Trough Level Compliance in Immunosuppression is Important to Protect Renal Function after Liver Transplantation – An Additional Analysis from the Hephaistos Study
1Hephaistos, Study Group, Germany, 2Novartis Pharma GmbH, Nürnberg, Germany
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 228
Keywords: Glomerular filtration rate (GFR), Immunosuppression, Liver transplantation, Renal function
Session Information
Session Name: Novel Tools to Assess Immunosuppressive Efficacy
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:15pm-4:27pm
Presentation Time: 4:15pm-4:27pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Most immunosuppressive drugs are dosed according to trough levels (C0-levels). To achieve the optimal balance between efficacy and safety, it is important to avoid both over- und underimmunosuppression. Many studies have been conducted to optimize immunosuppression, but it has been shown that C0-levels are often not met for various reasons. The Hephaistos study was designed in particular to show the impact of calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) reduction on renal function and CNI-induced nephrotoxicity after liver transplantation (LTx).
*Methods: In this 12 months [M] prospective, open-label, randomized de novo liver transplant study, the primary endpoint was to demonstrate that an immunosuppressive regimen based on everolimus (EVR: 3-5ng/ml) plus reduced tacrolimus (rTAC: <5ng/ml) shows superiority on renal function compared to TAC alone (TAC-C: 6-10ng/ml) at M12. The study revealed numerical but not significant improvement in the full analysis set. However, a large number of patients in the EVR+rTAC arm had TAC C0-levels above the pre-defined range (31- 42% at various timepoints). Thus, we performed an additional analysis of a compliance set, including only patients whose C0-levels were within the TAC target range for at least three different timepoints during the study.
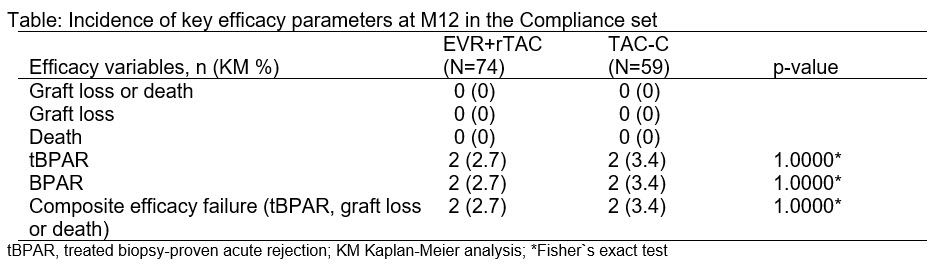
*Results: Of 333 randomized patients, the compliance set consisted of 74 of 169 patients in the EVR+rTAC and 59 of 164 in the TAC-C group. Mean eGFR (MDRD4) was significantly higher with EVR+rTAC at M12 (adjusted mean difference of 8.03 mL/min/1.73m2;p=0.0333). In contrast the non-compliance set (95 EVR+rTAC, 105 TAC-C) showed a difference of only 1.20 ml/min (p=0.7154). No difference was observed in efficacy and safety regardless of treatment regimen or compliance.
*Conclusions: This compliance set analysis clearly shows a significant improvement of renal function in the EVR+rTAC compared to TAC-C group at M12, without compromising efficacy and safety, when TAC C0-levels were maintained within the defined range. Thus, EVR with rTAC is well-tolerated and effective regimen, which allows CNI minimization and offers renal benefit after LTx.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schemmer P, Braun F, Schlitt HJ, Pascher A, Klein CG, Neumann U, Kroeger I, Wimmer P, Nashan B. Trough Level Compliance in Immunosuppression is Important to Protect Renal Function after Liver Transplantation – An Additional Analysis from the Hephaistos Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/trough-level-compliance-in-immunosuppression-is-important-to-protect-renal-function-after-liver-transplantation-an-additional-analysis-from-the-hephaistos-study/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress