The UKKDRI Score Predicts Outcomes of Deceased Donor Transplantation Using a Steroid Sparing Immunosuppressive Protocol.
Imperial College REnal and Transplant Centre, Hammersmith Hospital, London, United Kingdom.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B207
Keywords: Donors, Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, marginal, Renal dysfunction
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Transplantation: KDPI, HCV/Matching, Donor Age
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
The UK kidney donor risk-index (UKKDRI) was developed to provide a simplistic clinical tool to help determine quality of an allograft and aid informed consent. It has been demonstrated that a high UKKDRI score is associated with inferior allograft outcomes. To our knowledge the UKKDRI score does not adjust for different immunotherapy protocols. The aim of this study was to determine if the UKKDRI can be applied to renal allograft recipients receiving a steroid sparing immunosuppressive protocol.
756 recipients of a deceased donor transplant between 2005-2015 were analysed. All patients received monoclonal antibody induction, with a steroid sparing protocol. 295/756 (39.0%) of donors were high risk (HR) and had a UKKDRI score ≥1.35.
Recipients of high risk 'HR' kidneys had inferior patient [HR: 1.71(1.1-2.7), p=0.014] and censored allograft survival [HR: 2.30 (1.5-3.5), p<0.001) compared with the low risk 'LR' kidneys as shown in the graph below. Overall rejection risk was lower in the 'HR' group [HR: 0.66(0.5-0.9), p=0.015] which suggests a role of recipient related factors. Despite fewer rejection episodes, allograft function was inferior at all time points in the 'HR' kidneys, p<0.01, as shown in the figure below.
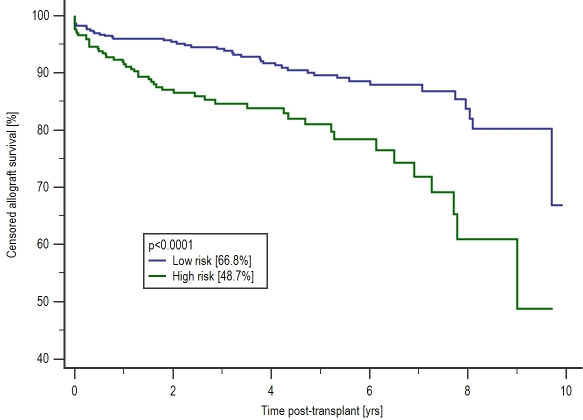
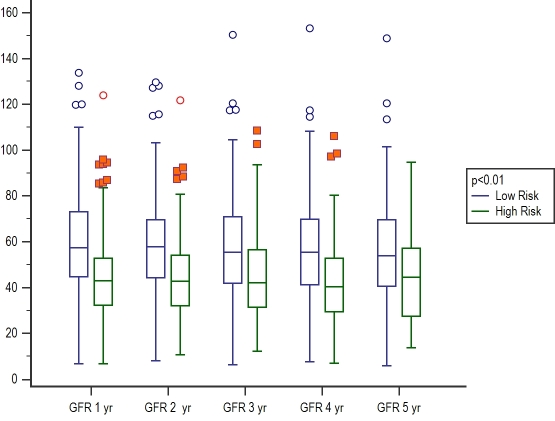
On multivariate analysis, where donor risk factors were defined by the UKKDRI score, variables known at the time of transplant associated with graft loss were: recipient diabetes (p=0.0037), preformed donor specific antibodies (p=0.032) and recipients of a 'HR' kidneys (p=0.0001)
These data shows that recipients of high risk 'HR' kidneys as defined by the UKKDRI score have similar inferior allograft outcomes in the setting of a steroid sparing immunotherapy regimen. Hence the UKKDRI score may also be used in centres using such protocols to predict risk and inform patients.
CITATION INFORMATION: Wardle A, Willicombe M, Goodall D, McLean A, Taube D. The UKKDRI Score Predicts Outcomes of Deceased Donor Transplantation Using a Steroid Sparing Immunosuppressive Protocol. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wardle A, Willicombe M, Goodall D, McLean A, Taube D. The UKKDRI Score Predicts Outcomes of Deceased Donor Transplantation Using a Steroid Sparing Immunosuppressive Protocol. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-ukkdri-score-predicts-outcomes-of-deceased-donor-transplantation-using-a-steroid-sparing-immunosuppressive-protocol/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
