Time Trends of Induction Agent Use in Older and Younger Kidney Transplantation Recipients.
Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C57
Keywords: Induction therapy, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Clinical Science - Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
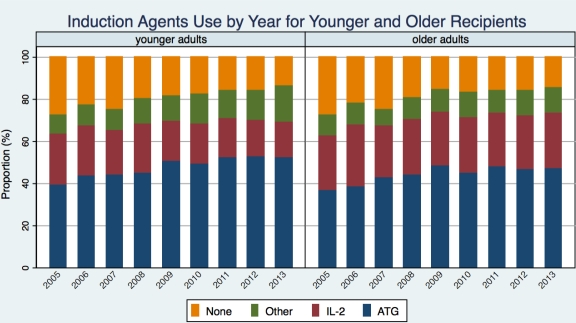
Older adults are increasingly gaining access to kidney transplantation (KT) yet the use of induction agents in this population is unclear. The goal of this study was to assess the temporal trends of induction agent use between older and younger KT recipients.
Methods: Data used for this study were deceased donor KT recipients (2005-2013) recorded by SRTR, including 15,204 older and 56,417 younger. Induction agents were categorized to three types: ATG, IL-2 and other. Years were stratified into 2005-2007, 2008-2010 and 2011-2013. The odds ratio of each type of induction agent use (vs. no use) across three strata (2005-2007 as reference) was estimated by logistic regression models adjusted for recipient, KT and donor factors. We explored effect modification of usage trends between younger and older recipients.
Results: For both older and younger recipients, the percentage of any induction agent use increased from 2005 to 2013 (P<0.001). After adjustment, we found that the odds of ATG use and other induction agent use was significantly increased across three strata for both younger and older (Table). Nevertheless, for younger the odds of IL-2 use was significantly decreased from 2005-2007 to 2008-2010 (OR=0.90), and to 2011-2013 (OR=0.74); while for older the odds of IL-2 use was not changed.
Conclusions: From 2005 to 2013, ATG and other induction agents were more and more likely to be used in both younger and older recipients. IL-2 was less and less likely to be used in younger recipients, but unchanged in older recipients.
| Induction agent use: older vs. younger (Odds Ratio) * P<0.05 and ** P<0.001 | |||
| Younger recipients | older recipients | P-value for interaction | |
| ATG | |||
| 2005-2007 | Ref | Ref | |
| 2008-2010 | 1.22 (1.17, 1.27) ** | 1.25 (1.16, 1.36)** | 0.543 |
| 2011-2013 | 1.43 (1.37, 1.49)** | 1.33 (1.23, 1.44)** | 0.106 |
| IL-2 | |||
| 2005-2007 | Ref | Ref | |
| 2008-2010 | 0.90 (0.85, 0.94)** | 1.02 (0.93, 1.12) | 0.015* |
| 2011-2013 | 0.74 (0.70, 0.78)** | 1.00 (0.91, 1.09) | <0.001** |
| Other Induction Agents | |||
| 2005-2007 | Ref | Ref | |
| 2008-2010 | 1.43 (1.34, 1.53)** | 1.21 (1.06, 1.38)* | 0.028* |
| 2011-2013 | 1.73 (1.62, 1.84)** | 1.29 (1.14, 1.47)** | <0.001** |
CITATION INFORMATION: Huang Q, Luo X, McAdams-DeMarco M, Segev D. Time Trends of Induction Agent Use in Older and Younger Kidney Transplantation Recipients. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huang Q, Luo X, McAdams-DeMarco M, Segev D. Time Trends of Induction Agent Use in Older and Younger Kidney Transplantation Recipients. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/time-trends-of-induction-agent-use-in-older-and-younger-kidney-transplantation-recipients/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
