Trends in Liver Transplantation in Patients with Renal Failure Since Implementation of Simultaneous Liver-Kidney Allocation Policy
Department of Surgery, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 40
Keywords: Cadaveric organs, Kidney, Liver, Renal failure
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: MELD, Allocation and Donor Issues (DCD/ECD) I
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:15pm-3:27pm
Presentation Time: 3:15pm-3:27pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: To reduce potentially unnecessary kidney utilization, as of August 10, 2017 a new allocation policy was implemented restricting Simultaneous Liver Kidney (SLK) transplant to patients meeting stringent criteria in acute or chronic renal failure. Here we evaluate the policy change by assessing one-year follow up results and its effects on number of transplants and outcomes.
*Methods: Retrospective review of the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network database was performed for liver transplant recipients across two distinct two-year ranges – pre-allocation policy (August 2016-2017) and post-allocation policy implementation (August 2017-2018). Patient characteristics and transplant rates were compared across time periods for SLK and patients in renal failure receiving liver transplant alone (LTA). Outcomes related to patient survival, liver and kidney allograft function were reviewed.
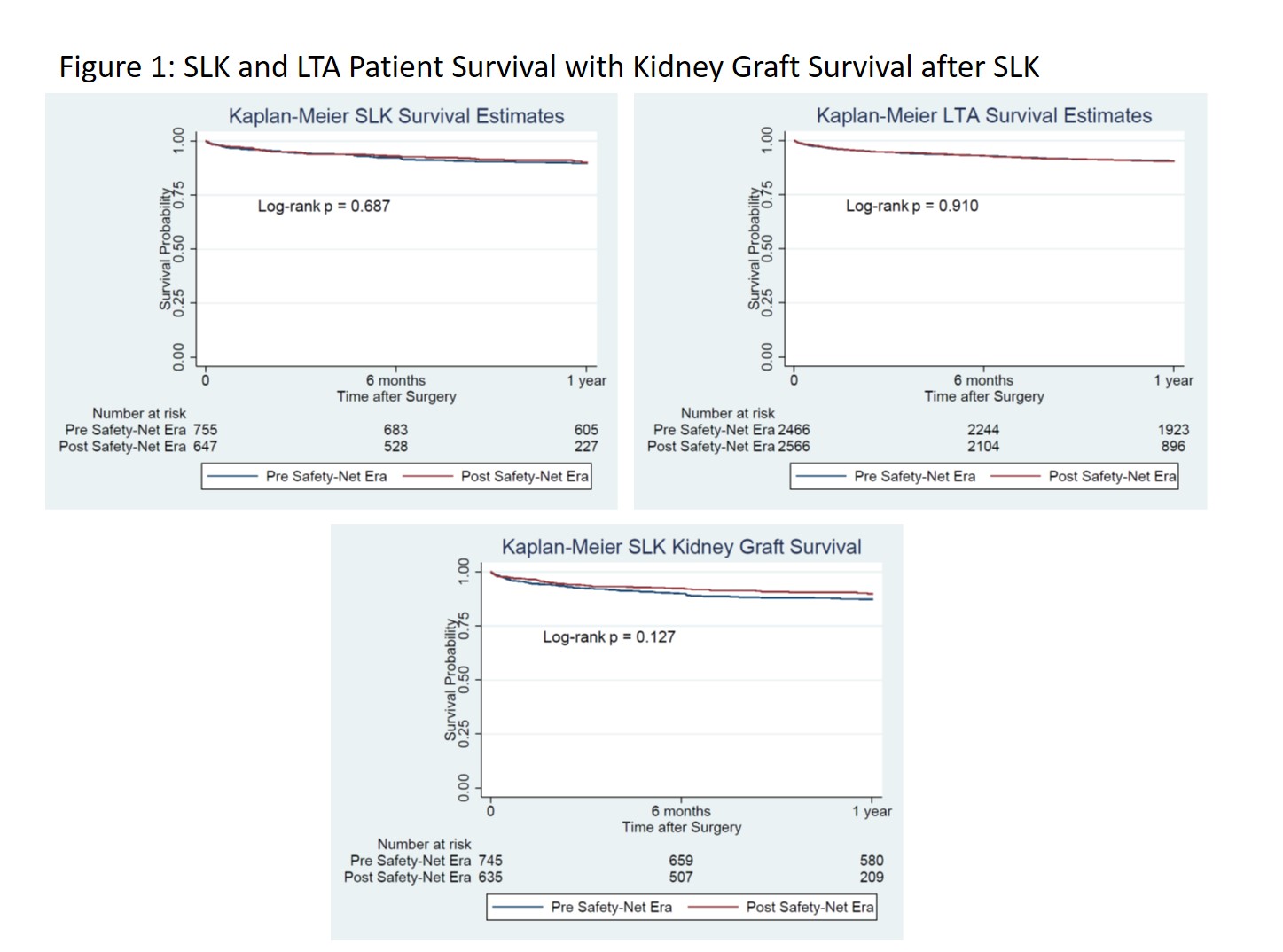
*Results: SLK decreased by 14.2% from pre to post-policy implementation, while LTA in renal failure rose by 3.8% as demonstrated in Table 1. Baseline characteristics were similar across time periods for both SLK and LTA cohorts, as were outcomes related to 1-year patient and graft survival, and incidence of primary non-function. Renal allograft function in SLK demonstrated a non-statistically significant trend towards improvement in the post-implementation era. In total, SLK represented 9.32% of all liver transplants the year prior to SLK allocation policy implementation, and 7.94% post-implementation.
*Conclusions: Since adoption of the SLK allocation policy there has been a reversal in recent trends of rising SLK transplants. This has not come at the expense of patient, liver, or renal allograft function, as 1-year outcomes are similar across groups. Further long-term follow up and in-depth analyses of the consequences of the policy are needed to fully evaluate the impact on the liver transplant community.
| SLK: Pre SLK Allocation | SLK: Post SLK Allocation | p-value | LTA in Renal Failure: Pre SLK Allocation | LTA in Renal Failure: Post SLK Allocation | p-value | |
| Number/(Total % of Liver Transplants) | 754 (9.32%) | 647 (7.94%) | 2493 (30.82%) | 2589 (31.78%) | ||
| Baseline: MELD | 29.4 (23-36) | 28.6 (22-34) | 0.437 | 23 (21-38) | 23 (32-38) | 0.437 |
| Dialysis Dependence | 517 (68.57%) | 460 (71.10%) | 0322 | 617 (24.74%) | 728 (28.11%) | 0.007 |
| Liver Outcomes: 1 year survival | 678 (89.92%) | 590 (91.19%) | 0.465 | 2237 (89.73%) | 2342 (90.46%) | 0.398 |
| 1 year graft survival | 670 (88.74%) | 581 (89.66%) | 0.606 | 2199 (88.17%) | 2312 (89.27%) | 0.231 |
| Primary Non-Function | 8 (1.06%) | 6 (0.93%) | 0.999 | 32 (1.28%) | 23 (0.89%) | 0.178 |
| Kidney Outcomes: Graft Failure at 1 year | 42 (5.56%) | 27 (4.17%) | 0.265 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Altshuler PJ, Shaheen O, Shah AP, Glorioso J, Frank A, Ramirez C, Maley W, Bodzin AS. Trends in Liver Transplantation in Patients with Renal Failure Since Implementation of Simultaneous Liver-Kidney Allocation Policy [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/trends-in-liver-transplantation-in-patients-with-renal-failure-since-implementation-of-simultaneous-liver-kidney-allocation-policy/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress