Tissue Edema Following Hypothermic Machine Perfusion of a Small Animal Hind Limb Graft
University of Colorado Anschutz Medical, Aurora, CO
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 954
Keywords: Machine preservation, Nerve allografts, Perfusion solutions
Topic: Basic & Clinical Science » Basic & Clinical Science » 20 - VCA
Session Information
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate the capability of preserving a small animal hind limb graft for 24 hours with hypothermic machine perfusion (HMP) in comparison to static cold storage (SCS) preservation.
*Methods: Male Brown Norway rats (14-18 weeks) were used as hind limb donors, with one limb subjected to 24 hours of HMP (flow rate of 0.2 ml/min) and the contralateral limb subjected to 24 hours of SCS. One group was flushed and perfused with heparnized normal saline and the other with heparinized University of Wisconsin Kidney Preservation Solution (KPS) 1. H&E slides of muscle, skin, and sciatic nerve were reviewed by a pathologist blinded to the treatment group and assigned an edema score (0 = none, 1 = mild, 2 = moderate, 3 = severe). Continuous variables are presented as mean (± standard deviation) and compared using two sample or paired Student’s t-test. Edema scores were compared using the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test.
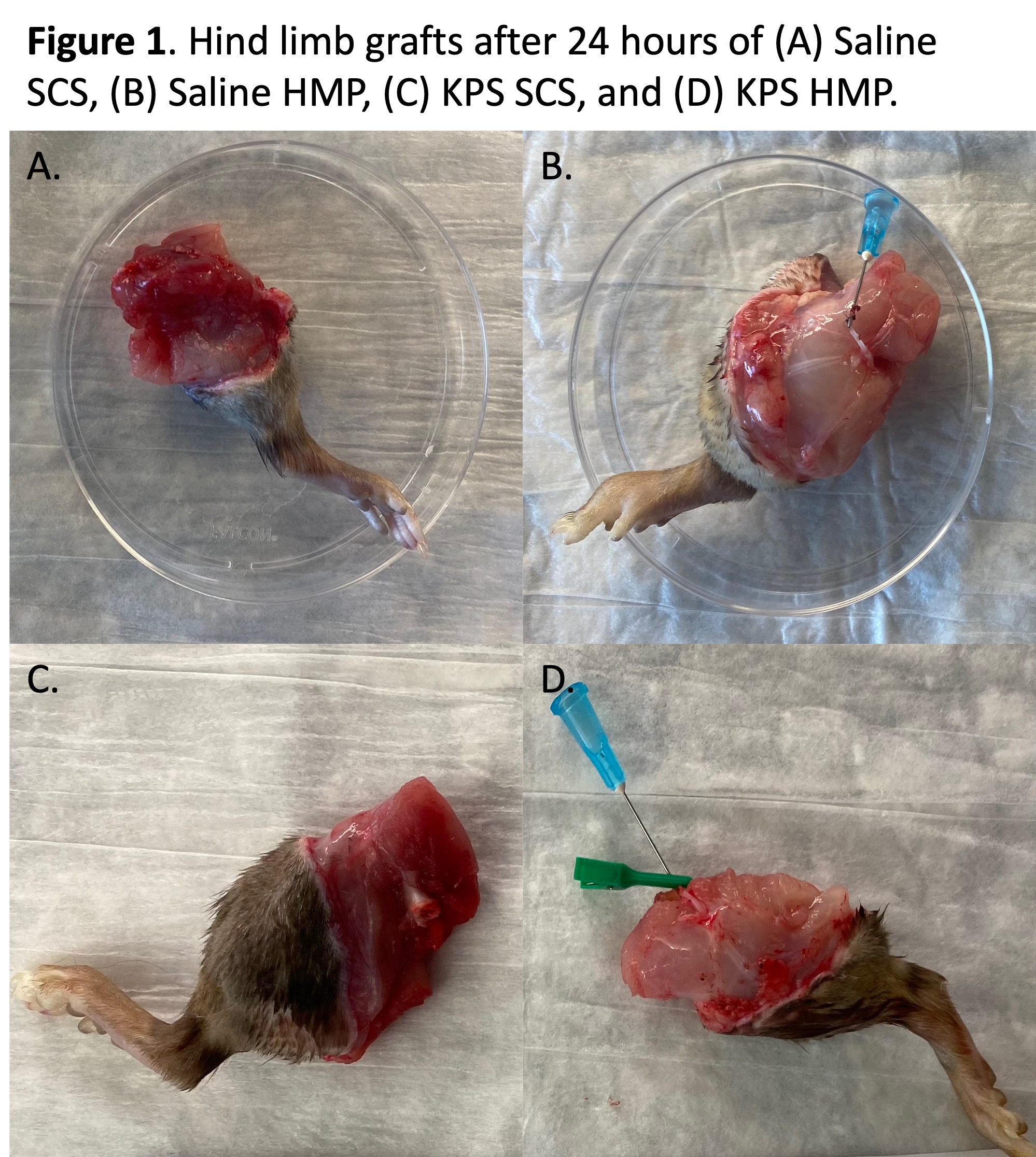
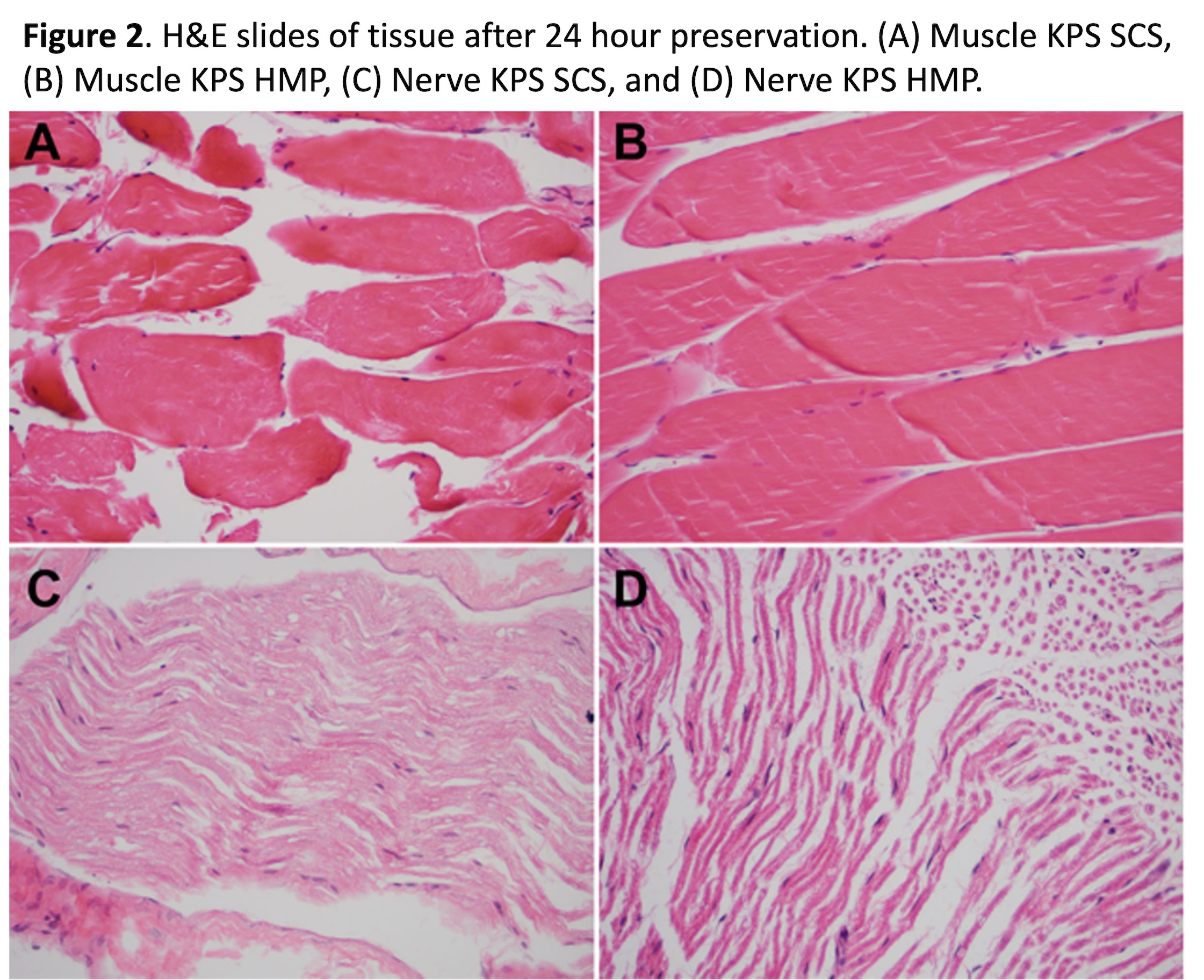
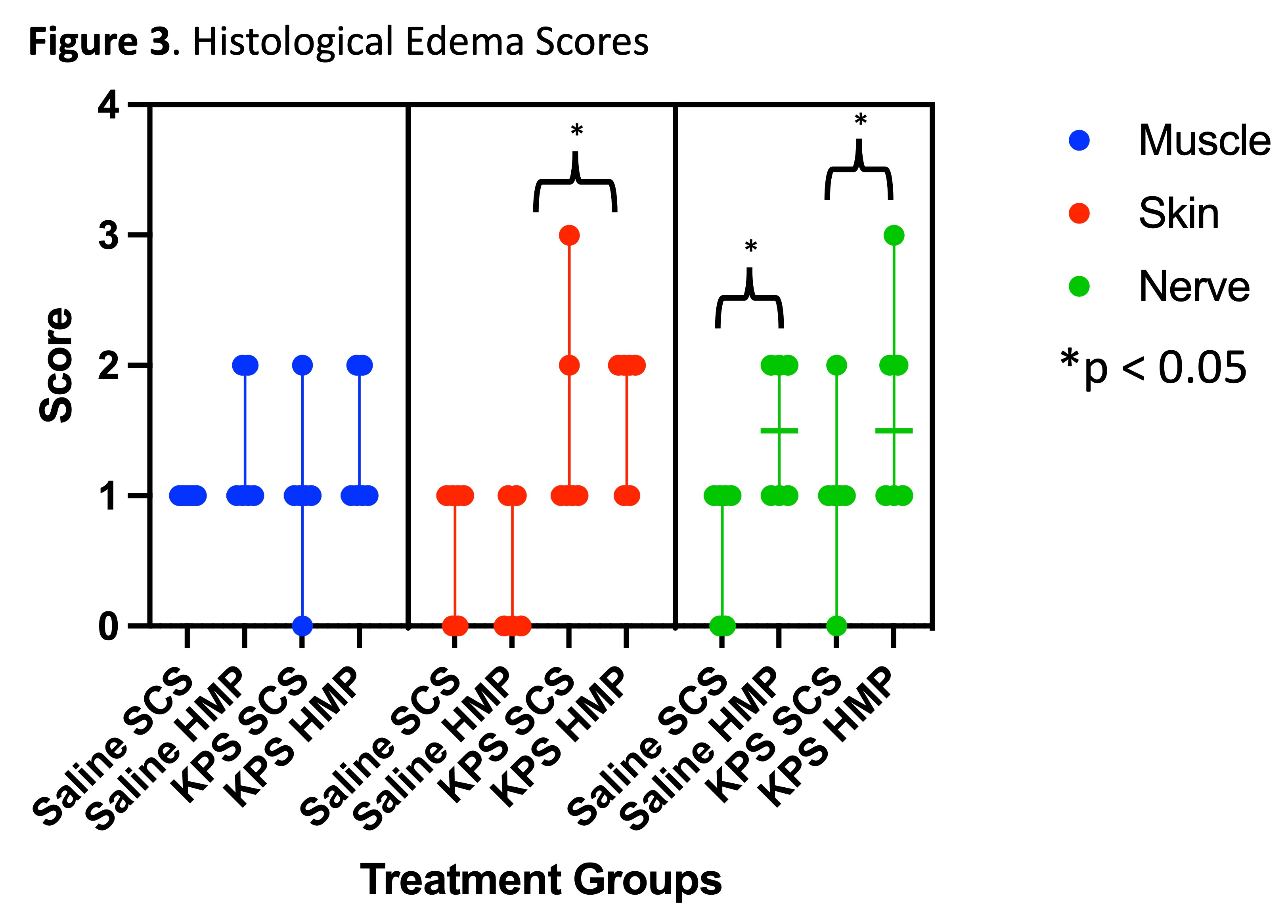
*Results: 6 animals were used in the saline cohort and 6 in the KPS cohort. The saline HMP group gained significantly more weight (12.4 ± 3.5 g) than the saline SCS (-0.3 ± 1.7 g, p < 0.001) and KPS HMP (1.9 ± 0.5 g, p < 0.001) groups (Figure 1). The KPS HMP group did not gain significantly more weight than the KPS SCS treated group (-0.2 ± 0.1 g, p = 0.08). Nerve demonstrated greater edema with HMP than SCS with both saline (p = 0.049) and KPS (p = 0.046), while no differences were observed in muscle or skin (p > 0.05) (Figure 2). More histological evidence of edema in the skin was observed after HMP with KPS in comparison to saline (p = 0.01, Figure 3).
*Conclusions: The sciatic nerve is especially susceptible to edema with HMP. Future studies will need to focus on the functional and survival implications of these findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoeli D, Wang Y, Li B, Huang J, Jain S, Wang Z, Nakra N, Rampalski K, Su A, Mathes D, Washington K, Farkash E, Jani A, Huang C. Tissue Edema Following Hypothermic Machine Perfusion of a Small Animal Hind Limb Graft [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/tissue-edema-following-hypothermic-machine-perfusion-of-a-small-animal-hind-limb-graft/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress