The Value of SCS Perfusate Biomarkers for Predicting DGF of DCD Donor Kidneys
Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B57
Keywords: Donors, non-heart-beating, Graft function, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: To explore the possibilities of simple cold stored(SCS) perfusate biomarkers predicting delayed graft function(DGF) in donor of cardiac death (DCD) kidneys.
*Methods: A total of 64 patients who received renal transplantation from DCD donor during Aug. 7th 2016 to Dec. 13th 2017, was included in this research. We performed analyzed the perfusate samples of SCS DCD kidneys for 4 unique biomarkers: Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin (NGAL), Kidney Injury Molecule (KIM-1), Liver-Fatty Acid Binding Proteins (L-FABP) and Interleukin-18 (IL-18) . Patients were divided into two groups by whom developed DGF, defined as DGF group and whom did not, defined as immediate graft functioning group(IGF). In order to predict donor kidney functions, we compared the concentration differences of the 4 biomarkers between the 2 groups to find out the correlativity of biomarker concentrations and DGF incidence. We also drew the receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC Curve) to find out the cut-off value to pre-diagnose DGF in DCD kidney receivers.
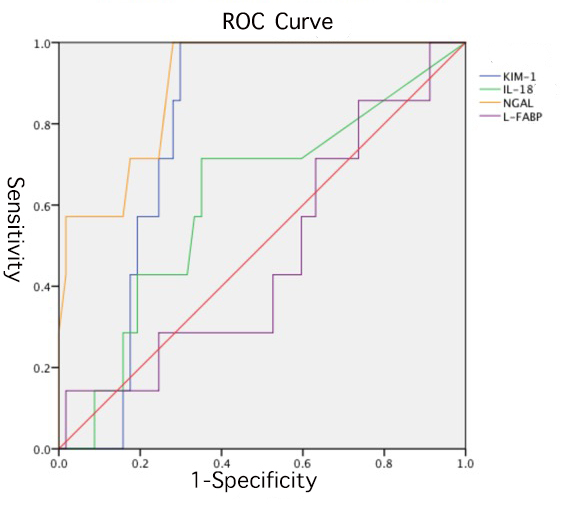
*Results: Among 64 patients, 7 patients developed DGF. The incidence of DGF was 10.9%. ALL four biomarkers were detectable in perfusate samples. Even though the detect rate of IL-18 was low, about 60.9% when compared with the other 3 markers which were all over 95%. Perfusate NGAL concentration was significantly different between DGF group and IGF group (p = 0.009). Neither L-FABP,KIM-1 nor IL-18 perfusate concentration was found statistically different between DGF group and IGF group. (p=0.834/0.124/0.318, respectively). Higher NGAL concentration in the perfusate was associated with DGF (r = 0.430, p< 0.001). The cut-off value of the NGAL concentration is 204.13ng/ml with AUC=0.879,pre-diagnose sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 71.9%. The highest pre-diagnostic value was seen with NGAL,KIM-1 and the third day creatinine level after operation combined analysis. The area under ROC curve was 0.975 with 100% in sensibility and 86% in specificity.
*Conclusions: This is the first time that all these four biomarkers are found detectable in SCS perfusate that is ever reported. We find out that the NGAL in perfusate samples is associated with the incidence of DGF. And some of the biomarkers (NGAL and KIM-1) are truly pre-diagnostic valuable in predicting DGF and even more so when combined with each other or with serum creatinine levels. This data suggests that these biomarkers may be used as an early biomarker to detect DGF and warrants further study.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li X, Wang W, Zhang X. The Value of SCS Perfusate Biomarkers for Predicting DGF of DCD Donor Kidneys [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-value-of-scs-perfusate-biomarkers-for-predicting-dgf-of-dcd-donor-kidneys/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress