Transcriptome-Based Study of Tim-1- B Cells and Tim-1+ Regulatory B Cells
Center for Transplant Science, MGH, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 544
Keywords: B cells
Session Information
Session Name: B-cells / Antibodies /Autoimmunity
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:03pm-4:15pm
Presentation Time: 4:03pm-4:15pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Tim-1 signaling has an important role in maintaining the function of Regulatory B cells. Our previous study suggested Tim-1+ Bregs can prolong the survival of islets significantly in an allo-transplantation model (Balb/c to B6). In this study, we analyzed transcriptional data to determine potential pathways of tolerance induction by TIM-1+ Bregs.
*Methods: C57BL/6 mice were given anti-TIM-1, anti-CD45RB, and irradiated BALB/c splenocytes. On day 14, TIM-1+ and TIM-1- B cells were sorted, and RNA was extracted for RNA sequencing. Naïve C57BL/6 B cell RNA was used as a control. The data were analyzed using R (version: 3.6.1).
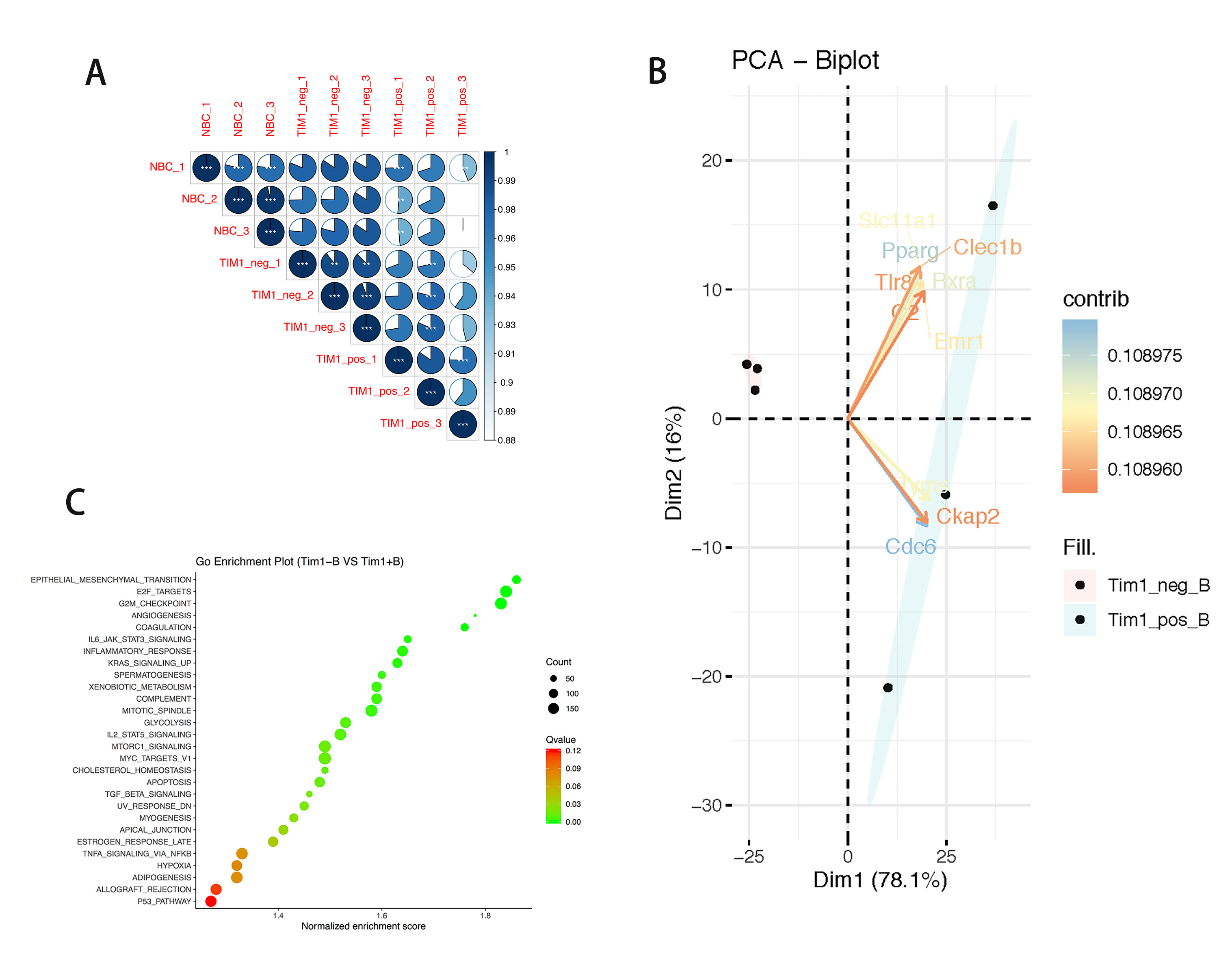
*Results: In comparison with the transcripts of the naïve B cell group, the Tim-1- B cell group (n=3) contained 139 differentially expressed genes (DEGs, Log2 |FC| > 1 and P < 0.05), among which 68 transcripts were up-regulated and 71 transcripts were down-regulated. In contrast, the Tim-1+ Breg group (n=3) contained 900 DEGs (759 up-regulated and 141 down-regulated). Between the Tim-1- and Tim-1+ B cell groups, there were 972 transcripts up-regulated and 53 transcripts down-regulated in the Tim-1+ group. Pearson correlation analysis (PCA) found the transcripts of Tim-1- B cells and Tim-1+ Bregs to be significantly different (P < 0.05, Fig. A). Ten of the most different DEGs (according to the contributed score) were: CDC6, Pparg, Rxra, Tyms, Slc11a1, Emr1, Clec1b, Tlr8, Ckap2, and C2 (Fig. B). GSEA enrichment analysis displayed up-regulated DEGs as mainly enriched in 28 different pathways (|NES|>1, NOM p-val<0.05, FDR q-val<0.25). Notable pathways include: angiogenesis, IL6-Jak-Stats signaling, IL-2-Stat5 signaling and TGF-beta signaling (Fig. C).
*Conclusions: Significant transcriptional differences were found between naïve B cells, Tim-1-B cells, and Tim-1+ Bregs. These differences indicate potential mechanistic pathways responsible for suppression of immune response and prolongation of graft survival by Tim-1+ Bregs. Further research on these DEGs is ongoing in vitro.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fu Q, Lee K, Rickert CG, Huai G, Deng K, Feeney N, Tanimine N, Cuenca AG, Deng S, Markmann JF. Transcriptome-Based Study of Tim-1- B Cells and Tim-1+ Regulatory B Cells [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/transcriptome-based-study-of-tim-1-b-cells-and-tim-1-regulatory-b-cells/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress