patients moving into the mature AR domain (6%).
*Conclusions: The observed alloimmunity flux suggests precision monitoring with QSant has the potential to differentiate higher-grade AR episodes from evolving/resolving rejection and/or potentially identify ones missed by biopsies. It also presents a paradigm which can potentially stage-shift the detection of rejection, resulting in improved graft and patient survival.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yazar W, Titzler N, Sarwal R, Sarwal M, Ghosh S. Unravelling the Stage-Shift of Acute Rejection by Urine QSant [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/unravelling-the-stage-shift-of-acute-rejection-by-urine-qsant/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress